Mir Islam, a 21-year-old Brooklyn man who pleaded guilty to an impressive array of cybercrimes including cyberstalking, “doxing” and “swatting” celebrities and public officials (as well as this author), was sentenced in federal court today to two years in prison. Unfortunately, thanks to time served in this and other cases, Islam will only see a year of jail time in connection with some fairly heinous assaults that are becoming all too common.
While Islam’s sentence fell well short of the government’s request for punishment, the case raises novel legal issues as to how federal investigators intend to prosecute ongoing cases involving swatting — an extremely dangerous prank in which police are tricked into responding with deadly force to a phony hostage crisis or bomb scare at a residence or business.

Mir Islam, at his sentencing hearing today. Sketches copyright by Hennessy / CourtroomArt.com. Yours Truly is pictured in the blue shirt behind Islam.
On March 14, 2014, Islam and a group of as-yet-unnamed co-conspirators used a text-to-speech (TTY) service for the deaf to relay a message to our local police department stating that there was an active hostage situation going on at our modest town home in Annandale, Va. Nearly a dozen heavily-armed officers responded to the call, forcing me out of my home at gunpoint and putting me in handcuffs before the officer in charge realized it was all a hoax.
At the time, Islam and his pals were operating a Web site called Exposed[dot]su, which sought to “dox” public officials and celebrities by listing the name, birthday, address, previous address, phone number and Social Security number of at least 50 public figures and celebrities, including First Lady Michelle Obama, then-FBI director Robert Mueller, and then Central Intelligence Agency Director John Brennan.
Exposed.su also documented which of these celebrities and public figures had been swatted, including a raft of California celebrities and public figures, such as former California Governor Arnold Schwartzenegger, actor Ashton Kutcher, and performer Jay Z.
![Exposed[dot]su was built with the help of identity information obtained and/or stolen from ssndob[dot]ru.](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/exposed-su-600x462.png)
Exposed[dot]su was built with the help of identity information obtained and/or stolen from ssndob[dot]ru.
At the time, most media outlets covering the sheer amount of celebrity exposure at Exposed[dot]su focused on the apparently starling revelation that “if they can get this sensitive information on these people, they can get it on anyone.” But for my part, I was more interested in how they were obtaining this data in the first place.
On March 13, 2013 KrebsOnSecurity featured a story — Credit Reports Sold for Cheap in the Underweb –which sought to explain how the proprietors of Exposed[dot]su had obtained the records for the public officials and celebrities from a Russian online identity theft service called sssndob[dot]ru.
I noted in that story that sources close to the investigation said the assailants were using data gleaned from the ssndob[dot]ru ID theft service to gather enough information so that they could pull credit reports on targets directly from annualcreditreport.com, a site mandated by Congress to provide consumers a free copy of their credit report annually from each of the three major credit bureaus.
Peeved that I’d outed his methods for doxing public officials, Islam helped orchestrate my swatting the very next day. Within the span of 45 minutes, KrebsOnSecurity.com came under a sustained denial-of-service attack which briefly knocked my site offline.
At the same time, my hosting provider received a phony letter from the FBI stating my site was hosting illegal content and needed to be taken offline. And, then there was the swatting which occurred minutes after that phony communique was sent.
All told, the government alleges that Islam swatted at least 19 other people, although only seven of the victims (or their representatives) showed up in court today to tell similarly harrowing stories (I was asked to but did not testify).
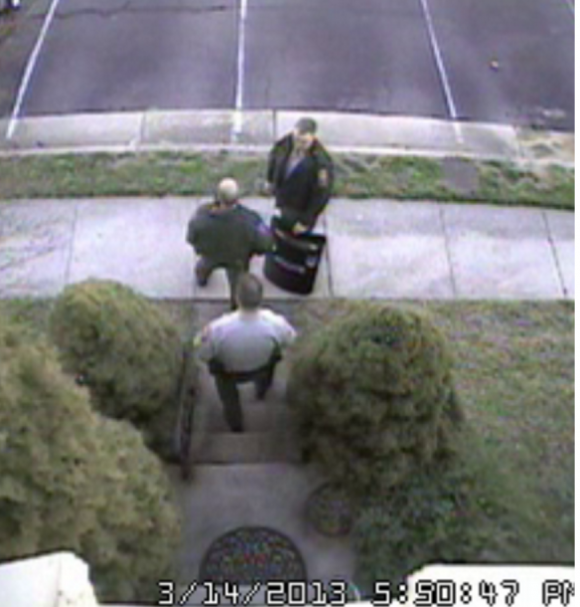

