Several articles here have delved into the history of John Bernard, the pseudonym used by a fake billionaire technology investor who tricked dozens of startups into giving him tens of millions of dollars. Bernard’s latest victim — a Norwegian company hoping to build a fleet of environmentally friendly shipping vessels — is now embroiled in a lawsuit over a deal gone bad, in which Bernard falsely claimed to have secured $100 million from six other wealthy investors, including the founder of Uber and the artist Abel Makkonen Tesfaye, better known as The Weeknd.

John Bernard is a pseudonym used by John Clifton Davies, a convicted fraudster from the United Kingdom who is currently a fugitive from justice and residing in Ukraine. Davies’ Bernard persona has fleeced dozens of technology companies out of an estimated $30 million with the promise of lucrative investments.
For several years until reinventing himself again quite recently, Bernard pretended to be a billionaire Swiss investor who made his fortunes in the dot-com boom 20 years ago and who was seeking investment opportunities. Bernard generated a stream of victims by offering extraordinarily generous finder’s fees for investment brokers who helped him secure new clients. But those brokers would eventually get stiffed as well because Bernard’s company would never consummate a deal.
In case after case, Bernard would promise to invest millions in tech startups, and then insist that companies pay tens of thousands of dollars worth of due diligence fees up front. However, the due diligence company he insisted on using — another Swiss firm called Inside Knowledge — also was secretly owned by Bernard, who would invariably pull out of the deal after receiving the due diligence money.
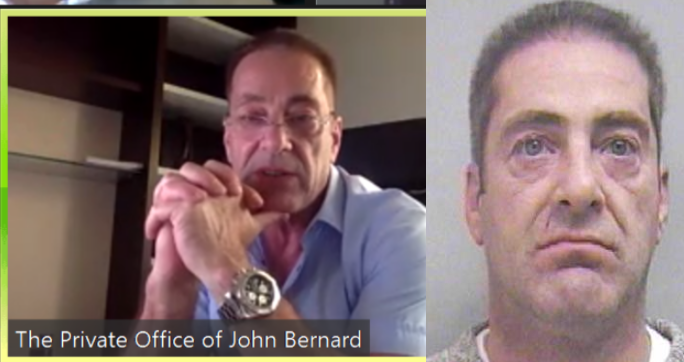
The scam artist John Bernard (left) in a recent Zoom call, and a photo of John Clifton Davies from 2015.
But Bernard would adopt a slightly different approach to stealing from Freidig Shipping Ltd., a Norwegian company formed in 2017 that was seeking the equivalent of USD $100 million investment to bring its green fleet of 30 new offshore service vessels to fruition.
Journalists Harald Vanvik and Harald Berglihn from the Norwegian Business Daily write that through investment advisors in London, Bernard was introduced to Nils-Odd Tønnevold, co-founder of Freidig Shipping and an investment advisor with 20 years of experience.
“Both Bernard and Inside Knowledge appeared to be professionals,” the reporters wrote in a story that’s behind a paywall. “Bernard appeared to be experienced. He knew a lot about start-ups and got into things quickly. Credible and reliable was the impression of him, said Tønnevold.”
“Bernard eventually took on the role of principal investor, claiming he had six other wealthy investors on the team, including artist Abel Makkonen Tesfaye, known as The Weeknd, Uber founder Garrett Camp and Norilsk Nickel owner Russian Vladimir Potanin,” the Norwegian journalists wrote. “These committed to contribute $99.25 million to Freidig.”
So in this case Bernard conveniently claimed he’d come up with almost all of the investment, which came $750,000 short of the goal. Another investor, a Belgian named Guy Devos, contributed the remaining $750,000.
But by the spring of 2020, it was clear that Devos and others involved in the shipping project had been tricked, and that all the money which had been paid to Bernard — an estimated NOK 15 million (~USD $1.67 million) — had been lost. By that time the two co-founders and their families had borrowed USD $1.5 million, and had transferred the funds to Inside Knowledge. Continue reading