The U.S. Justice Department today charged a Canadian and a Northern Ireland man for allegedly conspiring to build botnets that enslaved hundreds of thousands of routers and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices for use in large-scale distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. In addition, a defendant in the United States was sentenced today to drug treatment and 18 months community confinement for his admitted role in the botnet conspiracy.
Indictments unsealed by a federal court in Alaska today allege 20-year-old Aaron Sterritt from Larne, Northern Ireland, and 21-year-old Logan Shwydiuk of Saskatoon, Canada conspired to build, operate and improve their IoT crime machines over several years.
Prosecutors say Sterritt, using the hacker aliases “Vamp” and “Viktor,” was the brains behind the computer code that powered several potent and increasingly complex IoT botnet strains that became known by exotic names such as “Masuta,” “Satori,” “Okiru” and “Fbot.”
Shwydiuk, a.k.a. “Drake,” “Dingle, and “Chickenmelon,” is alleged to have taken the lead in managing sales and customer support for people who leased access to the IoT botnets to conduct their own DDoS attacks.
A third member of the botnet conspiracy — 22-year-old Kenneth Currin Schuchman of Vancouver, Wash. — pleaded guilty in Sept. 2019 to aiding and abetting computer intrusions in September 2019. Schuchman, whose role was to acquire software exploits that could be used to infect new IoT devices, was sentenced today by a judge in Alaska to 18 months of community confinement and drug treatment, followed by three years of supervised release.

