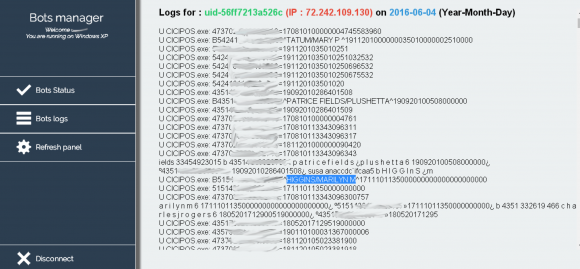
With the proliferation of shadowy black markets on the so-called “darknet” — hidden crime bazaars that can only be accessed through special software that obscures one’s true location online — it has never been easier for disgruntled employees to harm their current or former employer. At least, this is the fear driving a growing stable of companies seeking technical solutions to detect would-be insiders.
Avivah Litan, a fraud analyst with Gartner Inc., says she’s been inundated recently with calls from organizations asking what they can do to counter the following scenario: A disaffected or disgruntled employee creates a persona on a darknet market and offers to sell his company’s intellectual property or access to his employer’s network.
Litan said a year ago she might have received one such inquiry a month; now Litan says she’s getting multiple calls a week, often from companies that are in a panic.
“I’m getting calls from lots of big companies, including manufacturers, banks, pharmaceutical firms and retailers,” she said. “A year ago, no one wanted to say whether they had or were seriously worried about insiders, but that’s changing.”
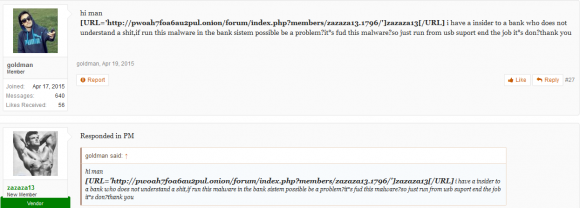
Insiders don’t have to be smart or sophisticated to be dangerous, as this darknet forum discussion thread illustrates.
Some companies with tremendous investments in intellectual property — particularly pharmaceutical and healthcare firms — are working with law enforcement or paying security firms to monitor and track actors on the darknet that promise access to specific data or organizations, Litan said. Continue reading




 Owned by Santa Clara, Calif. based networking giant
Owned by Santa Clara, Calif. based networking giant  The latest update brings Flash to v. 22.0.0.192 for Windows and Mac users alike. If you have Flash installed, you should update, hobble or remove Flash as soon as possible.
The latest update brings Flash to v. 22.0.0.192 for Windows and Mac users alike. If you have Flash installed, you should update, hobble or remove Flash as soon as possible. According to
According to  FBI Special Agent Timothy J. Wilkins wrote that investigators also subpoenaed and got access to that michaelp77x@gmail.com account, and found emails between Persaud and at least four affiliate programs that hire spammers to send junk email campaigns.
FBI Special Agent Timothy J. Wilkins wrote that investigators also subpoenaed and got access to that michaelp77x@gmail.com account, and found emails between Persaud and at least four affiliate programs that hire spammers to send junk email campaigns. Yes, that’s right it’s once again Patch Tuesday, better known to mere mortals as the second Tuesday of each month. Microsoft isn’t kidding around this particular Tuesday — pushing out
Yes, that’s right it’s once again Patch Tuesday, better known to mere mortals as the second Tuesday of each month. Microsoft isn’t kidding around this particular Tuesday — pushing out  During the height of tax-filing season in 2015, KrebsOnSecurity
During the height of tax-filing season in 2015, KrebsOnSecurity  On January 27, 2016, this publication was the first
On January 27, 2016, this publication was the first