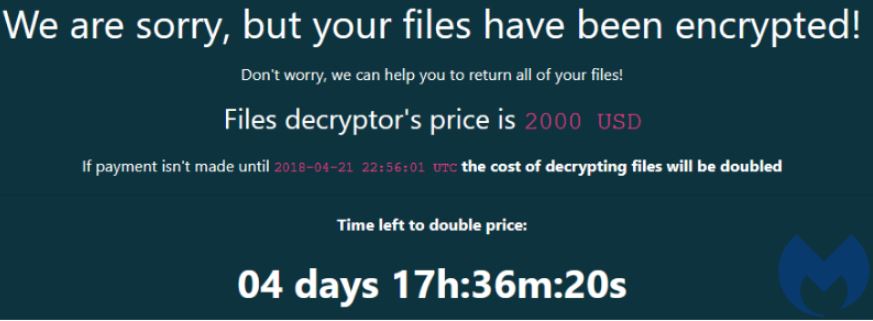
Cloud hosting provider iNSYNQ says it is trying to recover from a ransomware attack that shut down its network and has left customers unable to access their accounting data for the past three days. Unfortunately for iNSYNQ, the company appears to be turning a deaf ear to the increasingly anxious cries from its users for more information about the incident.

A message from iNSYNQ to customers.
Gig Harbor, Wash.-based iNSYNQ specializes in providing cloud-based QuickBooks accounting software and services. In a statement posted to its status page, iNSYNQ said it experienced a ransomware attack on July 16, and took its network offline in a bid to contain the spread of the malware.
“The attack impacted data belonging to certain iNSYNQ clients, rendering such data inaccessible,” the company said. “As soon as iNSYNQ discovered the attack, iNSYNQ took steps to contain it. This included turning off some servers in the iNSYNQ environment.”
iNSYNQ said it has engaged outside cybersecurity assistance and to determine whether any customer data was accessed without authorization, but that so far it has no estimate for when those files might be available again to customers.
Meanwhile, iNSYNQ’s customers — many of them accountants who manage financial data for a number of their own clients — have taken to Twitter to vent their frustration over a lack of updates since that initial message to users.
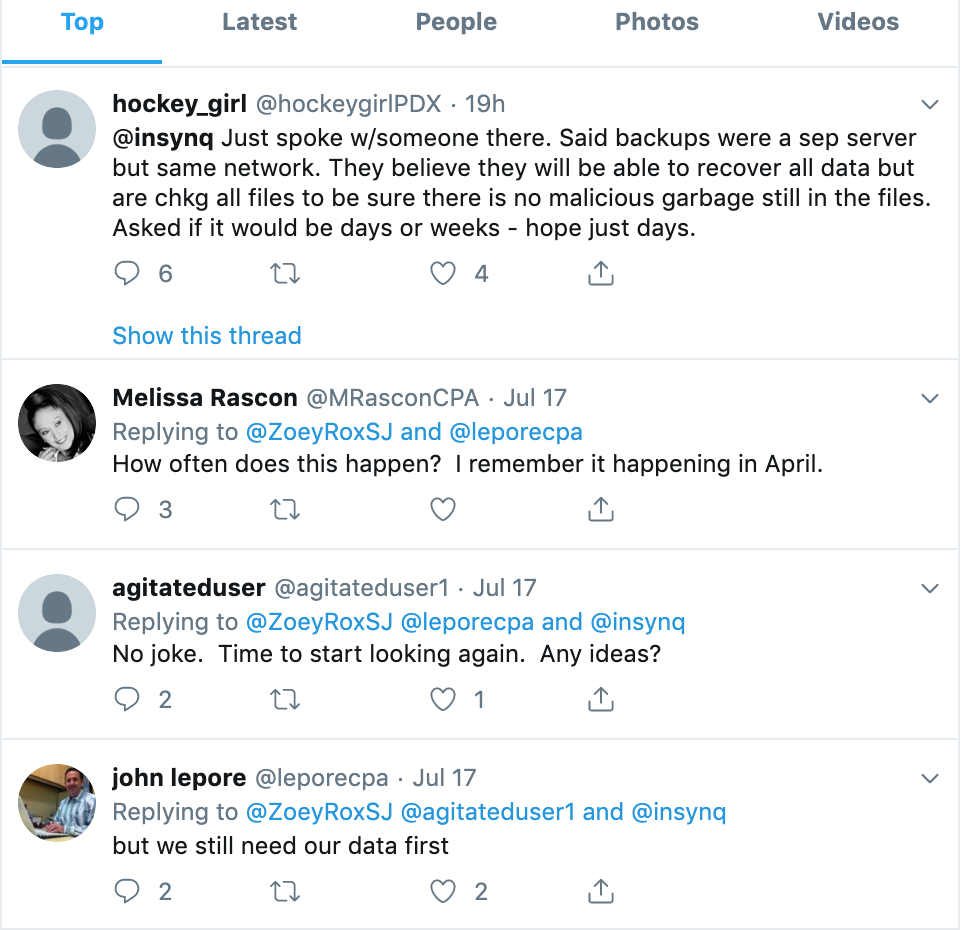
In response, the company appears to have simply deleted or deactivated its Twitter account (a cached copy from June 2019 is available here). Several customers venting about the outage on Twitter also accused the company of unpublishing negative comments about the incident from its Facebook page.
Some of those customers also said iNSYNQ initially blamed the outage on an alleged problem with U.S.-based nationwide cable ISP giant Comcast. Meanwhile, competing cloud hosting providers have been piling on to the tweetstorms about the iNSYNQ outage by marketing their own services, claiming they would never subject their customers to a three-day outage.
iNSYNQ has not yet responded to requests for comment.
Update, 4:35 p.m. ET: I just heard from iNSYNQ’s CEO Elliot Luchansky, who shared the following:
While we have continually updated our website and have emailed customers once if not twice daily during this malware attack, I acknowledge we’ve had to keep the detail fairly minimal.
Unfortunately, and as I’m sure you’re familiar with, the lack of detailed information we’ve shared has been purposeful and in an effort to protect our customers and their data- we’re in a behind the scenes trench warfare doing everything we possibly can to secure and restore our system and customer data and backups. I understand why our customers are frustrated, and we want more than anything to share every piece of information that we have.
Our customers and their businesses are our number one priority right now. Our team is working around the clock to secure and restore access to all impacted data, and we believe we have an end in sight in the near future.
You know as well as we that no one is 100% impervious to this – businesses large and small, governments and individuals are susceptible. iNSYNQ and our customers were the victims of a malware attack that’s a totally new variant that hadn’t been detected before, confirmed by the experienced and knowledgeable cybersecurity team we’ve employed.







 Zero-days and publicly disclosed flaws aside for the moment, probably the single most severe vulnerability addressed in this month’s patch batch (at least for enterprises) once again resides in the component of Windows responsible for automatically assigning Internet addresses to host computers — a function called the “Windows DHCP server.”
Zero-days and publicly disclosed flaws aside for the moment, probably the single most severe vulnerability addressed in this month’s patch batch (at least for enterprises) once again resides in the component of Windows responsible for automatically assigning Internet addresses to host computers — a function called the “Windows DHCP server.”