Most people who operate DDoS-for-hire businesses attempt to hide their true identities and location. Proprietors of these so-called “booter” or “stresser” services — designed to knock websites and users offline — have long operated in a legally murky area of cybercrime law. But until recently, their biggest concern wasn’t avoiding capture or shutdown by the feds: It was minimizing harassment from unhappy customers or victims, and insulating themselves against incessant attacks from competing DDoS-for-hire services.
And then there are booter store operators like John Dobbs, a 32-year-old computer science graduate student living in Honolulu, Hawaii. For at least a decade until late last year, Dobbs openly operated IPStresser[.]com, a popular and powerful attack-for-hire service that he registered with the state of Hawaii using his real name and address. Likewise, the domain was registered in Dobbs’s name and hometown in Pennsylvania.
Dobbs, in an undated photo from his Github profile. Image: john-dobbs.github.io
The only work experience Dobbs listed on his resume was as a freelance developer from 2013 to the present day. Dobbs’s resume doesn’t name his booter service, but in it he brags about maintaining websites with half a million page views daily, and “designing server deployments for performance, high-availability and security.”
In December 2022, the U.S. Department of Justice seized Dobbs’s IPStresser website and charged him with one count of aiding and abetting computer intrusions. Prosecutors say his service attracted more than two million registered users, and was responsible for launching a staggering 30 million distinct DDoS attacks.
The government seized four-dozen booter domains, and criminally charged Dobbs and five other U.S. men for allegedly operating stresser services. This was the Justice Department’s second such mass takedown targeting DDoS-for-hire services and their accused operators. In 2018, the feds seized 15 stresser sites, and levied cybercrime charges against three men for their operation of booter services.
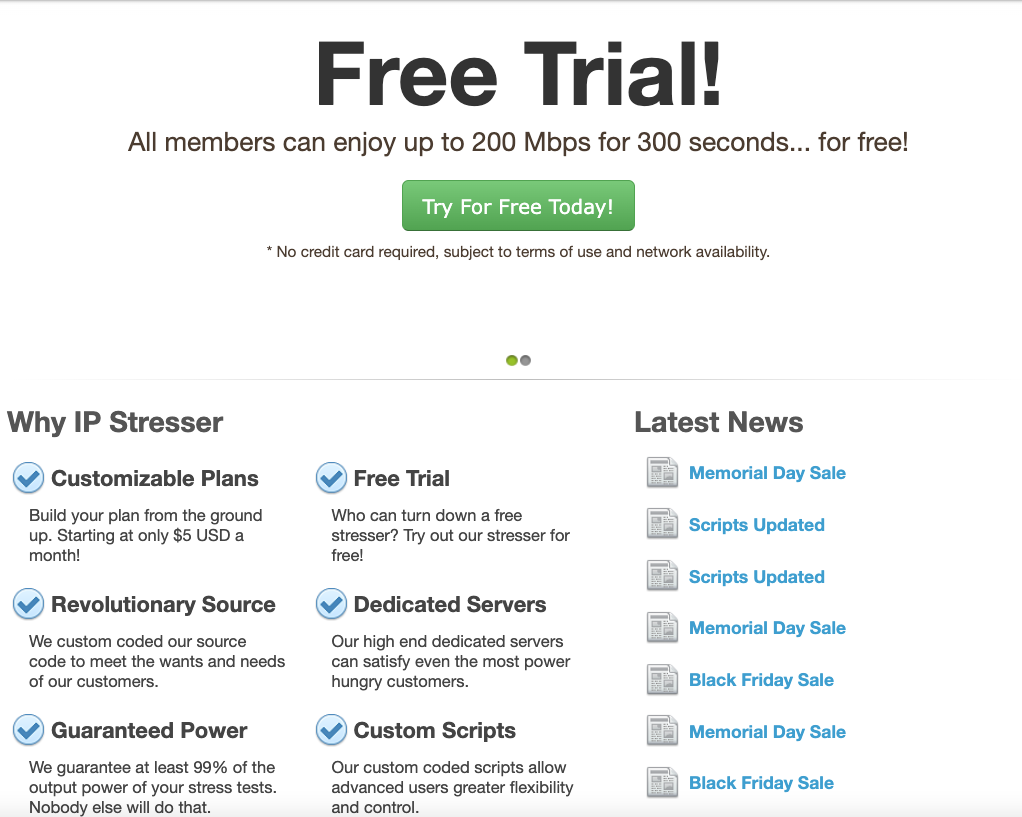
Dobbs’s booter service, IPStresser, in June 2020. Image: archive.org.
