The U.S. Justice Department today announced a series of actions against more than 100 people accused of purchasing and using “Blackshades,” a password-stealing Trojan horse program designed to infect computers throughout the world to spy on victims through their web cameras, steal files and account information, and log victims’ key strokes. While any effort that discourages the use of point-and-click tools for ill-gotten gains is a welcome development, the most remarkable aspect of this crackdown is that those who were targeted in this operation lacked any clue that it was forthcoming.
To be sure, Blackshades is an effective and easy-to-use tool for remotely compromising and spying on your targets. Early on in its development, researchers at CitzenLab discovered that Blackshades was being used to spy on activists seeking to overthrow the regime in Syria.
The product was sold via well-traveled and fairly open hacker forums, and even included an active user forum where customers could get help configuring and wielding the powerful surveillance tool. Although in recent years a license to Blackshades sold for several hundred Euros, early versions of the product were sold via PayPal for just USD $40.
In short, Blackshades was a tool created and marketed principally for buyers who wouldn’t know how to hack their way out of a paper bag. From the Justice Department’s press release today:
“After purchasing a copy of the RAT, a user had to install the RAT on a victim’s computer – i.e., “infect” a victim’s computer. The infection of a victim’s computer could be accomplished in several ways, including by tricking victims into clicking on malicious links or by hiring others to install the RAT on victims’ computers.
The RAT contained tools known as ‘spreaders’ that helped users of the RAT maximize the number of infections. The spreader tools generally worked by using computers that had already been infected to help spread the RAT further to other computers. For instance, in order to lure additional victims to click on malicious links that would install the RAT on their computers, the RAT allowed cybercriminals to send those malicious links to others via the initial victim’s social media service, making it appear as if the message had come from the initial victim.”
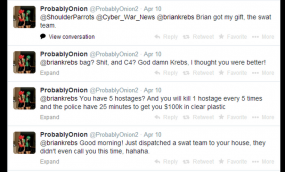
News that the FBI and other national law enforcement organizations had begun rounding up Blackshades customers started surfacing online last week, when multiple denizens of the noob-friendly hacker forum Hackforums[dot]net began posting firsthand experiences of receiving a visit from local authorities related to their prior alleged Blackshades use. See the image gallery at the end of this post for a glimpse into the angst that accompanied that development.
While there is a certain amount of schadenfreude in today’s action, the truth is that any longtime Blackshades customer who didn’t know this day would be coming should turn in his hacker card immediately. In June 2012, the Justice Department announced a series of indictments against at least two dozen individuals who had taken the bait and signed up to be active members of “Carderprofit,” a fraud forum that was created and maintained by the Federal Bureau of Investigation.
Among those arrested in the CarderProfit sting was Michael Hogue, the alleged co-creator of Blackshades. That so many of the customers of this product are teenagers who wouldn’t know a command line prompt from a hole in the ground is evident by the large number of users who vented their outrage over their arrests and/or visits by the local authorities on Hackforums, which by the way was the genesis of the CarderProfit sting from Day One.
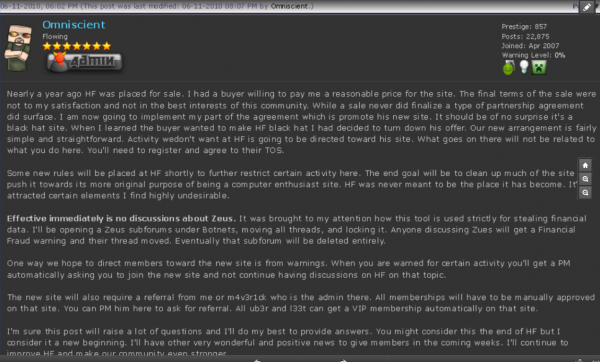
In June 2010, Hackforums administrator Jesse Labrocca — a.k.a. “Omniscient” — posted a message to all users of the forum, notifying them that the forum would no longer tolerate the posting of messages about ways to buy and use the ZeuS Trojan, a far more sophisticated remote-access Trojan that is heavily used by cybercriminals worldwide and has been implicated in the theft of hundreds of millions of dollars from small- to mid-sized businesses worldwide.