On any given day, nation-states and criminal hackers have access to an entire arsenal of zero-day vulnerabilities — undocumented and unpatched software flaws that can be used to silently slip past most organizations’ digital defenses, new research suggests. That sobering conclusion comes amid mounting evidence that thieves and cyberspies are ramping up spending to acquire and stockpile these digital armaments.
Security experts have long suspected that governments and cybercriminals alike are stockpiling zero-day bugs: After all, the thinking goes, if the goal is to exploit these weaknesses in future offensive online attacks, you’d better have more than a few tricks up your sleeve because it’s never clear whether or when those bugs will be independently discovered by researchers or fixed by the vendor. Those suspicions were confirmed very publicly in 2010 with the discovery of Stuxnet, a weapon apparently designed to delay Iran’s nuclear ambitions and one that relied upon at least four zero-day vulnerabilities.
Documents recently leaked by National Security Agency whistleblower Edward Snowden indicate that the NSA spent more than $25 million this year alone to acquire software vulnerabilities from vendors. But just how many software exploits does that buy, and what does that say about the number of zero-day flaws in private circulation on any given day?
These are some of the questions posed by Stefan Frei, research director for Austin, Texas-based NSS Labs. Frei pored over reports from and about some of those private vendors — including boutique exploit providers like Endgame Systems, Exodus Intelligence, Netragard, ReVuln and VUPEN — and concluded that jointly these firms alone have the capacity to sell more than 100 zero-day exploits per year.
According to Frei, if we accept that the average zero-day exploit persists for about 312 days before it is detected (an estimate made by researchers at Symantec Research Labs), this means that these firms probably provide access to at least 85 zero-day exploits on any given day of the year. These companies all say they reserve the right to restrict which organizations, individuals and nation states may purchase their products, but they all expressly do not share information about exploits and flaws with the affected software vendors.
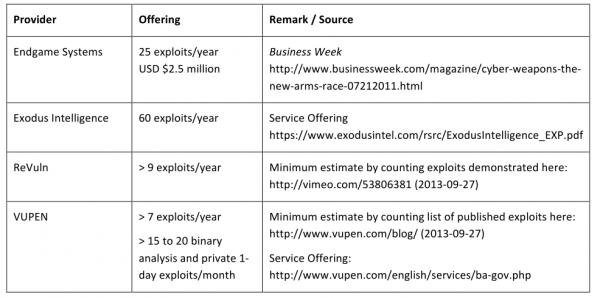
Frei’s minimum estimate of exploits offered by boutique exploit providers each year.
KNOWN UNKNOWNS
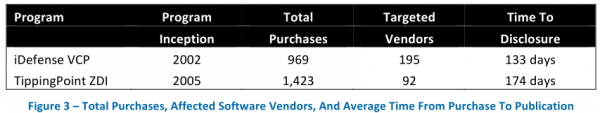
That approach stands apart from the likes of HP TippingPoint‘s Zero-Day Initiative (ZDI) and Verisign‘s iDefense Vulnerability Contributor Program (VCP), which pay researchers in exchange for the rights to their vulnerability research. Both ZDI and iDefense also manage the communication with the affected vendors, ship stopgap protection for the vulnerabilities to their customers, and otherwise keep mum on the flaws until the vendor ships an update to fix the bugs.
Frei also took stock of the software vulnerabilities collected by these two companies, and found that between 2010 and 2012, the ZDI and VCP programs together published 1,026 flaws, of which 425 (44 percent) targeted flaws in Microsoft, Apple, Oracle, Sun and Adobe products. The average time from purchase to publication was 187 days.
“On any given day during these three years, the VCP and ZDI programs possessed 58 unpublished vulnerabilities affecting five vendors, or 152 vulnerabilities total,” Frei wrote in a research paper released today.
Frei notes that the VCP and ZDI programs use the information they purchase only for the purpose of building better protection for their customers, and since they share the information with the software vendors in order to develop and release patches, the overall risk is comparatively low. Also, the vulnerabilities collected and reported by VCP and ZDI are not technically zero-days, since one important quality of a zero-day is that it is used in-the-wild to attack targets before the responsible vendor can ship a patch to fix the problem.
In any case, Frei says his analysis clearly demonstrates that critical vulnerability information is available in significant quantities for private groups, for extended periods and at a relatively low cost.
“So everybody knows there are zero days, but when we talk to C-Level executives, very often we find that these guys don’t have a clue, because they tell us, ‘Yeah, but we’ve never been compromised’,” Frei said in an interview. “And we always ask them, ‘How do you know?'”
Continue reading →







![Makhost[dot]net sells access to thousands of hacked RDP installations. Prices range from $3 to $10 based on a variety of qualities, such as the number of CPUs, the operating system version and the PC's upload and download speeds.](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/rdps-1-600x348.png)