A Ukrainian hacker who once hatched a plot to have heroin sent to my Virginia home and then alert police when the drugs arrived had his first appearance in a U.S. court today, after being extradited to the United States to face multiple cybercrime charges.
Sergey Vovnenko, a.k.a. “Fly,” “Flycracker” and “MUXACC1” (muxa is transliterated Russian for “муха” which means “fly”), was set to appear in a Newark courtroom today on charges of stealing and selling credit card and banking data, emptying bank accounts, and running a botnet of more than 12,000 hacked computers and servers, among other alleged crimes.
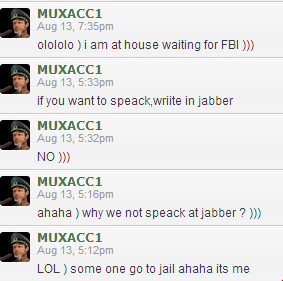
I first became acquainted with Fly in 2013, when his Twitter persona (warning: images here may not be safe for work) began sending me taunting tweets laced with epithets and occasional attempts to get me to click dodgy-looking Web links. Fly also took to his Livejournal blog to post copies of my credit report, directions to my home and pictures of my front door.
After consulting with cybercrime researchers at Russian security firm Group-IB, I learned that Fly was the administrator of a closely-guarded but now-defunct cybercrime forum dedicated to financial fraud called thecc[dot]bz (“cc” is a reference to credit cards).
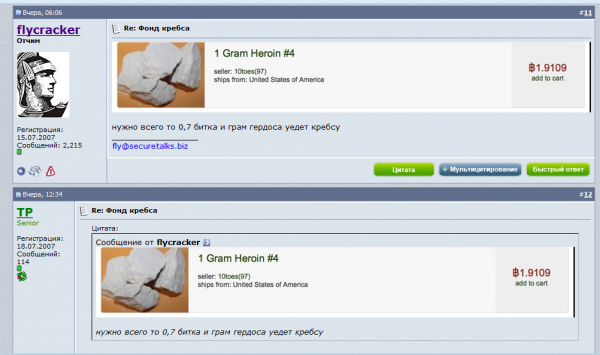
Not long after that, I secretly gained access to his forum. And none too soon: In one lengthy discussion thread on the forum, I found that Fly had solicited donations from fellow fraudsters on the forum to donate Bitcoin currency for a slush fund Fly created for the express purpose of purchasing heroin off of the Silk Road — which was at the time the leading source of illicit drugs on the Dark Web.
Fly’s plan was simple: Have the drugs delivered to my home in my name, and then spoof a call from one of my neighbors to the local police informing them that I was a druggie, that I had druggie friends coming in and out of my house all day long, and that I was even having drugs delivered to my home.
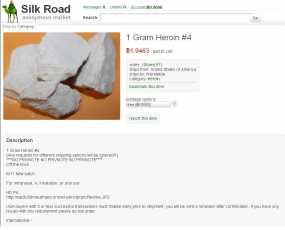
The forum members took care to find the most reputable sellers of heroin on the Silk Road. After purchasing a gram of the stuff from the Silk Road’s top smack seller — a drug dealer who used the nickname “Maestro” — Fly posted the USPS tracking link for the package into the discussion thread on his forum.
At that point, I called the local police and had a cop come out to take an official police report. The officer asked me to contact him again if the drugs actually arrived. Three days later, our local Postal Service carrier hand delivered a thin USPS Express Mail envelope that was postmarked from Chicago. Inside was another blank envelope containing a May 2013 copy of Chicago Confidential, a weekly glossy magazine from the Chicago Tribune.
On the back of the magazine, taped to a full-page ad for jewelry from LesterLampert, were a baker’s dozen individually wrapped packets emblazoned with the same black and gold skull motif that was on Maestro’s Silk Road ad. I immediately contacted the police, who came and dutifully retrieved the drugs, which turned out to be almost pure heroin.
I wrote about the experience of foiling Fly’s plan in a story titled Mail From the (Velvet) Cybercrime Underground. This did not sit well with Fly, who was made to look bad in front of his forum members who’d contributed roughly two Bitcoins to the scheme.
Angry that I’d foiled his plan to have me arrested for drug possession, Fly had a local florist send a gaudy floral arrangement in the shape of a giant cross to my home, complete with a menacing message that addressed my wife and was signed, “Velvet Crabs.”
After this incident, I became intensely curious about the identity of this Fly individual, so I began looking through databases of hacked carding and cybercrime forums. My first real break came when Group-IB provided a key piece of the puzzle: Group-IB researchers found that on the now-defunct vulnes[dot]com, Fly maintained an account under the nickname Flycracker, and signed up with the email address mazafaka@libero.it(.it is the country code for Italy).
According to a trusted source in the security community, that email account was somehow compromised in 2013. The source said the account was full of emailed reports from a keylogging device that was tied to another email address — 777flyck777@gmail.com (according to Google, mazafaka@libero.it is the recovery email address for 777flyck777@gmail.com).
Those keylog reports contained some valuable information, and indicated that Fly had planted a keylogger on his then-fiancee Irina’s computer. On several occasions, those emails show Fly’s wife typed in her Gmail address, which included her real first and last name — Irina Gumenyuk. Continue reading