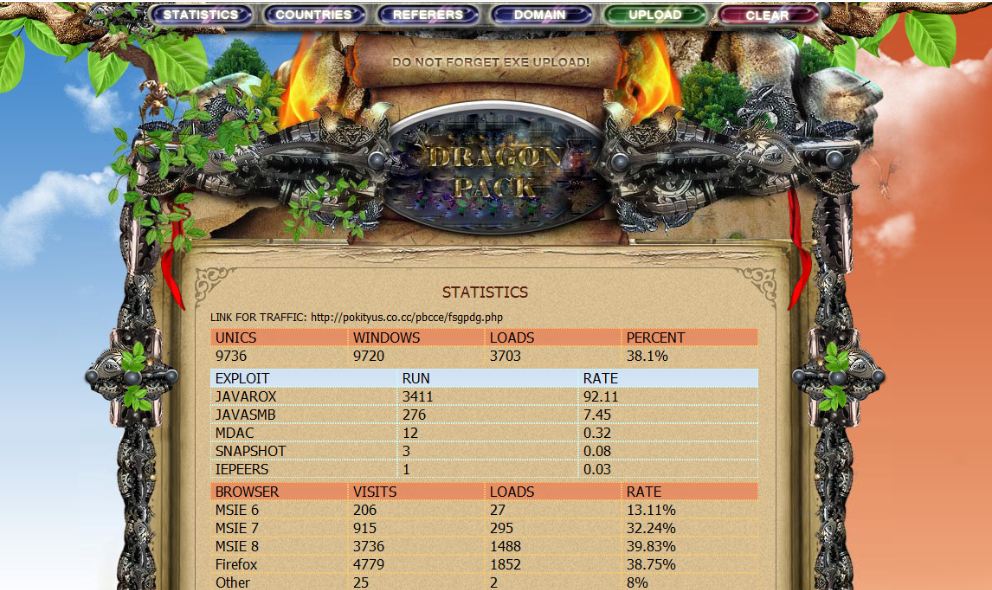
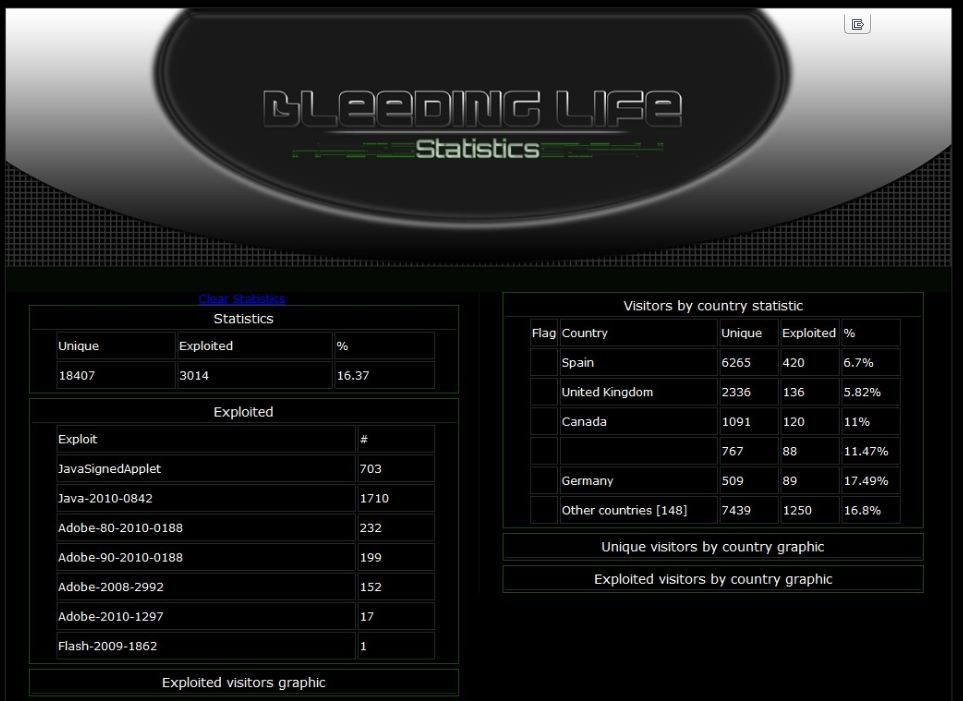
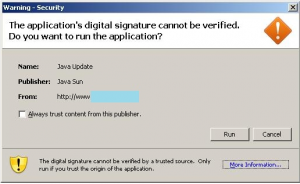
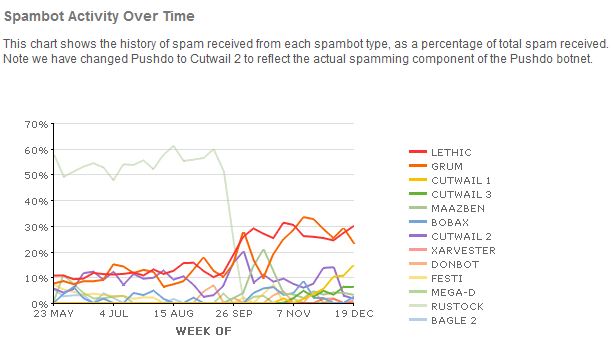
A malware-laced e-mail that spoofed seasons greetings from The White House siphoned gigabytes of sensitive documents from dozens of victims over the holidays, including a number of government employees and contractors who work on cybersecurity matters.
The attack appears to be the latest salvo from ZeuS malware gangs whose activities over the past year have blurred the boundaries between online financial crime and espionage, by stealing both financial data and documents from victim machines. This activity is unusual because most criminals using ZeuS are interested in money-making activities – such as swiping passwords and creating botnets – whereas the hoovering up of sensitive government documents is activity typically associated with so-called advanced persistent threat attacks, or those deployed to gather industrial and military intelligence.
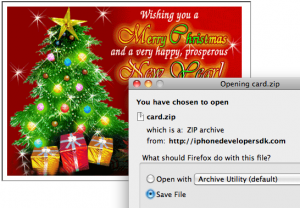 On Dec. 23, the following message was sent to an unknown number of recipients;
On Dec. 23, the following message was sent to an unknown number of recipients;
“As you and your families gather to celebrate the holidays, we wanted to take
a moment to send you our greetings. Be sure that we’re profoundly grateful
for your dedication to duty and wish you inspiration and success in
fulfillment of our core mission.
Greeting card:
hxxp://xtremedefenceforce.com/[omitted]
hxxp://elvis.com.au/[omitted]
Merry Christmas!
___________________________________________
Executive Office of the President of the United States
The White House
1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW
Washington, DC 20500
