China-based phishing groups blamed for non-stop scam SMS messages about a supposed wayward package or unpaid toll fee are promoting a new offering, just in time for the holiday shopping season: Phishing kits for mass-creating fake but convincing e-commerce websites that convert customer payment card data into mobile wallets from Apple and Google. Experts say these same phishing groups also are now using SMS lures that promise unclaimed tax refunds and mobile rewards points.
Over the past week, thousands of domain names were registered for scam websites that purport to offer T-Mobile customers the opportunity to claim a large number of rewards points. The phishing domains are being promoted by scam messages sent via Apple’s iMessage service or the functionally equivalent RCS messaging service built into Google phones.
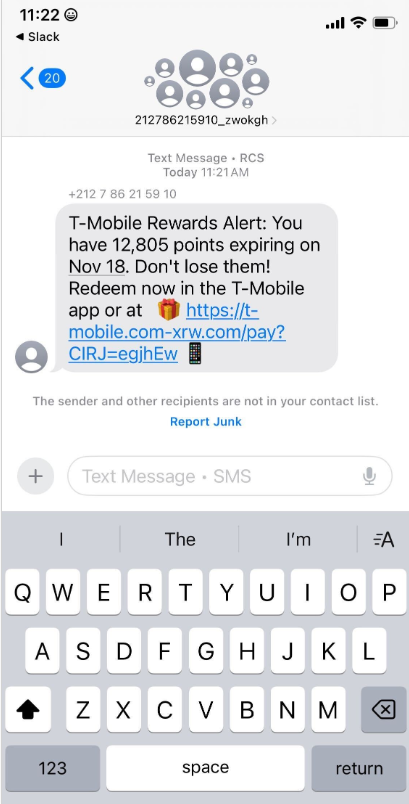
An instant message spoofing T-Mobile says the recipient is eligible to claim thousands of rewards points.
The website scanning service urlscan.io shows thousands of these phishing domains have been deployed in just the past few days alone. The phishing websites will only load if the recipient visits with a mobile device, and they ask for the visitor’s name, address, phone number and payment card data to claim the points.
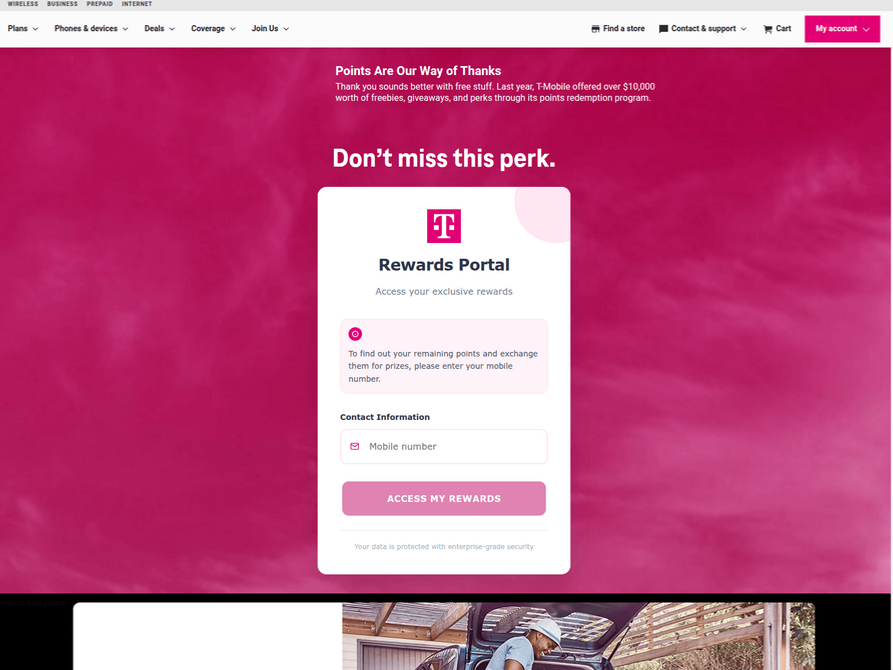
A phishing website registered this week that spoofs T-Mobile.
If card data is submitted, the site will then prompt the user to share a one-time code sent via SMS by their financial institution. In reality, the bank is sending the code because the fraudsters have just attempted to enroll the victim’s phished card details in a mobile wallet from Apple or Google. If the victim also provides that one-time code, the phishers can then link the victim’s card to a mobile device that they physically control.
