The consulting firm PricewaterhouseCoopers recently published lessons learned from the disruptive and costly ransomware attack in May 2021 on Ireland’s public health system. The unusually candid post-mortem found that nearly two months elapsed between the initial intrusion and the launching of the ransomware. It also found affected hospitals had tens of thousands of outdated Windows 7 systems, and that the health system’s IT administrators failed to respond to multiple warning signs that a massive attack was imminent.

PWC’s timeline of the days leading up to the deployment of Conti ransomware on May 14.
Ireland’s Health Service Executive (HSE), which operates the country’s public health system, got hit with Conti ransomware on May 14, 2021. A timeline in the report (above) says the initial infection of the “patient zero” workstation happened on Mar. 18, 2021, when an employee on a Windows computer opened a booby-trapped Microsoft Excel document in a phishing email that had been sent two days earlier.
Less than a week later, the attacker had established a reliable backdoor connection to the employee’s infected workstation. After infecting the system, “the attacker continued to operate in the environment over an eight week period until the detonation of the Conti ransomware on May 14, 2021,” the report states.
According to PWC’s report (PDF), there were multiple warnings about a serious network intrusion, but those red flags were either misidentified or not acted on quickly enough:
- On Mar. 31, 2021, the HSE’s antivirus software detected the execution of two software tools commonly used by ransomware groups — Cobalt Strike and Mimikatz — on the Patient Zero Workstation. But the antivirus software was set to monitor mode, so it did not block the malicious commands.”
- On May 7, the attacker compromised the HSE’s servers for the first time, and over the next five days the intruder would compromise six HSE hospitals. On May 10, one of the hospitals detected malicious activity on its Microsoft Windows Domain Controller, a critical “keys to the kingdom” component of any Windows enterprise network that manages user authentication and network access.
- On 10 May 2021, security auditors first identified evidence of the attacker compromising systems within Hospital C and Hospital L. Hospital C’s antivirus software detected Cobalt Strike on two systems but failed to quarantine the malicious files.
- On May 13, the HSE’s antivirus security provider emailed the HSE’s security operations team, highlighting unhandled threat events dating back to May 7 on at least 16 systems. The HSE Security Operations team requested that the Server team restart servers.
By then it was too late. At just after midnight Ireland time on May 14, the attacker executed the Conti ransomware within the HSE. The attack disrupted services at several Irish hospitals and resulted in the near complete shutdown of the HSE’s national and local networks, forcing the cancellation of many outpatient clinics and healthcare services. The number of appointments in some areas dropped by up to 80 percent.”
Conti initially demanded USD $20 million worth of virtual currency in exchange for a digital key to unlock HSE servers compromised by the group. But perhaps in response to the public outcry over the HSE disruption, Conti reversed course and gave the HSE the decryption keys without requiring payment.
Still, the work to restore infected systems would take months. The HSE ultimately enlisted members of the Irish military to bring in laptops and PCs to help restore computer systems by hand. It wasn’t until September 21, 2021 that the HSE declared 100 percent of its servers were decrypted.
As bad as the HSE ransomware attack was, the PWC report emphasizes that it could have been far worse. For example, it is unclear how much data would have been unrecoverable if a decryption key had not become available as the HSE’s backup infrastructure was only periodically backed up to offline tape.
The attack also could have been worse, the report found:
- if there had been intent by the Attacker to target specific devices within the HSE environment (e.g. medical devices);
- if the ransomware took actions to destroy data at scale;
- if the ransomware had auto-propagation and persistence capabilities, for example by using an exploit to propagate across domains and trust-boundaries to medical devices (e.g. the EternalBlue exploit used by the WannaCry and NotPetya15 attacks);
- if cloud systems had also been encrypted such as the COVID-19 vaccination system
The PWC report contains numerous recommendations, most of which center around hiring new personnel to lead the organization’s redoubled security efforts. But it is clear that the HSE has an enormous amount of work ahead to grow in security maturity. For example, the report notes the HSE’s hospital network had over 30,000 Windows 7 workstations that were deemed end of life by the vendor.
