Notifying people and companies about data breaches often can be a frustrating and thankless job. Despite my best efforts, sometimes a breach victim I’m alerting will come away convinced that I am not an investigative journalist but instead a scammer. This happened most recently this week, when I told a California credit union that its online banking site was compromised and apparently had been for nearly two months.
On Feb. 23, I contacted Coast Central Credit Union, a financial institution based in Eureka, Calif. that serves more than 60,000 customers. I explained who I was, how they’d likely been hacked, how they could verify the hack, and how they could fix the problem. Two days later when I noticed the site was still hacked, I contacted the credit union again, only to find they still didn’t believe me.
News of the compromise came to me via Alex Holden, a fellow lurker in the cybercrime underground and founder of Hold Security [full disclosure: While Holden’s site lists me as an advisor to his company, I receive zero compensation for that role]. Holden told me that crooks had hacked the credit union’s site and retrofitted it with a “Web shell,” a simple backdoor program that allows an attacker to remotely control the Web site and server using nothing more than a Web browser.
The credit union’s switchboard transferred me to a person in Coast Central’s tech department who gave his name only as “Vincent.” I told Vincent that the credit union’s site was very likely compromised, how he could verify it, etc. I also gave him my contact information, and urged him to escalate the issue. After all, I said, the intruders could use the Web shell program to upload malicious software that steals customer passwords directly from the credit union’s Web site. Vincent didn’t seem terribly alarmed about the news, and assured me that someone would be contacting me for more information.
This afternoon I happened to reload the login page for the Web shell on the credit union’s site and noticed it was still available. A call to the main number revealed that Vincent wasn’t in, but that Patrick in IT would take my call. For better or worse, Patrick was deeply skeptical that I was not impersonating the author of this site.
I commended him on his wariness and suggested several different ways he could independently verify my identity. When asked for a contact at the credit union that could speak to the media, Patrick said that person was him but declined to tell me his last name. He also refused to type in a Web address on his own employer’s Web site to verify the Web shell login page.
“I hope you do write about this,” Patrick said doubtfully, after I told him that I’d probably put something up on the site today about the hack. “That would be funny.”
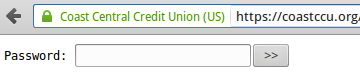
The login page for the Web shell that was removed today from Coast Central Credit Union’s Web site.
Exasperated, I told Patrick good luck and hung up. Thankfully, I did later hear from Ed Christians, vice president of information systems at Coast Central. Christians apologized for the runaround and said everyone in his department were regular readers of KrebsOnSecurity. “I was hoping I’d never get a call from you, but I guess I can cross that one off my list,” Christians said. “We’re going to get this thing taken down immediately.”
The credit union has since disabled the Web shell and is continuing to investigate the extent and source of the breach. There is some evidence to suggest the site may have been hacked via an outdated version of Akeeba Backup — a Joomla component that allows users to create and manage complete backups of a Joomla-based website. Screen shots of the files listed by the Web shell planted on Coast Central Credit Union indeed indicate the presence of Akeeba Backup on the financial institution’s Web server.
A Web search on one backdoor component that the intruders appear to have dropped on the credit union’s site on Dec. 29, 2015 — a file called “sfx.php” — turns up this blog post in which Swiss systems engineer Claudio Marcel Kuenzler described his investigation of a site that was hacked through the Akeeba Backup function.
“The file was uploaded with a simple GET request by using a vulnerability in the com_joomlaupdate (which is part of Akeeba Backup) component,” Kuenzler wrote, noting that there is a patch available for the vulnerability.
These Web shell components are extremely common, have been around for years, and are used by online miscreants for a variety of tasks — from selling ad traffic and spreading malware to promoting malicious and spammy Web sites.
It’s not clear yet whether the hackers who hit the credit union’s site did anything other than install the backdoor, but Kuenzler wrote that in his case the intruders indeed used their access to relay spam. The attackers could just have easily booby-trapped the credit union’s site to foist malicious software disguised as a security update when customers tried to log in at the site.
Holden said he’s discovered more than 13,000 sites that are currently infected with Web shells just like the one that hit Coast Central Credit Union, and that the vast majority of them are Joomla and WordPress blogs that get compromised through outdated and insecure third-party plugins for these popular content management systems. Worse yet, all of the 13,000+ backdoored sites are being remotely controlled with the same username and password.
“It’s a bot,” he said of the self-replicating malware used to deploy the Web shell that infested the credit union’s site. “It goes and exploits vulnerable sites and installs a backdoor with the same credentials.”
Holden said his company has been reaching out to the affected site owners, but that it hasn’t had much luck getting responses. In any case, Holden said he doesn’t relish the idea of dealing with pushback and suspicion from tons of victims.
“To be fair, most vulnerable sites belong to individuals or small companies that do not have contacts, and a good portion of them are outside of US,” Holden said. “We try to find owners for some but very few reply.”
If you run a Web site, please make sure to keep your content management system up to date with the latest patches, and don’t put off patching or disabling outdated third-party plugins. And if anyone wants to verify who I am going forward, please feel free contact me through this site, via encrypted email, or through Wickr (I’m “krebswickr”).




Thank you …
It is a big article. good and honest mind is the very important. Cyber attackshould be prohibited . I will really appreciate if you could add one more information to this article about how to detect “Web shell” into a website that uses WordPress or Joomla as CMS.This is the largest anonymous and free marketplace for hacking.check it out:
http://hackerslist.co