Pivoting off these T-Mobile phishing domains in urlscan.io reveals a similar scam targeting AT&T customers:
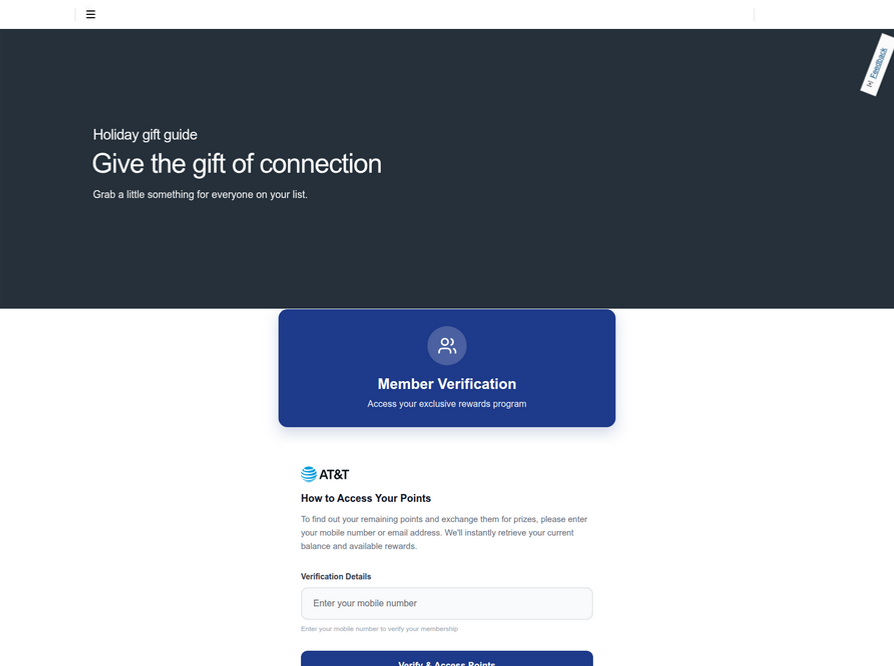
An SMS phishing or “smishing” website targeting AT&T users.
Ford Merrill works in security research at SecAlliance, a CSIS Security Group company. Merrill said multiple China-based cybercriminal groups that sell phishing-as-a-service platforms have been using the mobile points lure for some time, but the scam has only recently been pointed at consumers in the United States.
“These points redemption schemes have not been very popular in the U.S., but have been in other geographies like EU and Asia for a while now,” Merrill said.
A review of other domains flagged by urlscan.io as tied to this Chinese SMS phishing syndicate shows they are also spoofing U.S. state tax authorities, telling recipients they have an unclaimed tax refund. Again, the goal is to phish the user’s payment card information and one-time code.
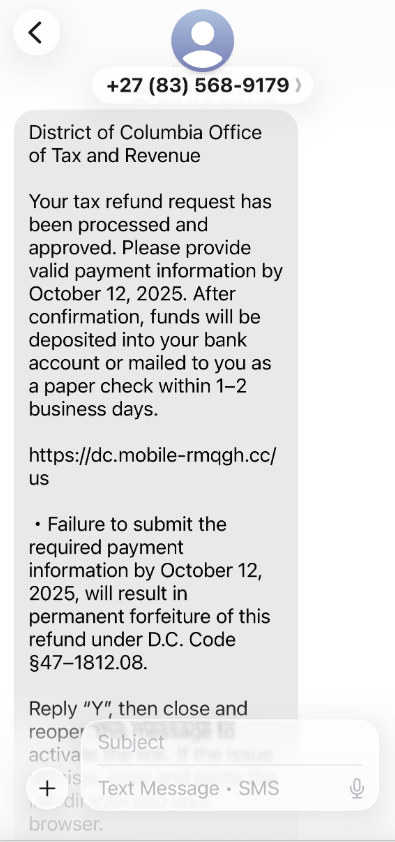
A text message that spoofs the District of Columbia’s Office of Tax and Revenue.
CAVEAT EMPTOR
Many SMS phishing or “smishing” domains are quickly flagged by browser makers as malicious. But Merrill said one burgeoning area of growth for these phishing kits — fake e-commerce shops — can be far harder to spot because they do not call attention to themselves by spamming the entire world.
Merrill said the same Chinese phishing kits used to blast out package redelivery message scams are equipped with modules that make it simple to quickly deploy a fleet of fake but convincing e-commerce storefronts. Those phony stores are typically advertised on Google and Facebook, and consumers usually end up at them by searching online for deals on specific products.
A machine-translated screenshot of an ad from a China-based phishing group promoting their fake e-commerce shop templates.
With these fake e-commerce stores, the customer is supplying their payment card and personal information as part of the normal check-out process, which is then punctuated by a request for a one-time code sent by your financial institution. The fake shopping site claims the code is required by the user’s bank to verify the transaction, but it is sent to the user because the scammers immediately attempt to enroll the supplied card data in a mobile wallet.