Many accused stresser site operators have pleaded guilty over the years after being hit with federal criminal charges. But the government’s core claim — that operating a booter site is a violation of U.S. computer crime laws — wasn’t properly tested in the courts until September 2021.
That was when a jury handed down a guilty verdict against Matthew Gatrel, a then 32-year-old St. Charles, Ill. man charged in the government’s first 2018 mass booter bust-up. Despite admitting to FBI agents that he ran two booter services (and turning over plenty of incriminating evidence in the process), Gatrel opted to take his case to trial, defended the entire time by court-appointed attorneys.
Prosecutors said Gatrel’s booter services — downthem[.]org and ampnode[.]com — helped some 2,000 paying customers launch debilitating digital assaults on more than 20,000 targets, including many government, banking, university and gaming websites.
Gatrel was convicted on all three charges of violating the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, including conspiracy to commit unauthorized impairment of a protected computer, conspiracy to commit wire fraud, and unauthorized impairment of a protected computer. He was sentenced to two years in prison.
Now, it appears Dobbs is also planning to take his chances with a jury. On Jan. 4, Dobbs entered a plea of not guilty. Neither Dobbs nor his court-appointed attorney responded to requests for comment.
But as it happens, Dobbs himself provided some perspective on his thinking in an email exchange with KrebsOnSecurity back in 2020. I’d reached out to Dobbs because it was obvious he didn’t mind if people knew he operated one of the world’s most popular DDoS-for-hire sites, and I was genuinely curious why he was so unafraid of getting raided by the feds.
“Yes, I am the owner of the domain you listed, however you are not authorized to post an article containing said domain name, my name or this email address without my prior written permission,” Dobbs replied to my initial outreach on March 10, 2020 using his email address from the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
A few hours later, I received more strident instructions from Dobbs, this time via his official email address at ipstresser[.]com.
“I will state again for absolute clarity, you are not authorized to post an article containing ipstresser.com, my name, my GitHub profile and/or my hawaii.edu email address,” Dobbs wrote, as if taking dictation from a lawyer who doesn’t understand how the media works.
When pressed for particulars on his business, Dobbs replied that the number of IPStresser customers was “privileged information,” and said he didn’t even advertise the service. When asked whether he was concerned that many of his competitors were by then serving jail time for operating similar booter services, Dobbs maintained that the way he’d set up the business insulated him from any liability.
“I have been aware of the recent law enforcement actions against other operators of stress testing services,” Dobbs explained. “I cannot speak to the actions of these other services, but we take proactive measures to prevent misuse of our service and we work with law enforcement agencies regarding any reported abuse of our service.”
What were those proactive measures? In a 2015 interview with ZDNet France, Dobbs asserted that he was immune from liability because his clients all had to submit a digital signature attesting that they wouldn’t use the site for illegal purposes.
“Our terms of use are a legal document that protects us, among other things, from certain legal consequences,” Dobbs told ZDNet. “Most other sites are satisfied with a simple checkbox, but we ask for a digital signature in order to imply real consent from our customers.”
Dobbs told KrebsOnSecurity his service didn’t generate much of a profit, but rather that he was motivated by “filling a legitimate need.”
“My reason for offering the service is to provide the ability to test network security measures before someone with malicious intent attacks said network and causes downtime,” he said. “Sure, some people see only the negatives, but there is a long list of companies I have worked with over the years who would say my service is a godsend and has helped them prevent tens of thousands of dollars in downtime resulting from a malicious attack.”
“I do not believe that providing such a service is illegal, assuming proper due diligence to prevent malicious use of the service, as is the case for IPstresser[.]com,” Dobbs continued. “Someone using such a service to conduct unauthorized testing is illegal in many countries, however, the legal liability is that of the user, not of the service provider.”
Dobbs’s profile on GitHub includes more of his ideas about his work, including a curious piece on “software engineering ethics.” In his January 2020 treatise “My Software Engineering Journey,” Dobbs laments that nothing in his formal education prepared him for the reality that a great deal of his work would be so tedious and repetitive (this tracks closely with a 2020 piece here called Career Choice Tip: Cybercrime is Mostly Boring).
“One area of software engineering that I think should be covered more in university classes is maintenance,” Dobbs wrote. “Projects are often worked on for at most a few months, and students do not experience the maintenance aspect of software engineering until they reach the workplace. Let’s face it, ongoing maintenance of a project is boring; there is nothing like the euphoria of completing a project you have been working on for months and releasing it to the world, but I would say that half of my professional career has been related to maintenance.” Continue reading →