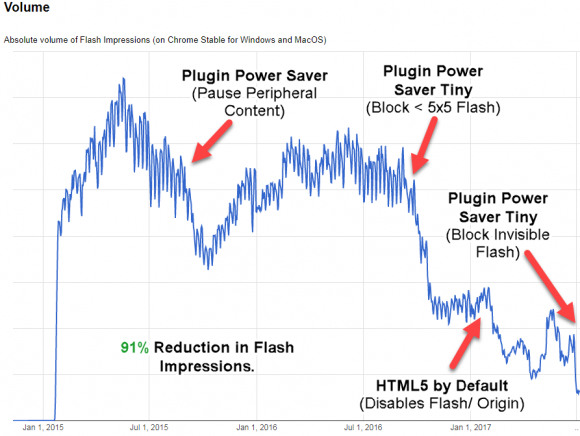
An October 2015 piece published here about the potential dangers of tossing out or posting online your airline boarding pass remains one of the most-read stories on this site. One reason may be that the advice remains timely and relevant: A talk recently given at a Czech security conference advances that research and offers several reminders of how being careless with your boarding pass could jeopardize your privacy or even cause trip disruptions down the road.
In What’s In a Boarding Pass Barcode? A Lot, KrebsOnSecurity told the story of a reader whose friend posted a picture of a boarding pass on Facebook. The reader was able to use the airline’s Web site combined with data printed on the boarding pass to discover additional information about his friend. That data included details of future travel, the ability to alter or cancel upcoming flights, and a key component need to access the traveler’s frequent flyer account.
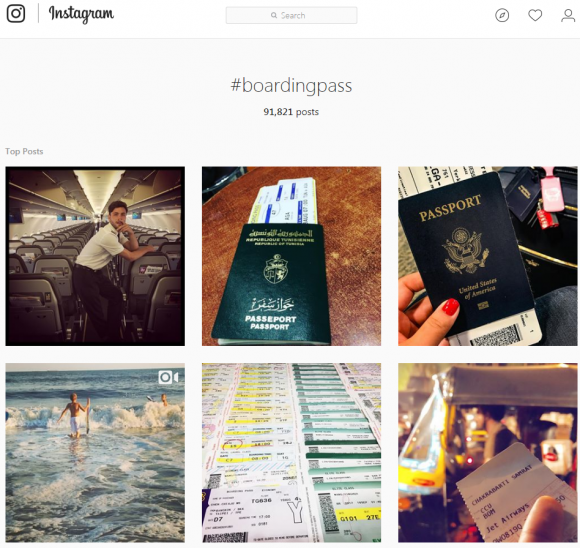
A search on Instagram for “boarding pass” returned 91,000+ results.
More recently, security researcher Michal Špaček gave a talk at a conference in the Czech Republic in which he explained how a few details gleaned from a picture of a friend’s boarding pass posted online give him the ability to view passport information on his friend via the airline’s Web site, and to change the password for another friend’s United Airlines frequent flyer account.
Working from a British Airways boarding pass that a friend posted to Instagram, Špaček found he could log in to the airline’s passenger reservations page using the six-digit booking code (a.k.a. PNR or passenger name record) and the last name of the passenger (both are displayed on the front of the BA boarding pass).
Once inside his friend’s account, Špaček saw he could cancel future flights, and view or edit his friend’s passport number, citizenship, expiration date and date of birth. In my 2015 story, I showed how this exact technique permitted access to the same information on Lufthansa customers (this still appears to be the case).
Špaček also reminds readers about the dangers of posting boarding pass barcodes or QR codes online, noting there are several barcode scanning apps and Web sites that can extract text data stored in bar codes and QR codes. Boarding pass bar codes and QR codes usually contain all of the data shown on the front of a boarding pass, and some boarding pass barcodes actually conceal even more personal information than what’s printed on the boarding pass.
As I noted back in 2015, United Airlines treats its customers’ frequent flyer numbers as secret access codes. For example, if you’re looking for your United Mileage Plus number, and you don’t have the original document or member card they mailed to you, good luck finding this information in your email correspondence with the company.
When United does include this code in correspondence, all but the last three characters are replaced with asterisks. The same is true with United’s boarding passes. However, the customer’s full Mileage Plus number is available if you take the time to decode the barcode on any United boarding pass.
Until very recently, if you knew the Mileage Plus number and last name of a United customer, you would have been able to reset their frequent flyer account password simply by guessing the multiple-choice answer to two secret questions about the customer. However, United has since added a third step — requiring the customer to click a link in an email that gets generated when someone successfully guesses the multiple-choice answers to the two secret questions. Continue reading





 As noted in
As noted in ![The P.A.S. Web shell, as previously offered for free on the now-defunct site profexer[dot]name.](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/pas30.png)

 More than two dozen of the vulnerabilities fixed in today’s Windows patch bundle address “critical” flaws that can be exploited by malware or miscreants to assume complete, remote control over a vulnerable PC with little or no help from the user.
More than two dozen of the vulnerabilities fixed in today’s Windows patch bundle address “critical” flaws that can be exploited by malware or miscreants to assume complete, remote control over a vulnerable PC with little or no help from the user. In
In