A rash of recent and ongoing targeted attacks involving compromises at high-profile Web sites should serve as a sobering reminder of the need to be vigilant about applying browser updates. Hackers have hit a number of prominent foreign policy and human rights group Web sites, configuring them to serve spyware by exploiting newly patched flaws in widely used software from Adobe and Oracle.
The latest reports of this apparent cyberspy activity come from security experts at Shadowserver.org, a nonprofit that tracks malware attacks typically associated with so-called “advanced persistent threat” (APT) actors. APT is a controversial term that means many things to different folks, but even detractors of the acronym’s overuse acknowledge that it has become a useful shorthand for “We’re pretty sure it came from China.”
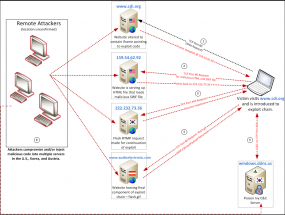
A diagram depicting the (since-cleaned) attack on the Website of the Center for Defense Information.
One look at the list of the sites found to be currently serving an exploit to attack a newly-patched Adobe Flash Player vulnerability (CVE-2012-0779) shows how that shorthand is earned. Shadowserver uncovered Flash exploits waiting for visitors of the Web sites for Amnesty International Hong Kong and the Center for Defense Information, a Washington, D.C. think-tank. The home page for the International Institute for Counter-Terrorism was found to be serving up malware via a recent Oracle Java vulnerability (CVE-2012-0507), while the Cambodian Ministry of Foreign Affairs site was pointing to both Flash and Java exploits.
“In recent months we have continued to observe 0-day vulnerabilities emerging following discovery of their use in the wild to conduct cyber espionage attacks,” wrote Shadowserver volunteers Steven Adair and Ned Moran, in a blog post about the attacks, which they dubbed “strategic Web compromises.”
“Frequently by the time a patch is released for the vulnerabilities, the exploit has already been the wild for multiple weeks or months — giving the attackers a very large leg up,” they wrote. “The goal is not large-scale malware distribution through mass compromises. Instead the attackers place their exploit code on websites that cater towards a particular set of visitors that they might be interested in.”
The discoveries come just days after security vendor Websense found that the site for Amnesty International United Kingdom (AIUK) was hosting the same Java exploit. According to Shadowserver, other sites that were compromised by remarkably similar attacks but since cleaned include those belonging to the American Research Center in Egypt, the Institute for National Security Studies, and the Center for European Policy Studies.










