vDOS — a “booter” service that has earned in excess of $600,000 over the past two years helping customers coordinate more than 150,000 so-called distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks designed to knock Web sites offline — has been massively hacked, spilling secrets about tens of thousands of paying customers and their targets.
The vDOS database, obtained by KrebsOnSecurity.com at the end of July 2016, points to two young men in Israel as the principal owners and masterminds of the attack service, with support services coming from several young hackers in the United States.
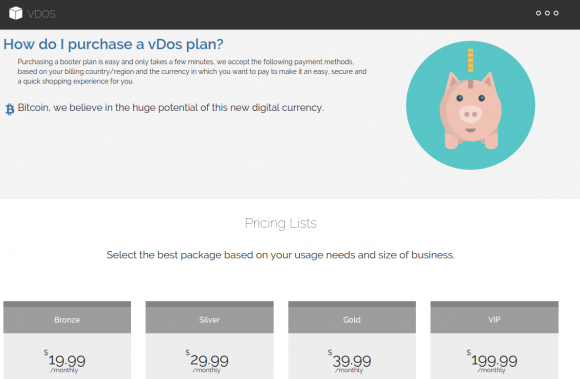
The vDos home page.
To say that vDOS has been responsible for a majority of the DDoS attacks clogging up the Internet over the past few years would be an understatement. The various subscription packages to the service are sold based in part on how many seconds the denial-of-service attack will last. And in just four months between April and July 2016, vDOS was responsible for launching more than 277 million seconds of attack time, or approximately 8.81 years worth of attack traffic.
Let the enormity of that number sink in for a moment: That’s nearly nine of what I call “DDoS years” crammed into just four months. That kind of time compression is possible because vDOS handles hundreds — if not thousands — of concurrent attacks on any given day.
Although I can’t prove it yet, it seems likely that vDOS is responsible for several decades worth of DDoS years. That’s because the data leaked in the hack of vDOS suggest that the proprietors erased all digital records of attacks that customers launched between Sept. 2012 (when the service first came online) and the end of March 2016.
HOW vDOS GOT HACKED
The hack of vDOS came about after a source was investigating a vulnerability he discovered on a similar attack-for-hire service called PoodleStresser. The vulnerability allowed my source to download the configuration data for PoodleStresser’s attack servers, which pointed back to api.vdos-s[dot]com. PoodleStresser, as well as a large number of other booter services, appears to rely exclusively on firepower generated by vDOS.
From there, the source was able to exploit a more serious security hole in vDOS that allowed him to dump all of the service’s databases and configuration files, and to discover the true Internet address of four rented servers in Bulgaria (at Verdina.net) that are apparently being used to launch the attacks sold by vDOS. The DDoS-for-hire service is hidden behind DDoS protection firm Cloudflare, but its actual Internet address is 82.118.233.144.
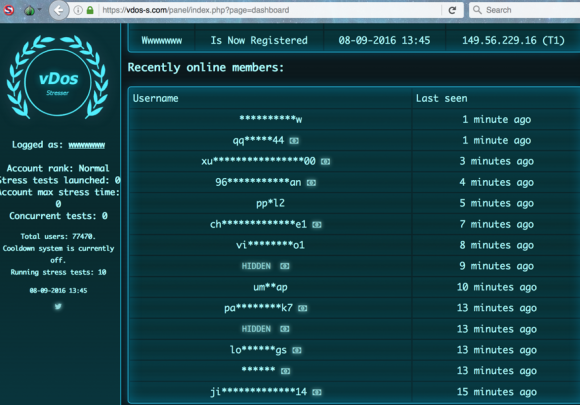
vDOS had a reputation on cybercrime forums for prompt and helpful customer service, and the leaked vDOS databases offer a fascinating glimpse into the logistical challenges associated with running a criminal attack service online that supports tens of thousands of paying customers — a significant portion of whom are all trying to use the service simultaneously.
