Security experts have long opined that one way to make software more secure is to hold software makers liable for vulnerabilities in their products. This idea is often dismissed as unrealistic and one that would stifle innovation in an industry that has been a major driver of commercial growth and productivity over the years. But a new study released this week presents perhaps the clearest economic case yet for compelling companies to pay for information about security vulnerabilities in their products.
Before I delve into this modest proposal, let’s postulate a few assumptions that hopefully aren’t terribly divisive:
- Modern societies are becoming increasingly dependent on software and computer programs.
- After decades of designing software, human beings still build imperfect, buggy, and insecure programs.
- Estimates of the global damage from cybercrime ranges from the low billions to hundreds of billions of dollars annually.
- The market for finding, stockpiling and hoarding (keeping secret) software flaws is expanding rapidly.
- Vendor-driven “bug bounty” programs which reward researchers for reporting and coordinating the patching of flaws are expanding, but currently do not offer anywhere near the prices offered in the underground or by private buyers.
- Software security is a “negative externality”: like environmental pollution, vulnerabilities in software impose costs on users and on society as a whole, while software vendors internalize profits and externalize costs. Thus, absent any demand from their shareholders or customers, profit-driven businesses tend not to invest in eliminating negative externalities.
Earlier this month, I published a piece called How Many Zero-Days Hit You Today, which examined a study by vulnerability researcher Stefan Frei about the bustling market for “zero-day” flaws — security holes in software that not even the makers of those products know about. These vulnerabilities — particularly zero-days found in widely-used software like Flash and Java — are extremely valuable because attackers can use them to slip past security defenses unnoticed.
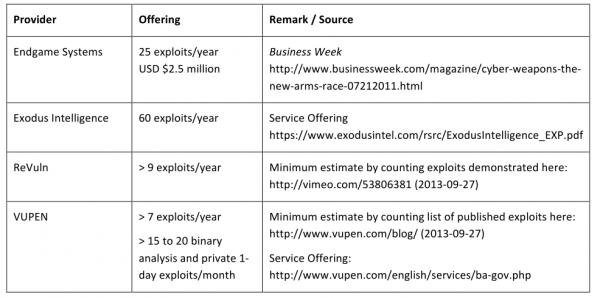
Frei’s analysis conservatively estimated that private companies which purchase software vulnerabilities for use by nation states and other practitioners of cyber espionage provide access to at least 85 zero-day exploits on any given day of the year. That estimate doesn’t even consider the number of zero-day bugs that may be sold or traded each day in the cybercrime underground.
At the end of that post, I asked readers whether it was possible and/or desirable to create a truly global, independent bug bounty program that would help level the playing field in favor of the defenders and independent security researchers. Frei’s latest paper outlines one possible answer.
BUYING ALL BUGS AT ABOVE BLACK-MARKET PRICES
Frei proposes creating a multi-tiered, “international vulnerability purchase program” (IVPP), in which the major software vendors would be induced to purchase all of the available and known vulnerabilities at prices well above what even the black market is willing to pay for them. But more on that in a bit.
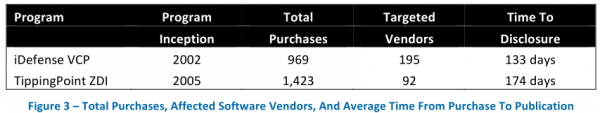
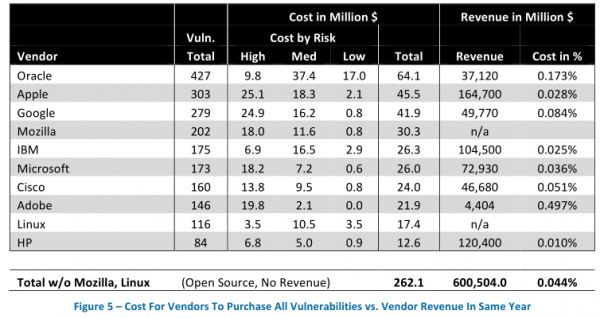
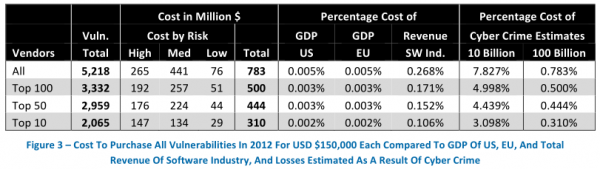
The director of research for Austin, Texas-based NSS Labs, Frei examined all of the software vulnerabilities reported in 2012, and found that the top 10 software makers were responsible for more than 30 percent of all flaws fixed. Frei estimates that if these vendors were to have purchased information on all of those flaws at a steep price of $150,000 per vulnerability — an amount that is well above what cybercriminals or vulnerability brokers typically offer for such bugs — this would still come to less than one percent of the annual revenues for these software firms.
Frei points out that the cost of purchasing all vulnerabilities for all products would be considerably lower than the savings that would occur as a result of the expected reduction in losses occurring as a result of cyber crime — even under the conservative estimate that these losses would be reduced by only 10 percent.
In the above chart, for example, we can see Oracle — the software vendor responsible for Java and a whole heap of database software code that is found in thousands of organizations — fixed more than 427 vulnerabilities last year. It also brought in more than $37 billion in revenues that year. If Oracle were to pay researchers top dollar ($150,000) for each vulnerability, that would still come to less than two-tenths of one percent of the company’s annual revenues (USD $67 million).
Frei posits that if vendors were required to internalize the cost of such a program, they would likely be far more motivated to review and/or enhance the security of their software development processes.
Likewise, Frei said, such a lucrative bug bounty system would virtually ensure that every release of commercial software products would be scrutinized by legions of security experts.
“In the short term, it would hit the vendors very badly,” Frei said in a phone interview with KrebsOnSecurity. “But in the long term, this would produce much more secure software.”
“When you look at new innovations like cars, airplanes and electricity, we see that security and reliability was enhanced tremendously with each as soon as there was independent testing,” said Frei, an experienced helicopter pilot. “I was recently reading a book about the history of aviation, and [it noted that in] the first iteration of the NTSB [National Transportation Safety Board] it was explicitly stated that when they investigate an accident, if they could not find a mechanical failure, they blamed the pilot. This is what we do now with software: We blame the user. We say, you should have installed antivirus, or done this and that.”




![Makhost[dot]net sells access to thousands of hacked RDP installations. Prices range from $3 to $10 based on a variety of qualities, such as the number of CPUs, the operating system version and the PC's upload and download speeds.](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/rdps-1-600x348.png)