Many sites and services require customers to present “proof” of their identity online by producing scanned copies of important documents, such as passports, utility bills, or diplomas. But these requests don’t really prove much, as there are a number of online services that will happily forge these documents quite convincingly for a small fee.
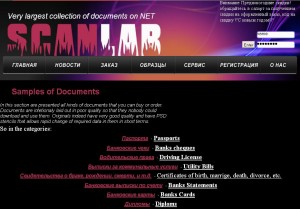 Services like scanlab.name, for example, advertise the ability to create a variety of forged documents made to look like scanned copies of things like credit cards, passports, drivers licenses, utility bills, birth/death/marriage certificates and diplomas. In fact, Scanlab boasts that it has a large database of templates — 17 gb worth from more than 120 countries — which it can draw upon to forge scanned copies of just about any document you might need.
Services like scanlab.name, for example, advertise the ability to create a variety of forged documents made to look like scanned copies of things like credit cards, passports, drivers licenses, utility bills, birth/death/marriage certificates and diplomas. In fact, Scanlab boasts that it has a large database of templates — 17 gb worth from more than 120 countries — which it can draw upon to forge scanned copies of just about any document you might need.
When Scanlab site first surfaced in 2008, it was a fairly bustling place and had a decent number of clients. That is, until not long after I wrote about them in August 2008, when the site just vanished for some reason. The service reappeared this summer, but it’s tough to tell whether Scanlab 2.0 attracts much business.
Scanlab created this scan of a fake Missouri drivers license — shown here with the picture and made-up personal details of Wikileaks founder Julian Assange — using a photo from Google images, so the quality could certainly be better. But it’s probably enough to pass for a scan of a real ID for most online services that might ask for one as proof of identity.
And, like most online services that cater to carders, this one does not accept credit cards: Payments are made through WebMoney, a virtual currency popular in Eastern Europe and Russia.










