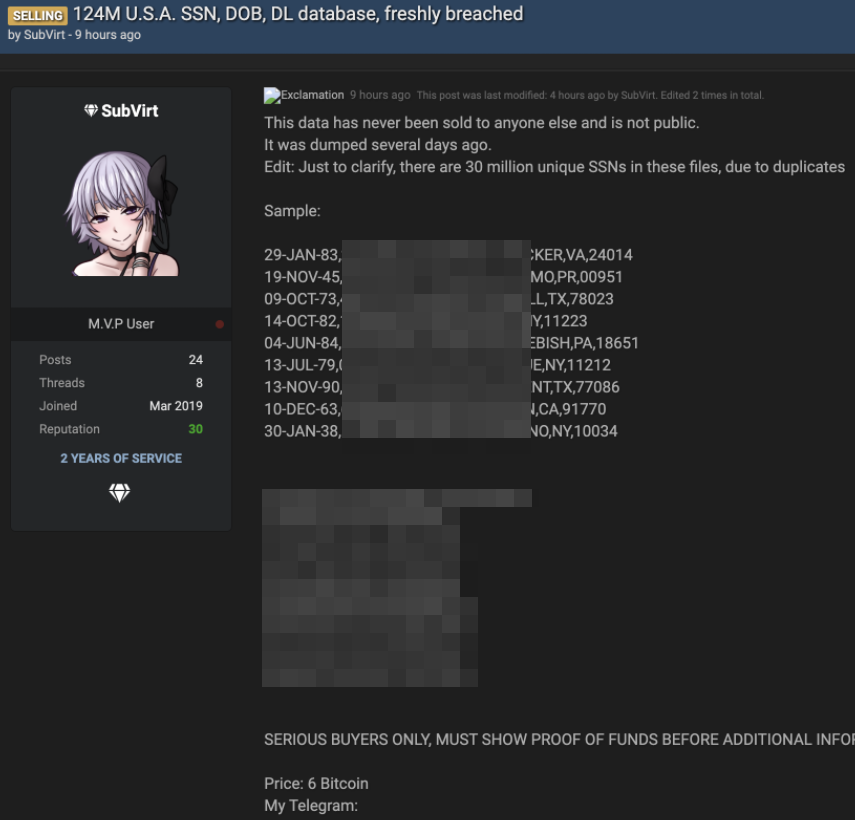
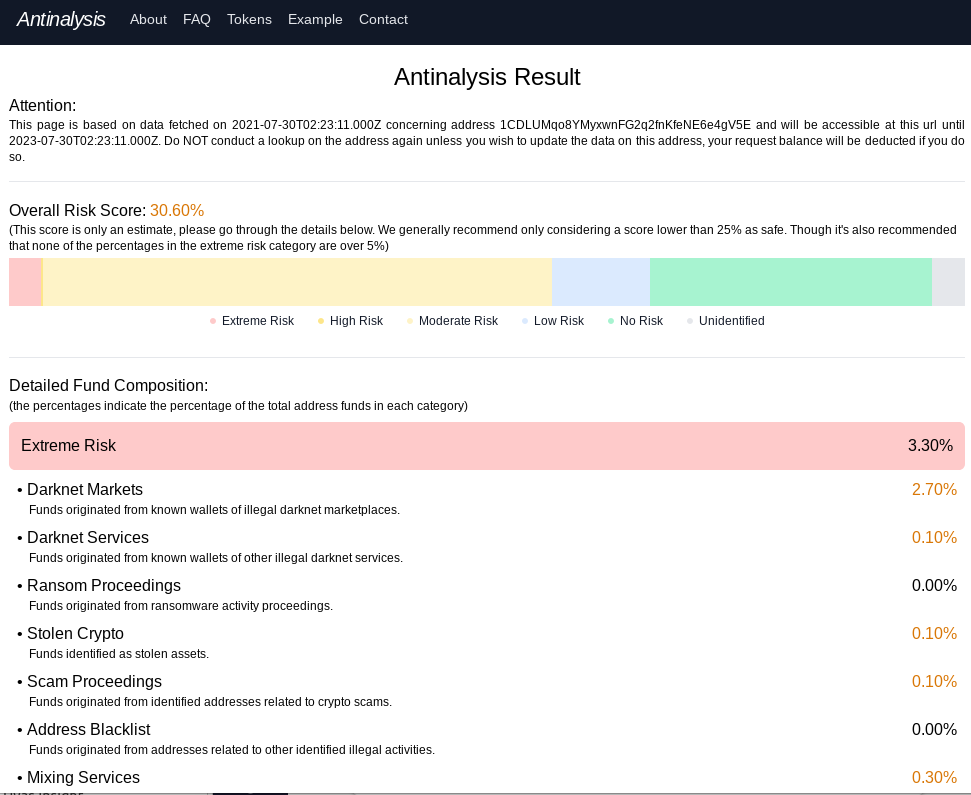
Criminal hackers will try almost anything to get inside a profitable enterprise and secure a million-dollar payday from a ransomware infection. Apparently now that includes emailing employees directly and asking them to unleash the malware inside their employer’s network in exchange for a percentage of any ransom amount paid by the victim company.