Recipients who clicked either of the above links and opened the file offered were infected with a ZeuS Trojan variant that steals passwords and documents and uploads them to a server in Belarus. I was able to analyze the documents taken in that attack, which hoovered up more than 2 gigabytes of PDFs, Microsoft Word and Excel documents from dozens of victims. I feel reasonably confident I have identified several victims, all of whom appear to be employees of some government or another. Among those who fell for the scam e-mail were:
-An employee at the National Science Foundation’s Office of Cyber Infrastructure. The documents collected from this victim include hundreds of NSF grant applications for new technologies and scientific approaches.
-An intelligence analyst in Massachusetts State Police gave up dozens of documents that appear to be records of court-ordered cell phone intercepts. Several documents included in the cache indicate the victim may have recently received top-secret clearance. Among this person’s cache of documents is a Department of Homeland Security tip sheet called “Safeguarding National Security Information.”
-An unidentified employee at the Financial Action Task Force, an intergovernmental body dedicated to the development and promotion of national and international policies to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
-An official with the Moroccan government’s Ministry of Industry, Commerce and New Technologies.
-An employee at the Millennium Challenge Corporation, a federal agency set up to provide foreign aid for development projects in 15 countries in Africa, Central America and other regions.
The most interesting component of this attack was not the ZeuS variant, which by most accounts was an older, well-understood version of the banking Trojan. Rather, researchers are focusing on the component responsible for stealing documents, which suggests the handiwork of a novice who was quite active in 2010.
Continue reading →