A recent scoop by Reuters revealed that mobile apps for the U.S. Army and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) were integrating software that sends visitor data to a Russian company called Pushwoosh, which claims to be based in the United States. But that story omitted an important historical detail about Pushwoosh: In 2013, one of its developers admitted to authoring the Pincer Trojan, malware designed to surreptitiously intercept and forward text messages from Android mobile devices.
Pushwoosh says it is a U.S. based company that provides code for software developers to profile smartphone app users based on their online activity, allowing them to send tailor-made notifications. But a recent investigation by Reuters raised questions about the company’s real location and truthfulness.
The Army told Reuters it removed an app containing Pushwoosh in March, citing “security concerns.” The Army app was used by soldiers at one of the nation’s main combat training bases.
Reuters said the CDC likewise recently removed Pushwoosh code from its app over security concerns, after reporters informed the agency Pushwoosh was not based in the Washington D.C. area — as the company had represented — but was instead operated from Novosibirsk, Russia.
Pushwoosh’s software also was found in apps for “a wide array of international companies, influential nonprofits and government agencies from global consumer goods company Unilever and the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) to the politically powerful U.S. gun lobby, the National Rifle Association (NRA), and Britain’s Labour Party.”
The company’s founder Max Konev told Reuters Pushwoosh “has no connection with the Russian government of any kind” and that it stores its data in the United States and Germany.
But Reuters found that while Pushwoosh’s social media and U.S. regulatory filings present it as a U.S. company based variously in California, Maryland and Washington, D.C., the company’s employees are located in Novosibirsk, Russia.
Reuters also learned that the company’s address in California does not exist, and that two LinkedIn accounts for Pushwoosh employees in Washington, D.C. were fake.
“Pushwoosh never mentioned it was Russian-based in eight annual filings in the U.S. state of Delaware, where it is registered, an omission which could violate state law,” Reuters reported.
Pushwoosh admitted the LinkedIn profiles were fake, but said they were created by a marketing firm to drum up business for the company — not misrepresent its location.
Pushwoosh told Reuters it used addresses in the Washington, D.C. area to “receive business correspondence” during the coronavirus pandemic. A review of the Pushwoosh founder’s online presence via Constella Intelligence shows his Pushwoosh email address was tied to a phone number in Washington, D.C. that was also connected to email addresses and account profiles for over a dozen other Pushwoosh employees.
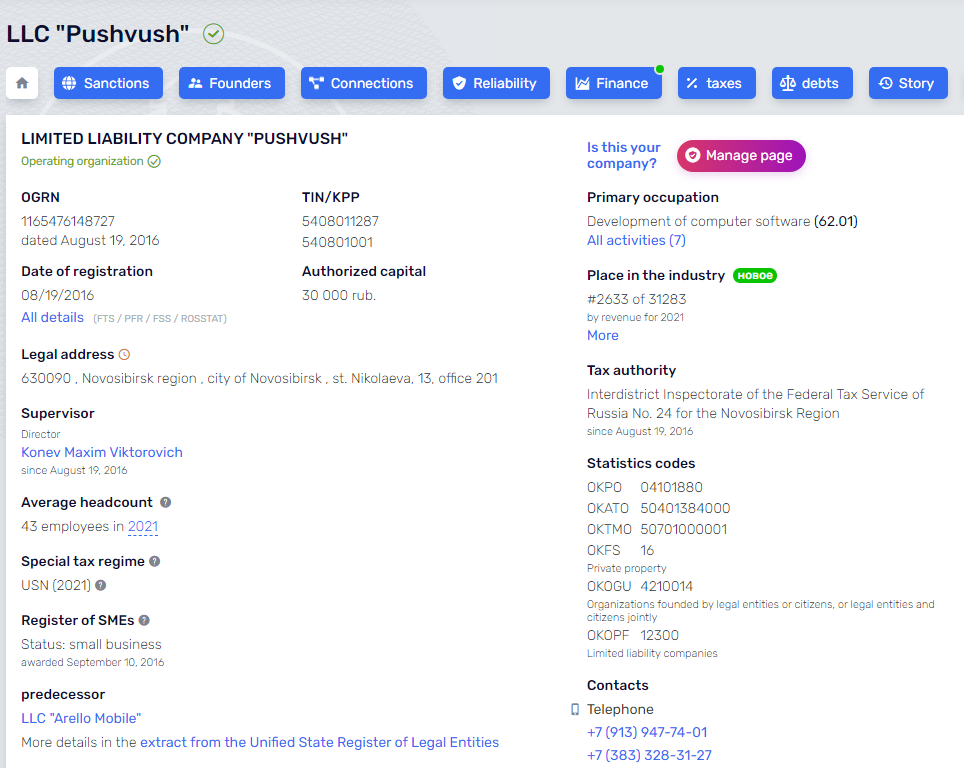
Pushwoosh was incorporated in Novosibirsk, Russia in 2016.
THE PINCER TROJAN CONNECTION
The dust-up over Pushwoosh came in part from data gathered by Zach Edwards, a security researcher who until recently worked for the Internet Safety Labs, a nonprofit organization that funds research into online threats.
Edwards said Pushwoosh began as Arello-Mobile, and for several years the two co-branded — appearing side by side at various technology expos. Around 2016, he said, the two companies both started using the Pushwoosh name.
A search on Pushwoosh’s code base shows that one of the company’s longtime developers is a 41-year-old from Novosibirsk named Yuri Shmakov. In 2013, KrebsOnSecurity interviewed Shmakov for the story, “Who Wrote the Pincer Android Trojan?” wherein Shmakov acknowledged writing the malware as a freelance project.
