Microsoft said Thursday that it convinced a U.S. federal court to grant it control over a botnet believed to be closely linked to counterfeit versions Windows that were sold in various computer stores across China. The legal victory also highlights a Chinese Internet service that experts say has long been associated with targeted, espionage attacks against U.S. and European corporations.
Microsoft said it sought to disrupt a counterfeit supply-chain operation that sold knockoff versions of Windows PCs that came pre-loaded with a strain of malware called “Nitol,” which lets attackers control the systems from afar for a variety of nefarious purposes.
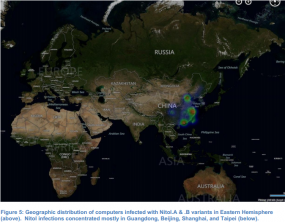
In legal filings unsealed Thursday by the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia, Microsoft described how its researchers purchased computers from various cities in China, and found that approximately 20 percent of them were already infected with Nitol.
It’s not clear precisely how many systems are infected with Nitol, but it does not appear to be a particularly major threat. Microsoft told the court that it had detected nearly 4,000 instances of Windows computers infected with some version of the malware, but that this number likely represented “only a subset of the number of infected computers.” The company said the majority of Nitol infections and Internet servers used to control the botnet were centered around China, although several U.S. states — including California, New York and Pennsylvania — were home to significant numbers of compromised hosts.
Dubbed “Operation b70” by Microsoft, the courtroom maneuvers are the latest in a series of legal stealth attacks that the software giant has executed against large-scale cybercrime operations. Previous targets included the Waledac, Rustock, Kelihos and ZeuS botnets.