Security camera footage of Fairfax County police officers responding to my 2013 swatting incident.
Going into today’s sentencing hearing, the court advised that under the government’s sentencing guidelines Islam was facing between 37 and 46 months in prison for the crimes to which he’d pleaded guilty. But U.S. District Court Judge Randolph Moss seemed especially curious about the government’s rationale for charging Islam with conspiracy to transmit a threat to kidnap or harm using a deadly weapon.
Judge Moss said the claim raises a somewhat novel legal question: Can the government allege the use of deadly force when the perpetrator of a swatting incident did not actually possess a weapon?
Corbin Weiss, an assistant US attorney and a cybercrime coordinator with the U.S. Department of Justice, argued that in most of the swatting attacks Islam perpetrated he expressed to emergency responders that any responding officers would be shot or blown up. Thus, the government argued, Islam was using police officers as a proxy for assault with a deadly weapon by ensuring that responding officers would be primed to expect a suspect who was armed and openly hostile to police. Continue reading →
 In a statement released Tuesday evening, Cici’s said that in early March 2016, the company received reports from several of its restaurant locations that point-of-sale systems were not working properly.
In a statement released Tuesday evening, Cici’s said that in early March 2016, the company received reports from several of its restaurant locations that point-of-sale systems were not working properly.



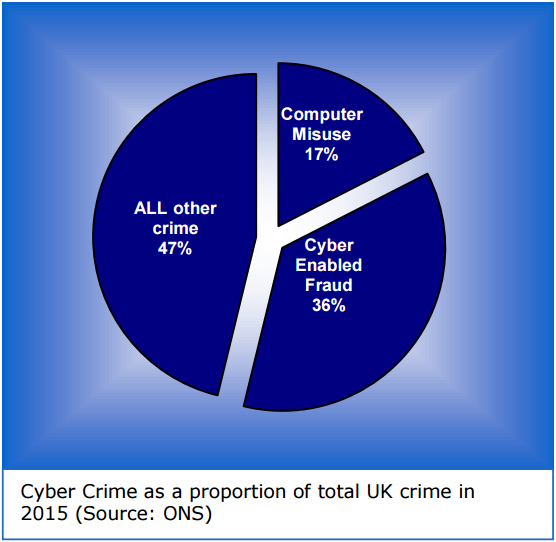
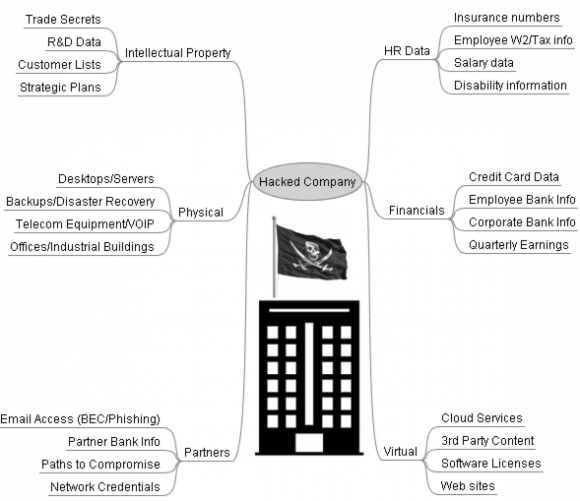
 First off, if you have Adobe Flash Player installed and haven’t yet hobbled this insecure program so that it runs only when you want it to, you are playing with fire. It’s bad enough that hackers are constantly finding and exploiting zero-day flaws in Flash Player before Adobe even knows about the bugs.
First off, if you have Adobe Flash Player installed and haven’t yet hobbled this insecure program so that it runs only when you want it to, you are playing with fire. It’s bad enough that hackers are constantly finding and exploiting zero-day flaws in Flash Player before Adobe even knows about the bugs.
![Exposed[dot]su was built with the help of identity information obtained and/or stolen from ssndob[dot]ru.](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/exposed-su-600x462.png)