The San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA) was hit with a ransomware attack on Friday, causing fare station terminals to carry the message, “You are Hacked. ALL Data Encrypted.” Turns out, the miscreant behind this extortion attempt got hacked himself this past weekend, revealing details about other victims as well as tantalizing clues about his identity and location.
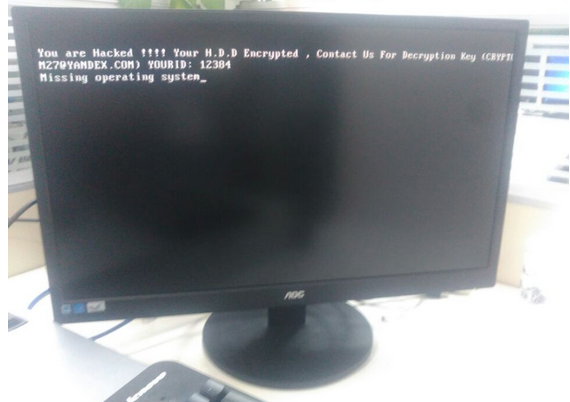
A copy of the ransom message left behind by the “Mamba” ransomware.
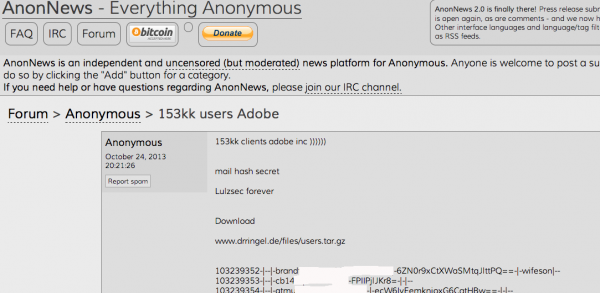
On Friday, The San Francisco Examiner reported that riders of SFMTA’s Municipal Rail or “Muni” system were greeted with handmade “Out of Service” and “Metro Free” signs on station ticket machines. The computer terminals at all Muni locations carried the “hacked” message: “Contact for key (cryptom27@yandex.com),” the message read.
The hacker in control of that email account said he had compromised thousands of computers at the SFMTA, scrambling the files on those systems with strong encryption. The files encrypted by his ransomware, he said, could only be decrypted with a special digital key, and that key would cost 100 Bitcoins, or approximately USD $73,000.
On Monday, KrebsOnSecurity was contacted by a security researcher who said he hacked this very same cryptom27@yandex.com inbox after reading a news article about the SFMTA incident. The researcher, who has asked to remain anonymous, said he compromised the extortionist’s inbox by guessing the answer to his secret question, which then allowed him to reset the attacker’s email password. A screen shot of the user profile page for cryptom27@yandex.com shows that it was tied to a backup email address, cryptom2016@yandex.com, which also was protected by the same secret question and answer.
Copies of messages shared with this author from those inboxes indicate that on Friday evening, Nov. 25, the attacker sent a message to SFMTA infrastructure manager Sean Cunningham with the following demand (the entirety of which has been trimmed for space reasons), signed with the pseudonym “Andy Saolis.”
“if You are Responsible in MUNI-RAILWAY !
All Your Computer’s/Server’s in MUNI-RAILWAY Domain Encrypted By AES 2048Bit!
We have 2000 Decryption Key !
Send 100BTC to My Bitcoin Wallet , then We Send you Decryption key For Your All Server’s HDD!!”
One hundred Bitcoins may seem like a lot, but it’s apparently not far from a usual payday for this attacker. On Nov. 20, hacked emails show that he successfully extorted 63 bitcoins (~$45,000) from a U.S.-based manufacturing firm.
The attacker appears to be in the habit of switching Bitcoin wallets randomly every few days or weeks. “For security reasons” he explained to some victims who took several days to decide whether to pay the ransom they’d been demanded. A review of more than a dozen Bitcoin wallets this criminal has used since August indicates that he has successfully extorted at least $140,000 in Bitcoin from victim organizations.
That is almost certainly a conservative estimate of his overall earnings these past few months: My source said he was unable to hack another Yandex inbox used by this attacker between August and October 2016, “w889901665@yandex.com,” and that this email address is tied to many search results for tech help forum postings from people victimized by a strain of ransomware known as Mamba and HDD Cryptor.
Copies of messages shared with this author answer many questions raised by news media coverage of this attack, such as whether the SFMTA was targeted. In short: No. Here’s why.
Messages sent to the attacker’s cryptom2016@yandex.com account show a financial relationship with at least two different hosting providers. The credentials needed to manage one of those servers were also included in the attacker’s inbox in plain text, and my source shared multiple files from that server.
KrebsOnSecurity sought assistance from several security experts in making sense of the data shared by my source. Alex Holden, chief information security officer at Hold Security Inc, said the attack server appears to have been used as a staging ground to compromise new systems, and was equipped with several open-source tools to help find and infect new victims.
“It appears our attacker has been using a number of tools which enabled the scanning of large portions of the Internet and several specific targets for vulnerabilities,” Holden said. “The most common vulnerability used ‘weblogic unserialize exploit’ and especially targeted Oracle Corp. server products, including Primavera project portfolio management software.”
According to a review of email messages from the Cryptom27 accounts shared by my source, the attacker routinely offered to help victims secure their systems from other hackers for a small number of extra Bitcoins. In one case, a victim that had just forked over a 20 Bitcoin ransom seemed all too eager to pay more for tips on how to plug the security holes that got him hacked. In return, the hacker pasted a link to a Web server, and urged the victim to install a critical security patch for the company’s Java applications.
“Read this and install patch before you connect your server to internet again,” the attacker wrote, linking to this advisory that Oracle issued for a security hole that it plugged in November 2015.
In many cases, the extortionist told victims their data would be gone forever if they didn’t pay the ransom in 48 hours or less. In other instances, he threatens to increase the ransom demand with each passing day. Continue reading →