According to Merrill, it is only during the check-out process that these fake shops will fetch the malicious code that gives them away as fraudulent, which tends to make it difficult to locate these stores simply by mass-scanning the web. Also, most customers who pay for products through these sites don’t realize they’ve been snookered until weeks later when the purchased item fails to arrive.
“The fake e-commerce sites are tough because a lot of them can fly under the radar,” Merrill said. “They can go months without being shut down, they’re hard to discover, and they generally don’t get flagged by safe browsing tools.”
Happily, reporting these SMS phishing lures and websites is one of the fastest ways to get them properly identified and shut down. Raymond Dijkxhoorn is the CEO and a founding member of SURBL, a widely-used blocklist that flags domains and IP addresses known to be used in unsolicited messages, phishing and malware distribution. SURBL has created a website called smishreport.com that asks users to forward a screenshot of any smishing message(s) received.
“If [a domain is] unlisted, we can find and add the new pattern and kill the rest” of the matching domains, Dijkxhoorn said. “Just make a screenshot and upload. The tool does the rest.”
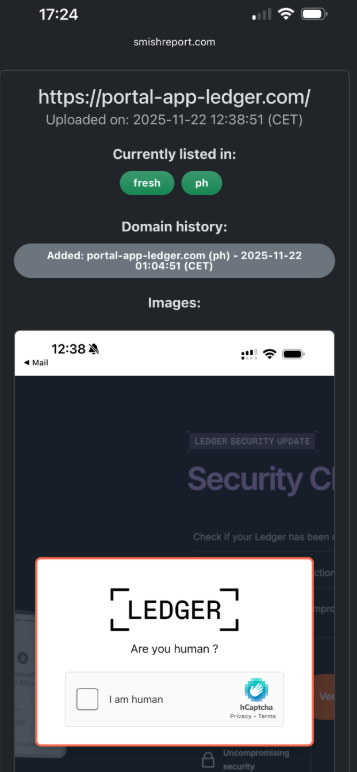
The SMS phishing reporting site smishreport.com.
Merrill said the last few weeks of the calendar year typically see a big uptick in smishing — particularly package redelivery schemes that spoof the U.S. Postal Service or commercial shipping companies.
“Every holiday season there is an explosion in smishing activity,” he said. “Everyone is in a bigger hurry, frantically shopping online, paying less attention than they should, and they’re just in a better mindset to get phished.”
SHOP ONLINE LIKE A SECURITY PRO
As we can see, adopting a shopping strategy of simply buying from the online merchant with the lowest advertised prices can be a bit like playing Russian Roulette with your wallet. Even people who shop mainly at big-name online stores can get scammed if they’re not wary of too-good-to-be-true offers (think third-party sellers on these platforms).
If you don’t know much about the online merchant that has the item you wish to buy, take a few minutes to investigate its reputation. If you’re buying from an online store that is brand new, the risk that you will get scammed increases significantly. How do you know the lifespan of a site selling that must-have gadget at the lowest price? One easy way to get a quick idea is to run a basic WHOIS search on the site’s domain name. The more recent the site’s “created” date, the more likely it is a phantom store.
If you receive a message warning about a problem with an order or shipment, visit the e-commerce or shipping site directly, and avoid clicking on links or attachments — particularly missives that warn of some dire consequences unless you act quickly. Phishers and malware purveyors typically seize upon some kind of emergency to create a false alarm that often causes recipients to temporarily let their guard down.
But it’s not just outright scammers who can trip up your holiday shopping: Often times, items that are advertised at steeper discounts than other online stores make up for it by charging way more than normal for shipping and handling.
So be careful what you agree to: Check to make sure you know how long the item will take to be shipped, and that you understand the store’s return policies. Also, keep an eye out for hidden surcharges, and be wary of blithely clicking “ok” during the checkout process.
Most importantly, keep a close eye on your monthly statements. If I were a fraudster, I’d most definitely wait until the holidays to cram through a bunch of unauthorized charges on stolen cards, so that the bogus purchases would get buried amid a flurry of other legitimate transactions. That’s why it’s key to closely review your credit card bill and to quickly dispute any charges you didn’t authorize.