“The HSE assessed its cybersecurity maturity rating as low,” PWC wrote. “For example, they do not have a CISO or a Security Operations Center established.” Continue reading







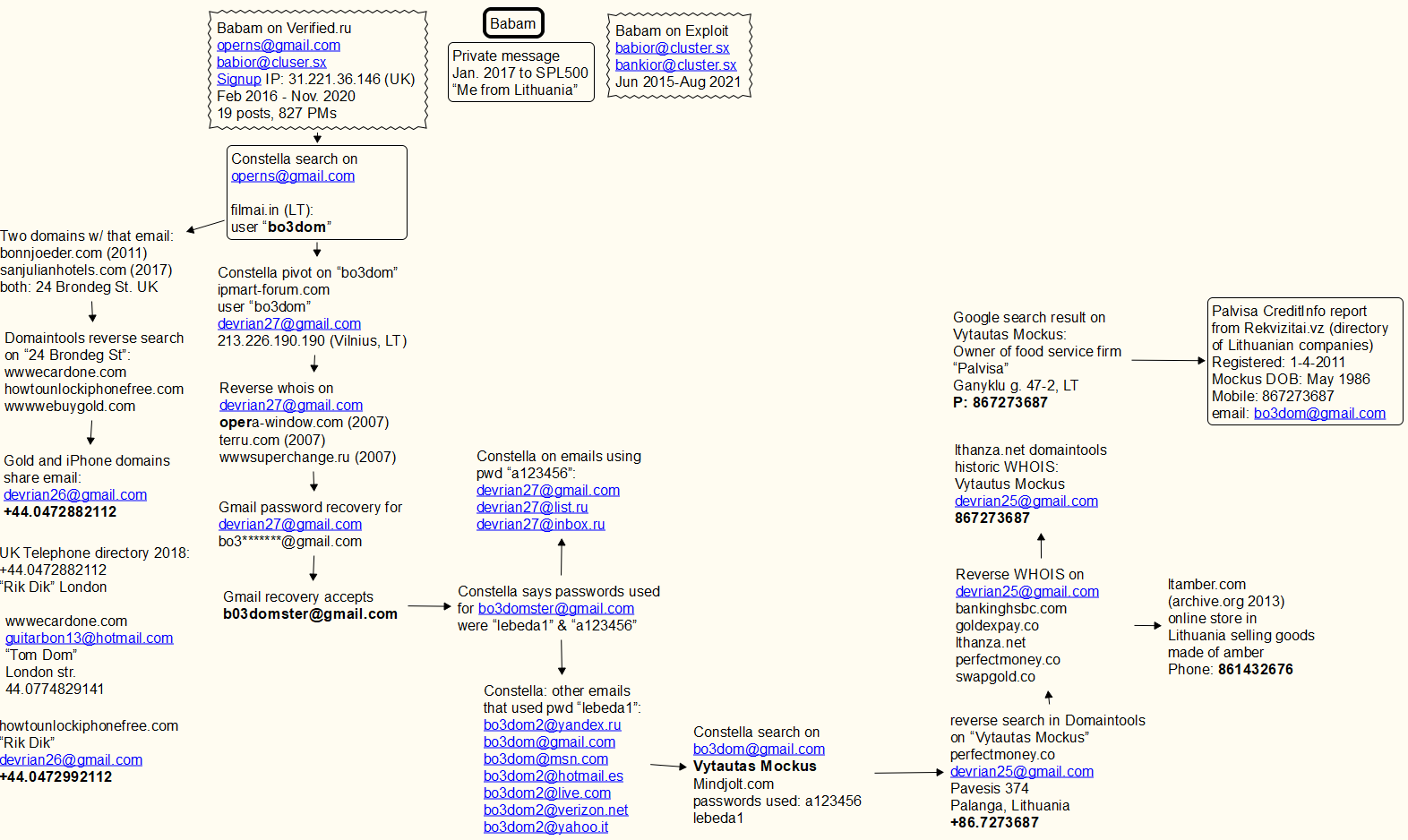


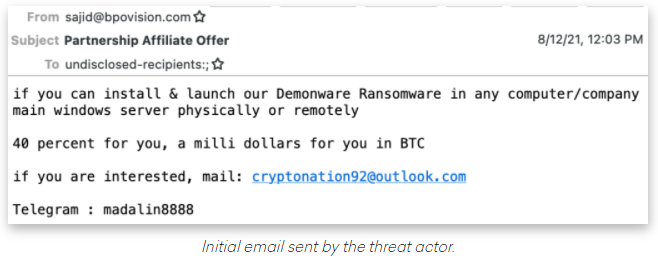
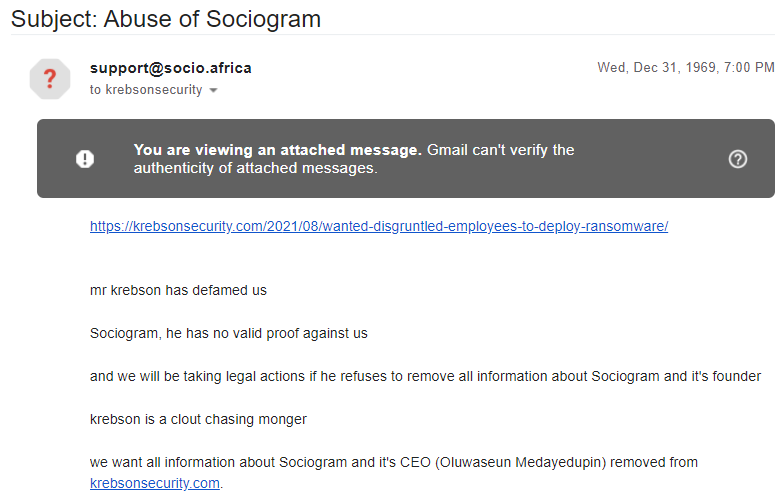



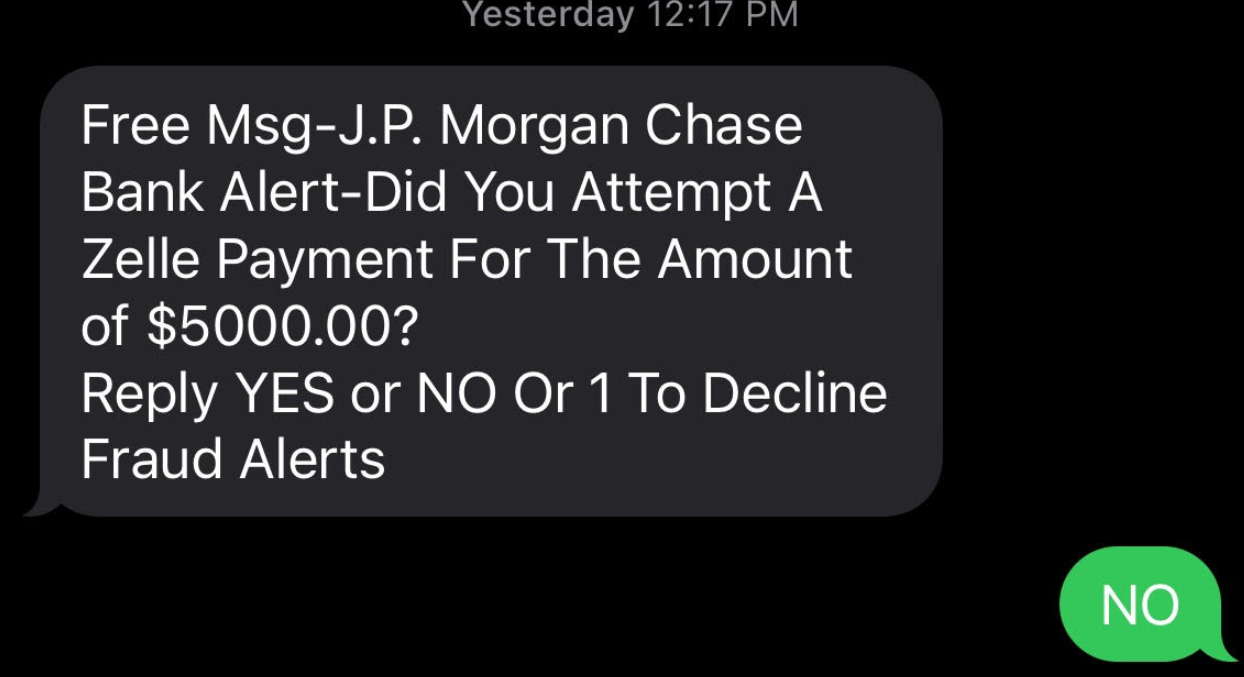
 The fraudster then uses the code to complete the password reset process, and then changes the victim’s online banking password. The fraudster then uses Zelle to transfer the victim’s funds to others.
The fraudster then uses the code to complete the password reset process, and then changes the victim’s online banking password. The fraudster then uses Zelle to transfer the victim’s funds to others.