Shmakov told me that, based on the client’s specifications, he suspected it might ultimately be put to nefarious uses. Even so, he completed the job and signed his work by including his nickname in the app’s code.
“I was working on this app for some months, and I was hoping that it would be really helpful,” Shmakov wrote. “[The] idea of this app is that you can set it up as a spam filter…block some calls and SMS remotely, from a Web service. I hoped that this will be [some kind of] blacklist, with logging about blocked [messages/calls]. But of course, I understood that client [did] not really want this.”
Shmakov did not respond to requests for comment. His LinkedIn profile says he stopped working for Arello Mobile in 2016, and that he currently is employed full-time as the Android team leader at an online betting company.
In a blog post responding to the Reuters story, Pushwoosh said it is a privately held company incorporated under the state laws of Delaware, USA, and that Pushwoosh Inc. was never owned by any company registered in the Russian Federation.
“Pushwoosh Inc. used to outsource development parts of the product to the Russian company in Novosibirsk, mentioned in the article,” the company said. “However, in February 2022, Pushwoosh Inc. terminated the contract.”
However, Edwards noted that dozens of developer subdomains on Pushwoosh’s main domain still point to JSC Avantel, an Internet provider based in Novosibirsk, Russia.
WAR GAMES

Pushwoosh employees posing at a company laser tag event.
Edwards said the U.S. Army’s app had a custom Pushwoosh configuration that did not appear on any other customer implementation.
“It had an extremely custom setup that existed nowhere else,” Edwards said. “Originally, it was an in-app Web browser, where it integrated a Pushwoosh javascript so that any time a user clicked on links, data went out to Pushwoosh and they could push back whatever they wanted through the in-app browser.”
An Army Times article published the day after the Reuters story ran said at least 1,000 people downloaded the app, which “delivered updates for troops at the National Training Center on Fort Irwin, Calif., a critical waypoint for deploying units to test their battlefield prowess before heading overseas.”
In April 2022, roughly 4,500 Army personnel converged on the National Training Center for a war games exercise on how to use lessons learned from Russia’s war against Ukraine to prepare for future fights against a major adversary such as Russia or China.
Edwards said despite Pushwoosh’s many prevarications, the company’s software doesn’t appear to have done anything untoward to its customers or users.
“Nothing they did has been seen to be malicious,” he said. “Other than completely lying about where they are, where their data is being hosted, and where they have infrastructure.” Continue reading →








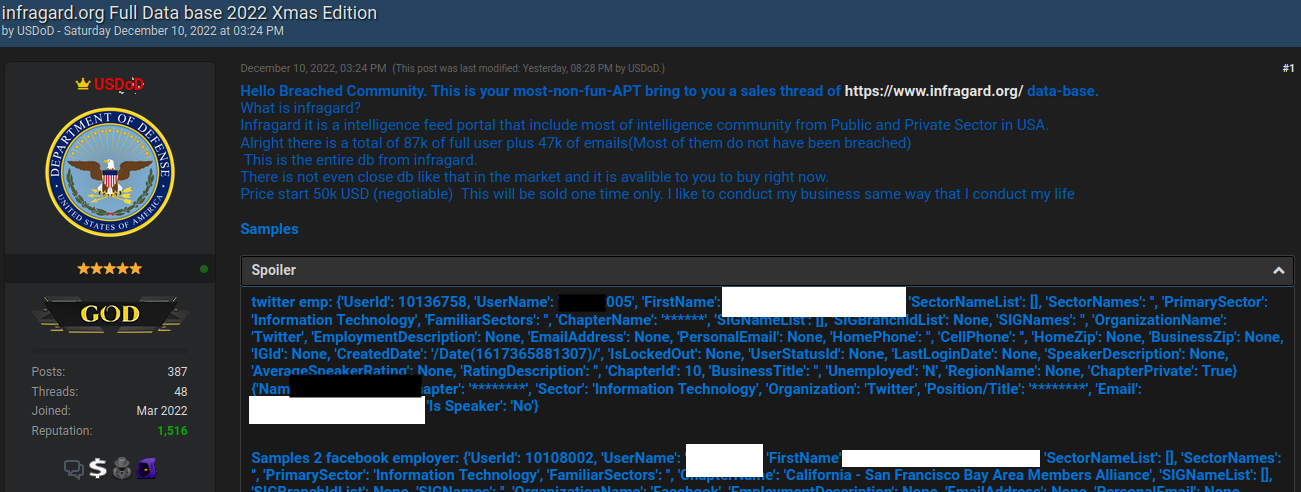
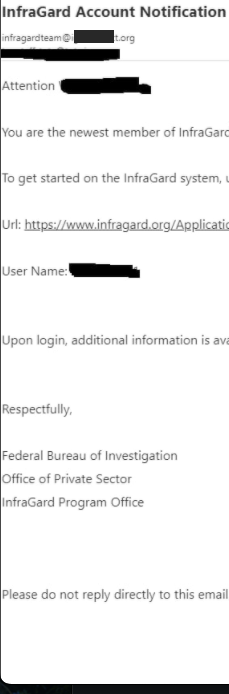 But USDoD said that in early December, their email address in the name of the CEO received a reply saying the application had been approved (see redacted screenshot to the right). While the FBI’s InfraGard system requires multi-factor authentication by default, users can choose between receiving a one-time code via SMS or email.
But USDoD said that in early December, their email address in the name of the CEO received a reply saying the application had been approved (see redacted screenshot to the right). While the FBI’s InfraGard system requires multi-factor authentication by default, users can choose between receiving a one-time code via SMS or email.