It seems to me the ‘convenience’ of 6 digit One Time Codes for doing significantly risky actions like adding a card to an e-wallet or similar could stand a little LESS convenience! 2FA –> 3/4/5 FA could make things significantly more complicated for these scams to work in a single shot – The automation works because people are fooled ONE TIME into providing that code. If there were 2-3 follow-on steps to actually finalize adding the card/account to the wallet, that would certainly be better than it is now. This is something the banks themselves could do pretty quickly I should think with minimal effort. Someone is going to say Yubikey 100 times and sure, that’s another way, but it’s going to be a slower migration for the easily-scammed masses. Adding simple steps to the existing affirmation process, even ONE step, that could incrementally trip up these AI automated schemes and warn users that they’re NOT entering a code ‘just to get bonus points’ or something, and denote to folks what they’re ACTUALLY doing by providing it. Even putting the action details in the body of the SMS itself would be a step up from what is currently opaque to users.
For our SMS MFA validations, we state the purpose for why the SMS message is sent (i.e. adding a card, authenticating a login to a new device, etc.). Few people read these. Android, and I believe Apple, make it simple to click a single button to copy an SMS code and never go into the actual message.
I prefer MFA apps (like Authenticator or Duo) but lots of our members like the SMS MFA. It’s definitely a challenge for financial institutions.
Northwest Fed Cred Union might just be ahead of the game if as you say they put the action item in the SMS body, giving users an idea what they’re actually doing it for – *if* they read it, of course, the usual caveat. But I don’t think the majority of OTC providers are doing even that… and it would be interesting to compare the scam rate successes between the two. If you just get “XYZ has sent you a code and it is 853921” that’s obviously useless for the purpose of detecting what is going on to warrant the code. Authenticator apps are better, yet unless they also disclose the action item per-auth instance, (and I’m not versed in all the various ones and how they actually UI) to me the same issue could be present, one-time fooling the user into supplying auth because they can’t see what it’s specifically doing. (Thanks for your info.)
I use Yubikey wherever I can, but the problem for me is places where I can’t use it . The worst is my credit union! It has the usual choices: email, sms, or phone call.
I’ve never used a YubiKey for exactly the reasons warned about.
Would you mind enlightening the general audience what those reasons might be?
I believe he’s referring to ‘places where I can’t use it’… ?
Fair call.
‘the problem for me is places where I can’t use it’
You can always change to a provider that DOES support it -> https://2fa.directory/us/#banking
Is it an effort to switch? Sure, but what do you value more? Security or Convenience? For the providers that only offer convenience; they are making a business decision at the cost of their clients security, therefore they shall not earn my business. Lets face it, they could all afford or have the know-how to implement decent MFA, except for reasons generally related to C Suite bonuses and Shareholder dividends, but they choose otherwise.
I have been using Security keys for well over a decade and if I cannot build them into my personal defence strategy, it’s not gonna happen. Keep at it my man, Security is ever evolving and there is always effort required to keep on top the latest threats.
“Security or Convenience?” Well TBH the market has spoken on that…
Humans are lazy given the option, and will always follow the path of least resistance, so I understand that the market will naturally follow. But I question why; if the Identity Management Sector for instance gets it -> 2fa.directory/us/#identity, why can’t the Bankers? A lot of their industry (not all) are the weakest link in the chain when it comes to the scam victims written about in Bryan’s’ articles and hardware keys are a proven methodology.
I saw a scam something like this pulled back in 2016, around the same time I saw a spate of email phishers attempting to convince people they were getting Christmas bonuses and/or inheritances that seemed to be mostly a front for something else (not just credentials or third party deposit schemes). Clearly it has gotten more sophisticated since then. And more Asian.
I learned to keep certain of my (defensive) security projects on separate disks and not use the cloud, for more safety. Doesn’t do much for the other stuff, but does prevent overlap if someone were breached at an inconvenient time (though, what isn’t?).
Too-good-to-be-true offers, are rarely true.
Doing the flying spaghetti monster’s work, as always Krebs, sent this article to my family.
… forever and ever. R’amen. 😉
Udon know what you’re saying! Ciao, it’s been fun.
Noodles (and spaghetti) originated in China.
I doubt that actually. Same for paper.
Archaeologically and textually documented as China. Published in Nature, and everything. If you know something about it they don’t then fine, otherwise why care? Paper’s origins somewhat more nebulous. IMHO, it was likely invented multiple places independently, like a lot of things during the pre-science period.
Lemme know when you’re finished attempting to stomp all over that butterfly, though, there, Jemima Bradbury.
Because the silk road invented a lot that China still claims credit for, due to trading with them and having “documentation” as far as is accessible.
“Lemme know” when you learn to think critically about what you read.
There are archaeological digs proving the noodle thing. Show me archaeological evidence predating that, and sure. I mean, I would rather discuss if we really know when the first successful long-term backdoor/sniffer of an ssh daemon was (and is it when we think?), but if you wanna argue noodles, go for it. Hah.
