Category Archives: A Little Sunshine
Ransomware Group Debuts Searchable Victim Data
Cybercrime groups that specialize in stealing corporate data and demanding a ransom not to publish it have tried countless approaches to shaming their victims into paying. The latest innovation in ratcheting up the heat comes from the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware group, which has traditionally published any stolen victim data on the Dark Web. Today, however, the group began publishing individual victim websites on the public Internet, with the leaked data made available in an easily searchable form.
Adconion Execs Plead Guilty in Federal Anti-Spam Case
On the eve of their federal criminal trial for allegedly stealing vast swaths of Internet addresses for use in large-scale email spam campaigns, three current or former executives at online advertising firm Adconion Direct have agreed to plead guilty to lesser misdemeanor charges of fraud and misrepresentation via email.
What Counts as “Good Faith Security Research?”
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) recently revised its policy on charging violations of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), a 1986 law that remains the primary statute by which federal prosecutors pursue cybercrime cases. The new guidelines state that prosecutors should avoid charging security researchers who operate in “good faith” when finding and reporting vulnerabilities. But legal experts continue to advise researchers to proceed with caution, noting the new guidelines can’t be used as a defense in court, nor are they any kind of shield against civil prosecution.
Costa Rica May Be Pawn in Conti Ransomware Group’s Bid to Rebrand, Evade Sanctions
Costa Rica’s national health service was hacked sometime earlier this morning by a Russian ransomware group known as Hive. The intrusion comes just weeks after Costa Rican President Rodrigo Chaves declared a state of emergency in response to a data ransom attack from a different Russian ransomware gang — Conti. Ransomware experts say there is good reason to believe the same cybercriminals are behind both attacks, and that Hive has been helping Conti rebrand and evade international sanctions targeting extortion payouts to cybercriminals operating in Russia.
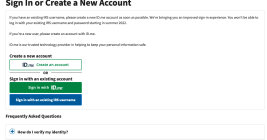
Senators Urge FTC to Probe ID.me Over Selfie Data
Some of more tech-savvy Democrats in the U.S. Senate are asking the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to investigate identity-proofing company ID.me for “deceptive statements” the company and its founder allegedly made over how they handle facial recognition data collected on behalf of the Internal Revenue Service, which until recently required anyone seeking a new IRS account online to provide a live video selfie to ID.me.
When Your Smart ID Card Reader Comes With Malware
Millions of U.S. government employees and contractors have been issued a secure smart ID card that enables physical access to buildings and controlled spaces, and provides access to government computer networks and systems at the cardholder’s appropriate security level. But many government employees aren’t issued an approved card reader device that lets them use these cards at home or remotely, and so turn to low-cost readers they find online. What could go wrong? Here’s one example.
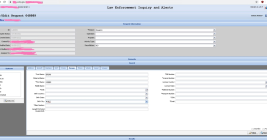
DEA Investigating Breach of Law Enforcement Data Portal
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) says it is investigating reports that hackers gained unauthorized access to an agency portal that taps into 16 different federal law enforcement databases. KrebsOnSecurity has learned the alleged compromise is tied to a cybercrime and online harassment community that routinely impersonates police and government officials to harvest personal information on their targets.
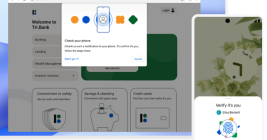
Your Phone May Soon Replace Many of Your Passwords
Apple, Google and Microsoft announced this week they will soon support an approach to authentication that avoids passwords altogether, and instead requires users to merely unlock their smartphones to sign in to websites or online services. Experts say the changes should help defeat many types of phishing attacks and ease the overall password burden on Internet users, but caution that a true passwordless future may still be years away for most websites.
Russia to Rent Tech-Savvy Prisoners to Corporate IT?
Faced with a brain drain of smart people fleeing the country following its invasion of Ukraine, the Russian Federation is floating a new strategy to address a worsening shortage of qualified information technology experts: Forcing tech-savvy people within the nation’s prison population to perform low-cost IT work for domestic companies.