Conventional wisdom says one reason so many hackers seem to hail from Russia and parts of the former Soviet Union is that these countries have traditionally placed a much greater emphasis than educational institutions in the West on teaching information technology in middle and high schools, and yet they lack a Silicon Valley-like pipeline to help talented IT experts channel their skills into high-paying jobs. This post explores the first part of that assumption by examining a breadth of open-source data.
The supply side of that conventional wisdom seems to be supported by an analysis of educational data from both the U.S. and Russia, which indicates there are several stark and important differences between how American students are taught and tested on IT subjects versus their counterparts in Eastern Europe.

Compared to the United States there are quite a few more high school students in Russia who choose to specialize in information technology subjects. One way to measure this is to look at the number of high school students in the two countries who opt to take the advanced placement exam for computer science.
According to an analysis (PDF) by The College Board, in the ten years between 2005 and 2016 a total of 270,000 high school students in the United States opted to take the national exam in computer science (the “Computer Science Advanced Placement” exam).
Compare that to the numbers from Russia: A 2014 study (PDF) on computer science (called “Informatics” in Russia) by the Perm State National Research University found that roughly 60,000 Russian students register each year to take their nation’s equivalent to the AP exam — known as the “Unified National Examination.” Extrapolating that annual 60,000 number over ten years suggests that more than twice as many people in Russia — 600,000 — have taken the computer science exam at the high school level over the past decade.
In “A National Talent Strategy,” an in-depth analysis from Microsoft Corp. on the outlook for information technology careers, the authors warn that despite its critical and growing importance computer science is taught in only a small minority of U.S. schools. The Microsoft study notes that although there currently are just over 42,000 high schools in the United States, only 2,100 of them were certified to teach the AP computer science course in 2011.
A HEAD START
If more people in Russia than in America decide to take the computer science exam in secondary school, it may be because Russian students are required to study the subject beginning at a much younger age. Russia’s Federal Educational Standards (FES) mandate that informatics be compulsory in middle school, with any school free to choose to include it in their high school curriculum at a basic or advanced level.
“In elementary school, elements of Informatics are taught within the core subjects ‘Mathematics’ and ‘Technology,” the Perm University research paper notes. “Furthermore, each elementary school has the right to make [the] subject “Informatics” part of its curriculum.” Continue reading





 According to security firm
According to security firm 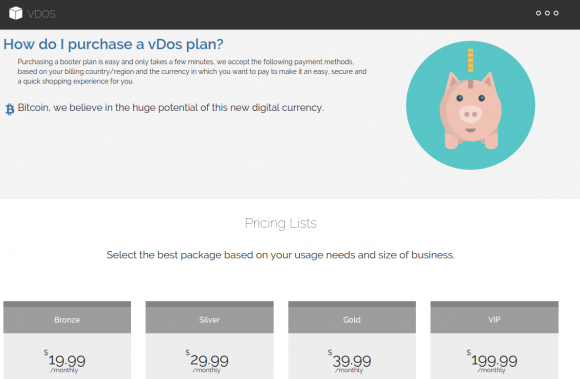
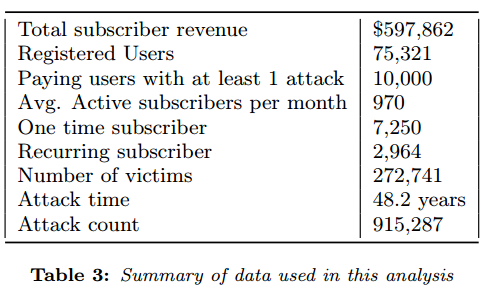 The NYU researchers found that vDOS had extremely low costs, and virtually all of its business was profit. Customers would pay up front for a subscription to the service, which was sold in booter packages priced from $5 to $300. The prices were based partly on the overall number of seconds that an attack may last (e.g., an hour would be 3,600 worth of attack seconds).
The NYU researchers found that vDOS had extremely low costs, and virtually all of its business was profit. Customers would pay up front for a subscription to the service, which was sold in booter packages priced from $5 to $300. The prices were based partly on the overall number of seconds that an attack may last (e.g., an hour would be 3,600 worth of attack seconds). Headquartered in San Francisco, OneLogin provides single sign-on and identity management for cloud-base applications. OneLogin counts among its customers some 2,000 companies in 44 countries, over 300 app vendors and more than 70 software-as-a-service providers.
Headquartered in San Francisco, OneLogin provides single sign-on and identity management for cloud-base applications. OneLogin counts among its customers some 2,000 companies in 44 countries, over 300 app vendors and more than 70 software-as-a-service providers.

 In April 2017 I received an anonymous tip from a reader who said he’d figured out that just by changing a single number in the Web address when accessing his recent medical claim at MolinaHealthcare.com he could then view any and all other patient claims.
In April 2017 I received an anonymous tip from a reader who said he’d figured out that just by changing a single number in the Web address when accessing his recent medical claim at MolinaHealthcare.com he could then view any and all other patient claims.