Kenneth “Nexus-Zeta” Schuchman, in an undated photo.
The government says the defendants built and maintained their IoT botnets by constantly scanning the Web for insecure devices. That scanning primarily targeted devices that were placed online with weak, factory default settings and/or passwords. But the group also seized upon a series of newly-discovered security vulnerabilities in these IoT systems — commandeering devices that hadn’t yet been updated with the latest software patches.
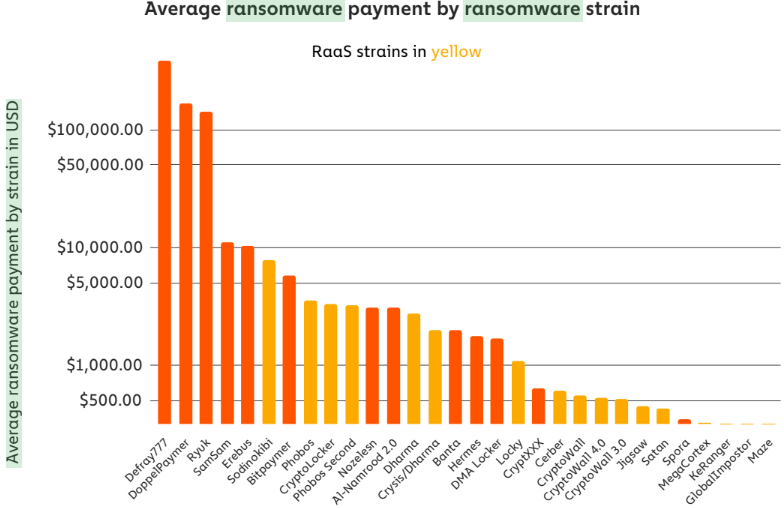
Some of the IoT botnets enslaved hundreds of thousands of hacked devices. For example, by November 2017, Masuta had infected an estimated 700,000 systems, allegedly allowing the defendants to launch crippling DDoS attacks capable of hurling 100 gigabits of junk data per second at targets — enough firepower to take down many large websites.
In 2015, then 15-year-old Sterritt was involved in the high-profile hack against U.K. telecommunications provider TalkTalk. Sterritt later pleaded guilty to his part in the intrusion, and at his sentencing in 2018 was ordered to complete 50 hours of community service.
The indictments against Sterritt and Shwydiuk (PDF) do not mention specific DDoS attacks thought to have been carried out with the IoT botnets. In an interview today with KrebsOnSecurity, prosecutors in Alaska declined to discuss any of their alleged offenses beyond building, maintaining and selling the above-mentioned IoT botnets.
But multiple sources tell KrebsOnSecuirty Vamp was principally responsible for the 2016 massive denial-of-service attack that swamped Dyn — a company that provides core Internet services for a host of big-name Web sites. On October 21, 2016, an attack by a Mirai-based IoT botnet variant overwhelmed Dyn’s infrastructure, causing outages at a number of top Internet destinations, including Twitter, Spotify, Reddit and others.
In 2018, authorities with the U.K.’s National Crime Agency (NCA) interviewed a suspect in connection with the Dyn attack, but ultimately filed no charges against the youth because all of his digital devices had been encrypted.
“The principal suspect of this investigation is a UK national resident in Northern Ireland,” reads a June 2018 NCA brief on their investigation into the Dyn attack (PDF), dubbed Operation Midmonth. “In 2018 the subject returned for interview, however there was insufficient evidence against him to provide a realistic prospect of conviction.”
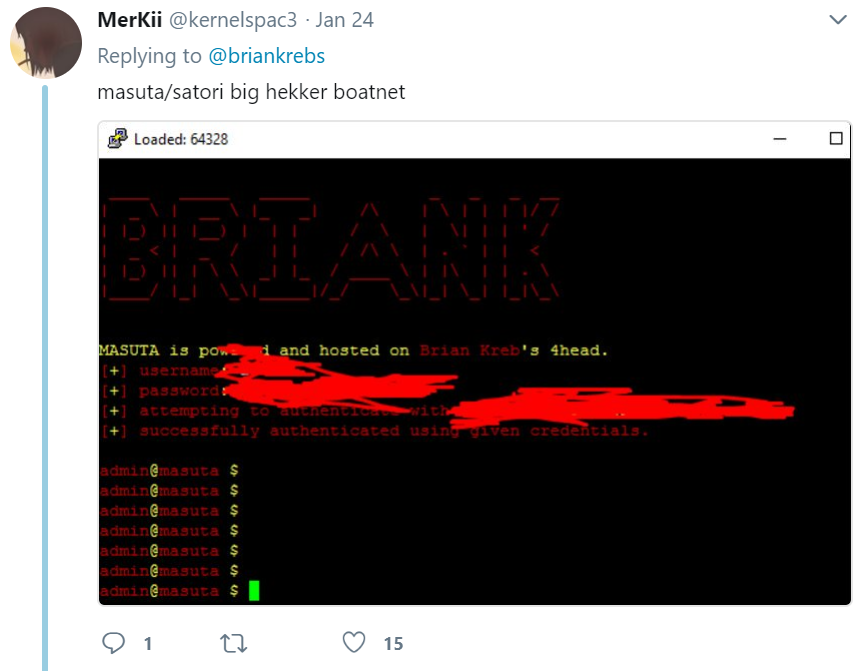
The login prompt for Nexus Zeta’s IoT botnet included the message “Masuta is powered and hosted on Brian Kreb’s [sic] 4head.” To be precise, it’s a 5head.





 On June 16, authorities in Michigan arrested 29-year-old Justin Sean Johnson in connection with a 43-count indictment on charges of conspiracy, wire fraud and aggravated identity theft.
On June 16, authorities in Michigan arrested 29-year-old Justin Sean Johnson in connection with a 43-count indictment on charges of conspiracy, wire fraud and aggravated identity theft.

 June marks the fourth month in a row that Microsoft has issued fixes to address more than 100 security flaws in its products. Eleven of the updates address problems Microsoft deems “critical,” meaning they could be exploited by malware or malcontents to seize complete, remote control over vulnerable systems without any help from users.
June marks the fourth month in a row that Microsoft has issued fixes to address more than 100 security flaws in its products. Eleven of the updates address problems Microsoft deems “critical,” meaning they could be exploited by malware or malcontents to seize complete, remote control over vulnerable systems without any help from users.