Multiple vDOS tech support tickets were filed by customers who complained that they were unable to order attacks on Web sites in Israel. Responses from the tech support staff show that the proprietors of vDOS are indeed living in Israel and in fact set the service up so that it was unable to attack any Web sites in that country — presumably so as to not attract unwanted attention to their service from Israeli authorities. Here are a few of those responses:
(‘4130′,’Hello `d0rk`,\r\nAll Israeli IP ranges have been blacklisted due to security reasons.\r\n\r\nBest regards,\r\nP1st.’,’03-01-2015 08:39),
(‘15462′,’Hello `g4ng`,\r\nMh, neither. I\’m actually from Israel, and decided to blacklist all of them. It\’s my home country, and don\’t want something to happen to them :)\r\n\r\nBest regards,\r\nDrop.’,’11-03-2015 15:35),
(‘15462′,’Hello `roibm123`,\r\nBecause I have an Israeli IP that is dynamic.. can\’t risk getting hit/updating the blacklist 24/7.\r\n\r\nBest regards,\r\nLandon.’,’06-04-2015 23:04),
(‘4202′,’Hello `zavi156`,\r\nThose IPs are in israel, and we have all of Israel on our blacklist. Sorry for any inconvinience.\r\n\r\nBest regards,\r\nJeremy.’,’20-05-2015 10:14),
(‘4202′,’Hello `zavi156`,\r\nBecause the owner is in Israel, and he doesn\’t want his entire region being hit offline.\r\n\r\nBest regards,\r\nJeremy.’,’20-05-2015 11:12),
(‘9057′,’There is a option to buy with Paypal? I will pay more than $2.5 worth.\r\nThis is not the first time I am buying booter from you.\r\nIf no, Could you please ask AplleJack? I know him from Israel.\r\nThanks.’,’21-05-2015 12:51),
(‘4120′,’Hello `takedown`,\r\nEvery single IP that\’s hosted in israel is blacklisted for safety reason. \r\n\r\nBest regards,\r\nAppleJ4ck.’,’02-09-2015 08:57),
WHO RUNS vDOS?
As we can see from the above responses from vDOS’s tech support, the owners and operators of vDOS are young Israeli hackers who go by the names P1st a.k.a. P1st0, and AppleJ4ck. The two men market their service mainly on the site hackforums[dot]net, selling monthly subscriptions using multiple pricing tiers ranging from $20 to $200 per month. AppleJ4ck hides behind the same nickname on Hackforums, while P1st goes by the alias “M30w” on the forum.
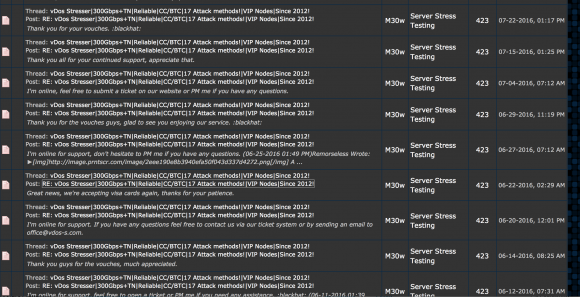
Some of P1st/M30W’s posts on Hackforums regarding his service vDOS.
vDOS appears to be the longest-running booter service advertised on Hackforums, and it is by far and away the most profitable such business. Records leaked from vDOS indicate that since July 2014, tens of thousands of paying customers spent a total of more than $618,000 at the service using Bitcoin and PayPal.
Incredibly, for brief periods the site even accepted credit cards in exchange for online attacks, although it’s unclear how much the site might have made in credit card payments because the information is not in the leaked databases.
The Web server hosting vDOS also houses several other sites, including huri[dot]biz, ustress[dot]io, and vstress[dot]net. Virtually all of the administrators at vDOS have an email account that ends in v-email[dot]org, a domain that also is registered to an Itay Huri with a phone number that traces back to Israel.
The proprietors of vDOS set their service up so that anytime a customer asked for technical assistance the site would blast a text message to six different mobile numbers tied to administrators of the service, using an SMS service called Nexmo.com. Two of those mobile numbers go to phones in Israel. One of them is the same number listed for Itay Huri in the Web site registration records for v-email[dot]org; the other belongs to an Israeli citizen named Yarden Bidani. Neither individual responded to requests for comment.
The leaked database and files indicate that vDOS uses Mailgun for email management, and the secret keys needed to manage that Mailgun service were among the files stolen by my source. The data shows that vDOS support emails go to itay@huri[dot]biz, itayhuri8@gmail.com and raziel.b7@gmail.com.
