I’ve written a great deal about “money mules,” people looking for part-time employment who unwittingly or willingly help organized cyber thieves launder stolen funds. The most common question I get about money mules is: “Do any of them ever get prosecuted?” The answer is generally “no” because it’s hard to prove that these mules weren’t scammed. But recently, I encountered a mule who made it abundantly clear that he understood exactly what he was doing.
In June 2011, I was investigating an online banking heist against a company called Jackson Properties. Thieves had broken into Jackson’s computers and stolen the firm’s online banking credentials. They added a half dozen money mules to the company’s payroll account, using mules they’d acquired from a gang I call the Back Office group. This mule gang uses multiple bogus corporate names, and the Back Office front company that supplied the mules in this attack was called AMR Company.
Reginald, a 45-year-0ld Texas resident, was among the mules hired by AMR Company. Reggie communicated with the mule recruiters by logging into a Web site set up by the fake company, and checking for new messages. A source who had figured out how to view the administrator’s account (and hence, all messages on the server) sent me some choice screenshots from several mule communications.
On June 7, the mule recruiters sent Reginald a transfer of $4,910, claiming that Jackson Properties was its client. Reginald was to withdraw the money in cash and wire it overseas, minus a small commission. The payment never landed in his account; it was blocked when Jackson detected the fraudulent transactions and worked with its bank to get them reversed.
But that apparently did not deter our Reginald, who told his recruiter and manager at AMR Company that he understood the whole thing was a scam, and that he had done this sort of thing before. He said he was ready and willing to open additional bank accounts to help with future fraud schemes.
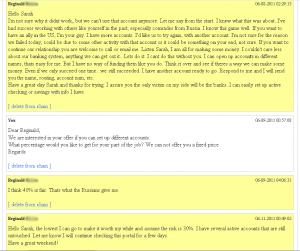
On June 8, Reggie signed into his account at AMR Company and wrote the following to Sarah, his erstwhile boss:
“Let me say from the start. I knew what this was about. I’ve had success working with others like yourself in the past, especially comrades from Russia. I know this game well. If you want to have an ally in the US, I’m your guy. I have more accounts. I’d like us to try again, with another account…Listen Sarah, I am all for making some money. I couldn’t care less about our banking system, anything we can get out [sic] it. Lets [sic] do it. I cant do this without you. I can open up accounts in different names, that’s easy for me. But I have no way of funding them like you do. Think it over and see if there’s a way we can make some money. Even if we only succeed one time…we will still succeeded. I have another account ready to go. Respond to me and I will send you the name, routing, account num, etc.”