Cybercriminals who specialize in phishing — or tricking people into giving up usernames and passwords at fake bank and ecommerce sites — aren’t generally considered the most sophisticated crooks, but occasionally they do exhibit creativity and chutzpah. That’s most definitely the case with a phishing gang that calls itself the “Manipulaters Team”, whose Web site boasts that it specializes in brand research and development.
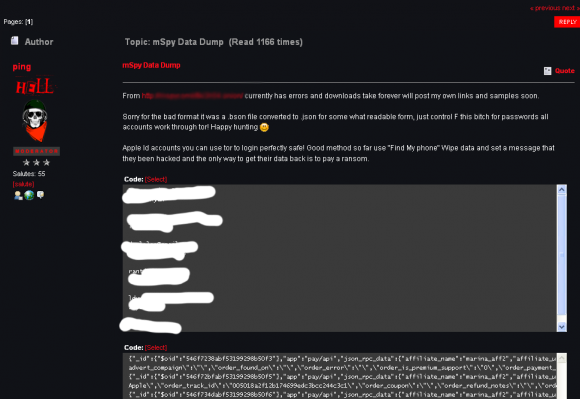
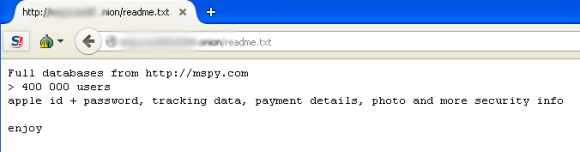
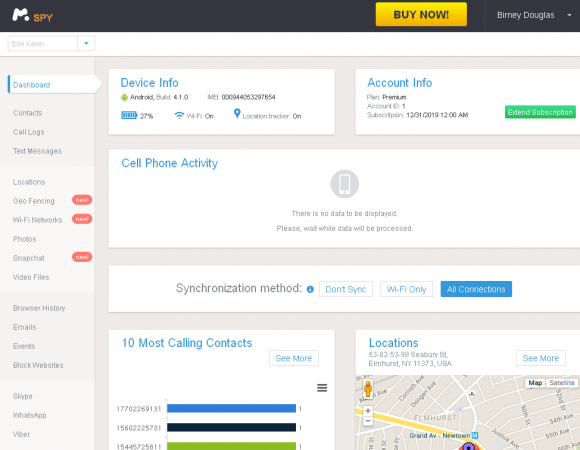
I first learned about the Manipulaters from a source at an Australian bank who clued me in to a phishing group that specializes in targeting Apple’s iCloud services and a whole mess of U.S., European and Asian banks. For whatever reason (probably because they’re proud of their work), these guys leave a calling card of sorts in the WHOIS Web site registration records for most of the phishing domains that they register: According to Domaintools.com, some 329 domains are registered to “admin@manipulaters[dot]com” (complete list of domains: in PDF and CSV).
The Web site for the “Manipulaters Team,” a phishing gang that brazenly advertises a specialization in “brand research.”
Manipulaters[dot]com is a pretty amusing site all around. Their home page advises that Mainpulaters “is an institute that caters to brand research & development. We have studied computer related products immensely, and are confident that we can get the job done. The learning never stops for us though, as we are always looking for ways to improve.” Brand research. Yeah, right.
“Our goal is to help each business and brand reach their ultimate potential,” explains the “Our Members” section of the site. “We have contracts with our members that allows us to have guidelines for them to follow on their path to success. We have put these in place for a reason. This provides the stability and direction that companies/brands need to succeed.” Points for brazenness.
Their site advises that interested parties can “become a member” of the Manipulaters Team just by paying a one-time membership fee of $15, and providing a driver’s license/ID card plus a phone or electricity bill. Ah, there’s nothing quite like phishers phishing phishers.
The scary aspect of this fraud gang is that they appear to play in the Web hosting space as well. Most of their phishing pages are in fact hosted on Internet address space that is assigned to Manipulaters[dot]com: Incredibly, the group is listed as the current occupants of an entire Class C range of Internet addresses, from 167.160.46.0 to 167.160.46.255. Continue reading