LAUNDERING THE PROCEEDS FROM DDOS ATTACKS
The $618,000 in earnings documented in the vDOS leaked logs is almost certainly a conservative income figure. That’s because the vDOS service actually dates back to Sept 2012, yet the payment records are not available for purchases prior to 2014. As a result, it’s likely that this service has made its proprietors more than $1 million.
vDOS does not currently accept PayPal payments. But for several years until recently it did, and records show the proprietors of the attack service worked assiduously to launder payments for the service through a round-robin chain of PayPal accounts.
They did this because at the time PayPal was working with a team of academic researchers to identify, seize and shutter PayPal accounts that were found to be accepting funds on behalf of booter services like vDOS. Anyone interested in reading more on their success in making life harder for these booter service owners should check out my August 2015 story, Stress-Testing the Booter Services, Financially.
People running dodgy online services that violate PayPal’s terms of service generally turn to several methods to mask the true location of their PayPal Instant Payment Notification systems. Here is an interesting analysis of how popular booter services are doing so using shell corporations, link shortening services and other tricks.
Turns out, AppleJ4ck and p1st routinely recruited other forum members on Hackforums to help them launder significant sums of PayPal payments for vDOS each week.
“The paypals that the money are sent from are not verified,” AppleJ4ck says in one recruitment thread. “Most of the payments will be 200$-300$ each and I’ll do around 2-3 payments per day.”
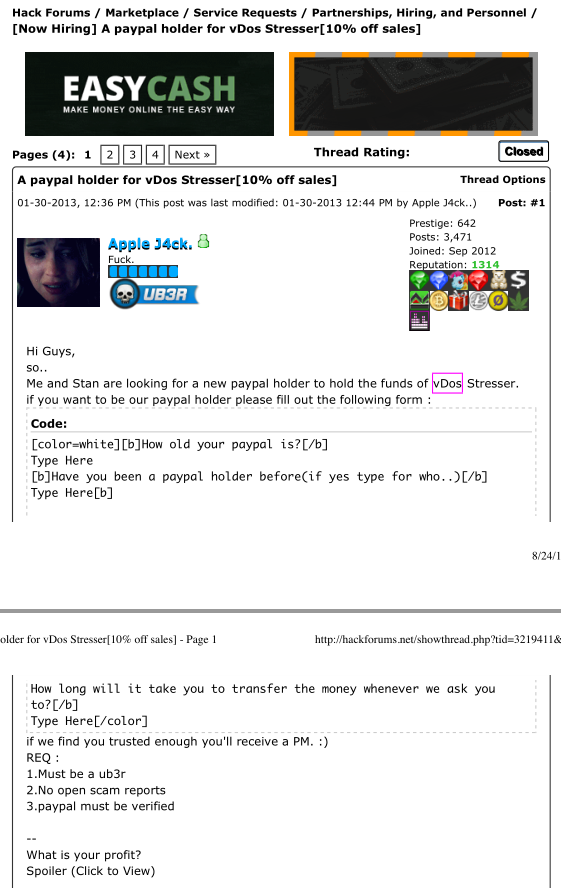
vDos co-owner AppleJ4ck recruiting Hackforums members to help launder PayPal payments for his booter service.
It is apparent from the leaked vDOS logs that in July 2016 the service’s owners implemented an additional security measure for Bitcoin payments, which they accept through Coinbase. The data shows that they now use an intermediary server (45.55.55.193) to handle Coinbase traffic. When a Bitcoin payment is received, Coinbase notifies this intermediary server, not the actual vDOS servers in Bulgaria.
A server situated in the middle and hosted at a U.S.-based address from Digital Ocean then updates the database in Bulgaria, perhaps because the vDOS proprietors believed payments from the USA would attract less interest from Coinbase than huge sums traversing through Bulgaria each day. Continue reading →






 Half of the updates Microsoft released Tuesday earned the company’s most dire “critical” rating, meaning they could be exploited by malware or miscreants to install malicious software with no help from the user, save for maybe just visiting a hacked or booby-trapped Web site. Security firms
Half of the updates Microsoft released Tuesday earned the company’s most dire “critical” rating, meaning they could be exploited by malware or miscreants to install malicious software with no help from the user, save for maybe just visiting a hacked or booby-trapped Web site. Security firms