The FBI’s takedown of the LockBit ransomware group last week came as LockBit was preparing to release sensitive data stolen from government computer systems in Fulton County, Ga. But LockBit is now regrouping, and the gang says it will publish the stolen Fulton County data on March 2 unless paid a ransom. LockBit claims the cache includes documents tied to the county’s ongoing criminal prosecution of former President Trump, but court watchers say teaser documents published by the crime gang suggest a total leak of the Fulton County data could put lives at risk and jeopardize a number of other criminal trials.
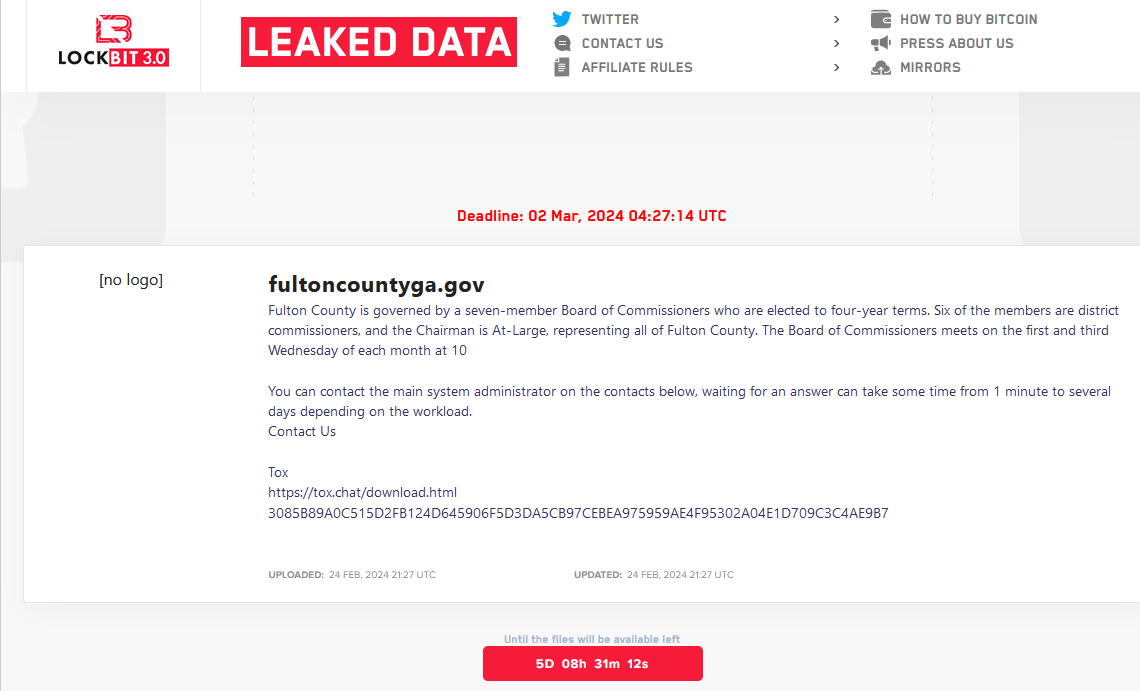
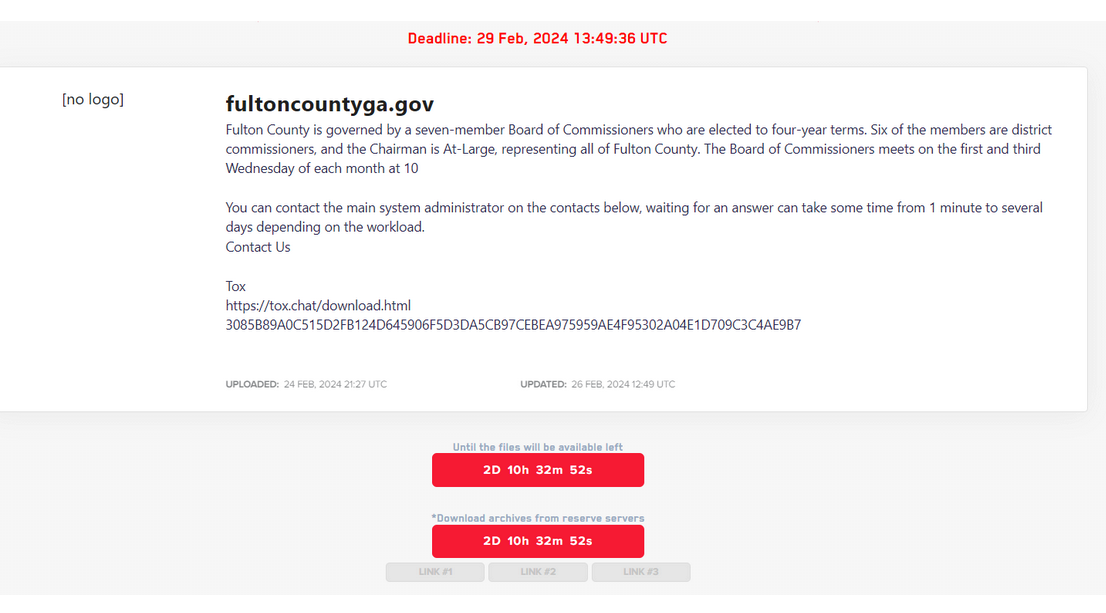
A new LockBit website listing a countdown timer until the promised release of data stolen from Fulton County, Ga.
In early February, Fulton County leaders acknowledged they were responding to an intrusion that caused disruptions for its phone, email and billing systems, as well as a range of county services, including court systems.
On Feb. 13, the LockBit ransomware group posted on its victim shaming blog a new entry for Fulton County, featuring a countdown timer saying the group would publish the data on Feb. 16 unless county leaders agreed to negotiate a ransom.
“We will demonstrate how local structures negligently handled information protection,” LockBit warned. “We will reveal lists of individuals responsible for confidentiality. Documents marked as confidential will be made publicly available. We will show documents related to access to the state citizens’ personal data. We aim to give maximum publicity to this situation; the documents will be of interest to many. Conscientious residents will bring order.”
Yet on Feb. 16, the entry for Fulton County was removed from LockBit’s site without explanation. This usually only happens after the victim in question agrees to pay a ransom demand and/or enters into negotiations with their extortionists.
However, Fulton County Commission Chairman Robb Pitts said the board decided it “could not in good conscience use Fulton County taxpayer funds to make a payment.”
“We did not pay nor did anyone pay on our behalf,” Pitts said at an incident briefing on Feb. 20.
Just hours before that press conference, LockBit’s various websites were seized by the FBI and the U.K.’s National Crime Agency (NCA), which replaced the ransomware group’s homepage with a seizure notice and used the existing design of LockBit’s victim shaming blog to publish press releases about the law enforcement action.

