One of the risks of using social media networks is having information you intend to share with only a handful of friends be made available to everyone. Sometimes that over-sharing happens because friends betray your trust, but more worrisome are the cases in which a social media platform itself exposes your data in the name of marketing.
 LinkedIn has built much of its considerable worth on the age-old maxim that “it’s all about who you know.” As a LinkedIn user, you can directly connect with those you attest to knowing professionally or personally, but also you can ask to be introduced to someone you’d like to meet by sending a request through someone who bridges your separate social networks. Celebrities, executives or any other LinkedIn users who wish to avoid unsolicited contact requests may do so by selecting an option that forces the requesting party to supply the personal email address of the intended recipient.
LinkedIn has built much of its considerable worth on the age-old maxim that “it’s all about who you know.” As a LinkedIn user, you can directly connect with those you attest to knowing professionally or personally, but also you can ask to be introduced to someone you’d like to meet by sending a request through someone who bridges your separate social networks. Celebrities, executives or any other LinkedIn users who wish to avoid unsolicited contact requests may do so by selecting an option that forces the requesting party to supply the personal email address of the intended recipient.
LinkedIn’s entire social fabric begins to unravel if any user can directly connect to any other user, regardless of whether or how their social or professional circles overlap. Unfortunately for LinkedIn (and its users who wish to have their email addresses kept private), this is the exact risk introduced by the company’s built-in efforts to expand the social network’s user base.
According to researchers at the Seattle, Wash.-based firm Rhino Security Labs, at the crux of the issue is LinkedIn’s penchant for making sure you’re as connected as you possibly can be. When you sign up for a new account, for example, the service asks if you’d like to check your contacts lists at other online services (such as Gmail, Yahoo, Hotmail, etc.). The service does this so that you can connect with any email contacts that are already on LinkedIn, and so that LinkedIn can send invitations to your contacts who aren’t already users.
LinkedIn assumes that if an email address is in your contacts list, that you must already know this person. But what if your entire reason for signing up with LinkedIn is to discover the private email addresses of famous people? All you’d need to do is populate your email account’s contacts list with hundreds of permutations of famous peoples’ names — including combinations of last names, first names and initials — in front of @gmail.com, @yahoo.com, @hotmail.com, etc. With any luck and some imagination, you may well be on your way to an A-list LinkedIn friends list (or a fantastic set of addresses for spear-phishing, stalking, etc.).
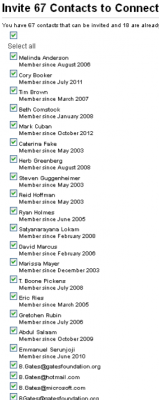
When you import your list of contacts from a third-party service or from a stand-alone file, LinkedIn will show you any profiles that match addresses in your contacts list. More significantly, LinkedIn helpfully tells you which email addresses in your contacts lists are not LinkedIn users.
It’s that last step that’s key to finding the email address of the targeted user to whom LinkedIn has just sent a connection request on your behalf. The service doesn’t explicitly tell you that person’s email address, but by comparing your email account’s contact list to the list of addresses that LinkedIn says don’t belong to any users, you can quickly figure out which address(es) on the contacts list correspond to the user(s) you’re trying to find.
Rhino Security founders Benjamin Caudill and Bryan Seely have a recent history of revealing how trust relationships between and among online services can be abused to expose or divert potentially sensitive information. Last month, the two researchers detailed how they were able to de-anonymize posts to Secret, an app-driven online service that allows people to share messages anonymously within their circle of friends, friends of friends, and publicly. In February, Seely more famously demonstrated how to use Google Maps to intercept FBI and Secret Service phone calls.
This time around, the researchers picked on Dallas Mavericks owner Mark Cuban to prove their point with LinkedIn. Using their low-tech hack, the duo was able to locate the Webmail address Cuban had used to sign up for LinkedIn. Seely said they found success in locating the email addresses of other celebrities using the same method about nine times out ten. Continue reading






![The cybercrime shop Rescator[dot]cc pushed out nine new batches of cards from the same "American Sanctions" base of cards that banks traced back to Home Depot.](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/AS6-12-600x558.png)