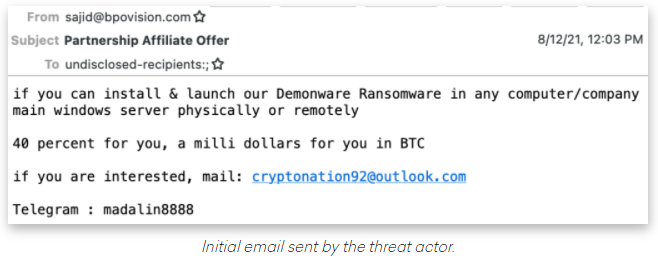
Image: Abnormal Security.
Crane Hassold, director of threat intelligence at Abnormal Security, described what happened after he adopted a fake persona and responded to the proposal in the screenshot above. It offered to pay him 40 percent of a million-dollar ransom demand if he agreed to launch their malware inside his employer’s network.
This particular scammer was fairly chatty, and over the course of five days it emerged that Hassold’s correspondent was forced to change up his initial approach in planning to deploy the DemonWare ransomware strain, which is freely available on GitHub.
“According to this actor, he had originally intended to send his targets—all senior-level executives—phishing emails to compromise their accounts, but after that was unsuccessful, he pivoted to this ransomware pretext,” Hassold wrote.
Abnormal Security documented how it tied the email back to a young man in Nigeria who acknowledged he was trying to save up money to help fund a new social network he is building called Sociogram.
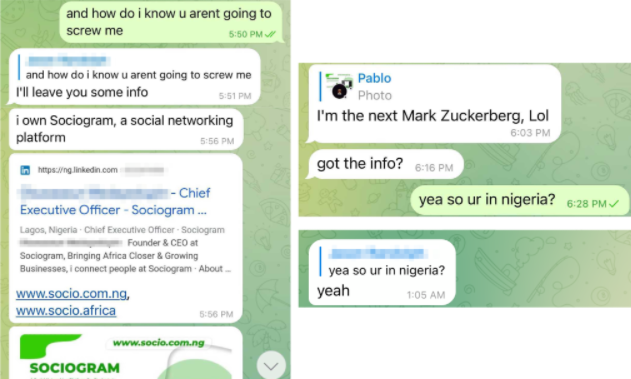
Image: Abnormal Security.
Reached via LinkedIn, Sociogram founder Oluwaseun Medayedupin asked to have his startup’s name removed from the story, although he did not respond to questions about whether there were any inaccuracies in Hassold’s report.
“Please don’t harm Sociogram’s reputation,” Medayedupin pleaded. “I beg you as a promising young man.”
This attacker’s approach may seem fairly amateur, but it would be a mistake to dismiss the threat from West African cybercriminals dabbling in ransomware. While multi-million dollar ransomware payments are hogging the headlines, by far the biggest financial losses tied to cybercrime each year stem from so-called Business Email Compromise (BEC) or CEO Scams, in which crooks mainly based in Africa and Southeast Asia will spoof communications from executives at the target firm in a bid to initiate unauthorized international wire transfers.
According to the latest figures (PDF) released by the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), the reported losses from BEC scams continue to dwarf other cybercrime loss categories, increasing to $1.86 billion in 2020.
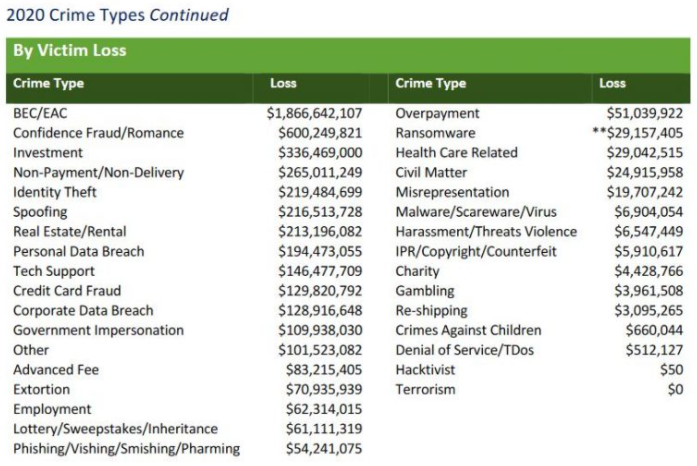
Image: FBI
“Knowing the actor is Nigerian really brings the entire story full circle and provides some notable context to the tactics used in the initial email we identified,” Hassold wrote. “For decades, West African scammers, primarily located in Nigeria, have perfected the use of social engineering in cybercrime activity.”
“While the most common cyber attack we see from Nigerian actors (and most damaging attack globally) is business email compromise (BEC), it makes sense that a Nigerian actor would fall back on using similar social engineering techniques, even when attempting to successfully deploy a more technically sophisticated attack like ransomware,” Hassold concluded.
DON’T QUIT YOUR DAY JOB
Cybercriminals trolling for disgruntled employees is hardly a new development. Big companies have long been worried about the very real threat of disgruntled employees creating identities on darknet sites and then offering to trash their employer’s network for a fee (for more on that, see my 2016 story, Rise of the Darknet Stokes Fear of the Insider). Continue reading