The feds used the existing design on LockBit’s victim shaming website to feature press releases and free decryption tools.
Dubbed “Operation Cronos,” the effort involved the seizure of nearly three-dozen servers; the arrest of two alleged LockBit members; the release of a free LockBit decryption tool; and the freezing of more than 200 cryptocurrency accounts thought to be tied to the gang’s activities. The government says LockBit has claimed more than 2,000 victims worldwide and extorted over $120 million in payments.
UNFOLDING DISASTER
In a lengthy, rambling letter published on Feb. 24 and addressed to the FBI, the ransomware group’s leader LockBitSupp announced that their victim shaming websites were once again operational on the dark web, with fresh countdown timers for Fulton County and a half-dozen other recent victims.
“The FBI decided to hack now for one reason only, because they didn’t want to leak information fultoncountyga.gov,” LockBitSupp wrote. “The stolen documents contain a lot of interesting things and Donald Trump’s court cases that could affect the upcoming US election.”

A screen shot released by LockBit showing various Fulton County file shares that were exposed.
LockBit has already released roughly two dozen files allegedly stolen from Fulton County government systems, although none of them involve Mr. Trump’s criminal trial. But the documents do appear to include court records that are sealed and shielded from public viewing.
George Chidi writes The Atlanta Objective, a Substack publication on crime in Georgia’s capital city. Chidi says the leaked data so far includes a sealed record related to a child abuse case, and a sealed motion in the murder trial of Juwuan Gaston demanding the state turn over confidential informant identities.
Chidi cites reports from a Fulton County employee who said the confidential material includes the identities of jurors serving on the trial of the rapper Jeffery “Young Thug” Williams, who is charged along with five other defendants in a racketeering and gang conspiracy.
“The screenshots suggest that hackers will be able to give any attorney defending a criminal case in the county a starting place to argue that evidence has been tainted or witnesses intimidated, and that the release of confidential information has compromised cases,” Chidi wrote. “Judge Ural Glanville has, I am told by staff, been working feverishly behind the scenes over the last two weeks to manage the unfolding disaster.”
LockBitSupp also denied assertions made by the U.K.’s NCA that LockBit did not delete stolen data as promised when victims agreed to pay a ransom. The accusation is an explosive one because nobody will pay a ransom if they don’t believe the ransomware group will hold up its end of the bargain.
The ransomware group leader also confirmed information first reported here last week, that federal investigators managed to hack LockBit by exploiting a known vulnerability in PHP, a scripting language that is widely used in Web development.
“Due to my personal negligence and irresponsibility I relaxed and did not update PHP in time,” LockBitSupp wrote. “As a result of which access was gained to the two main servers where this version of PHP was installed.”
LockBitSupp’s FBI letter said the group kept copies of its stolen victim data on servers that did not use PHP, and that consequently it was able to retain copies of files stolen from victims. The letter also listed links to multiple new instances of LockBit dark net websites, including the leak page listing Fulton County’s new countdown timer.

LockBit’s new data leak site promises to release stolen Fulton County data on March 2, 2024, unless paid a ransom demand.
“Even after the FBI hack, the stolen data will be published on the blog, there is no chance of destroying the stolen data without payment,” LockBitSupp wrote. “All FBI actions are aimed at destroying the reputation of my affiliate program, my demoralization, they want me to leave and quit my job, they want to scare me because they can not find and eliminate me, I can not be stopped, you can not even hope, as long as I am alive I will continue to do pentest with postpaid.” Continue reading →