I personally do not know if I believe the paper age, but pasta couldn’t be THAT much older unless it was some weird accident. Could happen, I guess.
wikipedia.org/wiki/Papyrus
“But it doesn’t SAY PAPER!” – enjoy your paper chase..
You said paper, I read that as paper. Not papyrus (or linen, or wood bark, or whatever).
Wonder if someone spontaneously invented a terminal/monitor back before they were on the market, sometimes, and never patented it.
This conversation is a totally mealy conversation, incidentally. You get hung up on the weirdest things, man.
I question all kinds of things people claim out of hand without firsthand knowledge. Thanks. It’s not liker personal, man.
All hail His noodley appendage!
“ Most importantly, keep a close eye on your monthly statements.”
A LONG time ago I set up every CC with SMS activity notifications (new transaction, bill is ready, due date, bill paid, etc — just about every option available.
I much prefer if an SMS option is available — easier to delete text messages/threads than to get even more email to filter through.
Many times I haven’t put my wallet away when a text message arrives about my purchase — easier to stay on top of purchases with the instant feedback compared to monthly statement reviews which are up to 1 month old.
If a transaction/purchase shows up out of the blue — big ❌ flag.
Right now, I’m doing more and more on virtual machines. For example, I have one virtual machine for normal browsing and another limited to banking.
I do need a better workstation since running three or more virtual machines running at a time really bogs this one down.
For what it’s worth, though, none of my development work is on my workstation — it’s all on separate OpenBSD servers. When I finish for the day, my last step is usually to run a backup with borg. Also, one or more weekly images of the work as well as copies of the borg backups is written to CD drives, labeled, and stored at home.
New opportunity for dear leader: Trump Phishing Kits
Guaranteed not be prosecuted by DOJ in exchange for 40% of profits purchasing $TRUMP coins.
This is not a pivot. We’re talking about text messages with a link. That’s it. How their fake sites are created means nothing different from a security pov. I find it very worrying that security professionals are saying phishing is evolving. I was one of the first people impersonated online in 1996. The reverse proxy is the only true upgrade. Everything else remains the same. The only thing that changes is the channel.
The rise of SMS phishers targeting people through points, taxes, and fake retailers is getting out of control, and it’s a reminder of how careful we need to be this season. What I love about pieces like the Gingerbread Land Oliver Hudson Thunderbird Cardigan is how they capture the festive vibe without the stress. While scammers are getting smarter, so are shoppers—choosing trusted sources, verified stores, and quality holiday outfits that actually feel worth it. Staying alert while enjoying cozy, stylish fashion is the best combo this year!
AI Slop Spam.
I created a simple Firefox browser addon with the help of ChatGTP that uses the Firefox trust certificate API that popped up a quick notification if a website’s certificate was created before the date you set with a threshold slider (defaults to $0 days or newer) and added an optional box to enter in an API key for a Whois search if the trust certificate was too new instead of showing the notification it would do a secondary search for the Whois site creation date.
Using only the built-in cert check didn’t send any site data out unless you checked a box that did the secondary Whois lookup.
It worked perfectly but I had to blacklist the trust certificate for Whois from the trust certificate date check or it would Firefox would pop up endless notifications in a loop.
Both ChatGPT and I should have thought of that when we created it. 🙂
I intend on making it available on Firefox’s addon store for free with no ads and fully open source on GitHub so people can add to its design.
This is the type of comment I’d like to see more of on this site. Thank you for your effort and sharing.
What stands out to me is how smart scammers are getting by mixing real-looking shopping websites with fake text messages. My grandma got scammed recently off of a facebook ad for fake headphones so it’s definitely a real world issue that should be prioritized. The part about fake reward points and tax refunds was interesting to see, because those are things people would normally trust. I didn’t realize that scammers could use one-time codes to load stolen cards into mobile wallets so easily. A lot of people probably fall for this just because they don’t know this is even possible.
AI Slop.
Smishing attacks like this are a good reminder to slow down before clicking links in unexpected texts. If you’re unsure whether an SMS is legitimate, tools like Checktxt can help you quickly check a message for common signs of malicious behavior. You can just forward the text to 44CHECKTXT (442-432-5898), or take a screenshot and email it to checktxt@checktxt.com
for a quick check. It’s not a replacement for good judgment, but it can be a useful extra layer of caution. (Disclosure: I work at Checktxt.)
AI Slop Spam.
Ugh, these scams are getting so sophisticated! The points and tax ones are particularly insidious because they play on things people are already worried about. Thanks for the heads-up, Brian, I’ll definitely be more careful.