At least 18 popular JavaScript code packages that are collectively downloaded more than two billion times each week were briefly compromised with malicious software today, after a developer involved in maintaining the projects was phished. The attack appears to have been quickly contained and was narrowly focused on stealing cryptocurrency. But experts warn that a similar attack with a slightly more nefarious payload could lead to a disruptive malware outbreak that is far more difficult to detect and restrain.
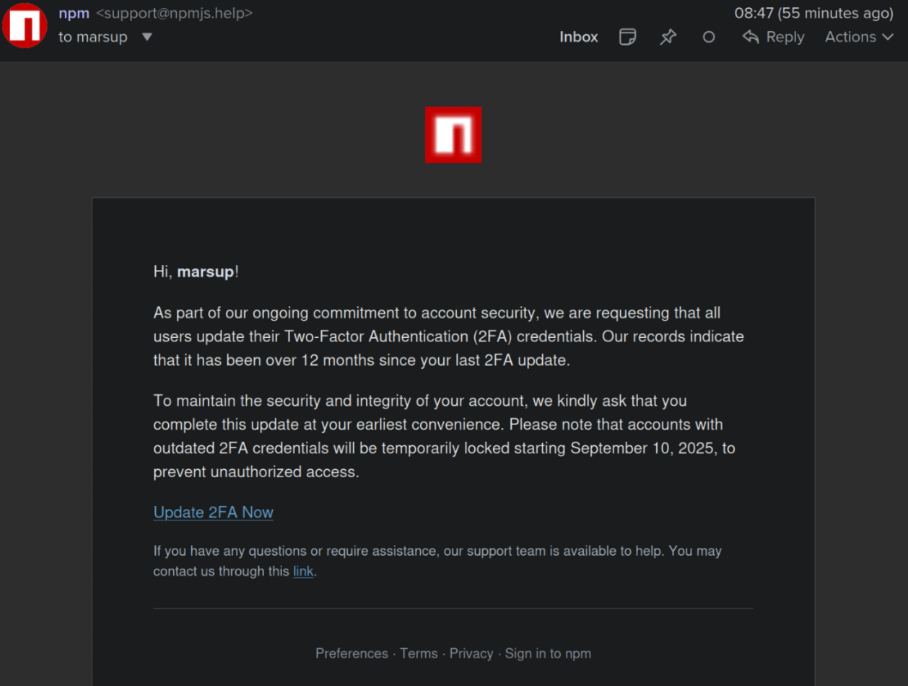
This phishing email lured a developer into logging in at a fake NPM website and supplying a one-time token for two-factor authentication. The phishers then used that developer’s NPM account to add malicious code to at least 18 popular JavaScript code packages.
Aikido is a security firm in Belgium that monitors new code updates to major open-source code repositories, scanning any code updates for suspicious and malicious code. In a blog post published today, Aikido said its systems found malicious code had been added to at least 18 widely-used code libraries available on NPM (short for) “Node Package Manager,” which acts as a central hub for JavaScript development and the latest updates to widely-used JavaScript components.
JavaScript is a powerful web-based scripting language used by countless websites to build a more interactive experience with users, such as entering data into a form. But there’s no need for each website developer to build a program from scratch for entering data into a form when they can just reuse already existing packages of code at NPM that are specifically designed for that purpose.
Unfortunately, if cybercriminals manage to phish NPM credentials from developers, they can introduce malicious code that allows attackers to fundamentally control what people see in their web browser when they visit a website that uses one of the affected code libraries.
According to Aikido, the attackers injected a piece of code that silently intercepts cryptocurrency activity in the browser, “manipulates wallet interactions, and rewrites payment destinations so that funds and approvals are redirected to attacker-controlled accounts without any obvious signs to the user.”
“This malware is essentially a browser-based interceptor that hijacks both network traffic and application APIs,” Aikido researcher Charlie Eriksen wrote. “What makes it dangerous is that it operates at multiple layers: Altering content shown on websites, tampering with API calls, and manipulating what users’ apps believe they are signing. Even if the interface looks correct, the underlying transaction can be redirected in the background.”
Aikido said it used the social network Bsky to notify the affected developer, Josh Junon, who quickly replied that he was aware of having just been phished. The phishing email that Junon fell for was part of a larger campaign that spoofed NPM and told recipients they were required to update their two-factor authentication (2FA) credentials. The phishing site mimicked NPM’s login page, and intercepted Junon’s credentials and 2FA token. Once logged in, the phishers then changed the email address on file for Junon’s NPM account, temporarily locking him out.
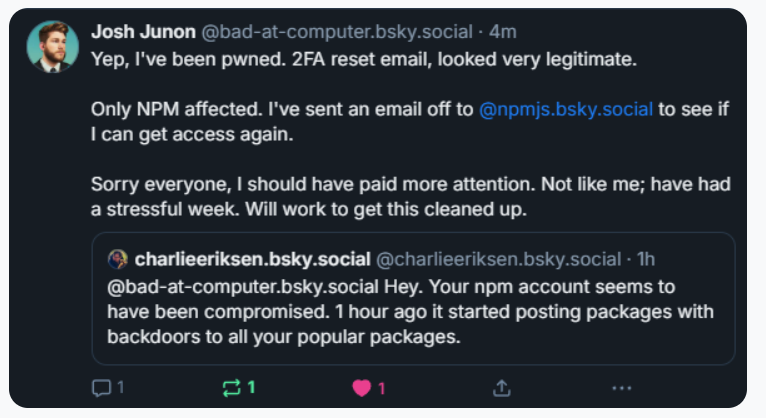
Aikido notified the maintainer on Bluesky, who replied at 15:15 UTC that he was aware of being compromised, and starting to clean up the compromised packages.
Junon also issued a mea culpa on HackerNews, telling the community’s coder-heavy readership, “Hi, yep I got pwned.”
“It looks and feels a bit like a targeted attack,” Junon wrote. “Sorry everyone, very embarrassing.” Continue reading