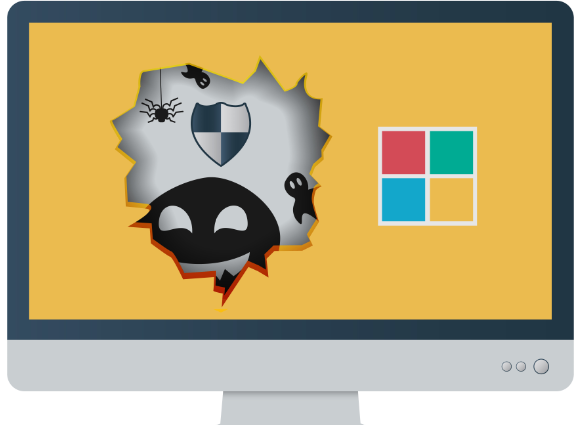
The U.S. Labor Department’s inspector general said this week that roughly $100 million in fraudulent unemployment insurance claims were paid in 2020 to criminals who are already in jail. That’s a tiny share of the estimated tens of billions of dollars in jobless benefits states have given to identity thieves in the past year. To help reverse that trend, many states are now turning to a little-known private company called ID.me. This post examines some of what that company is seeing in its efforts to stymie unemployment fraud.

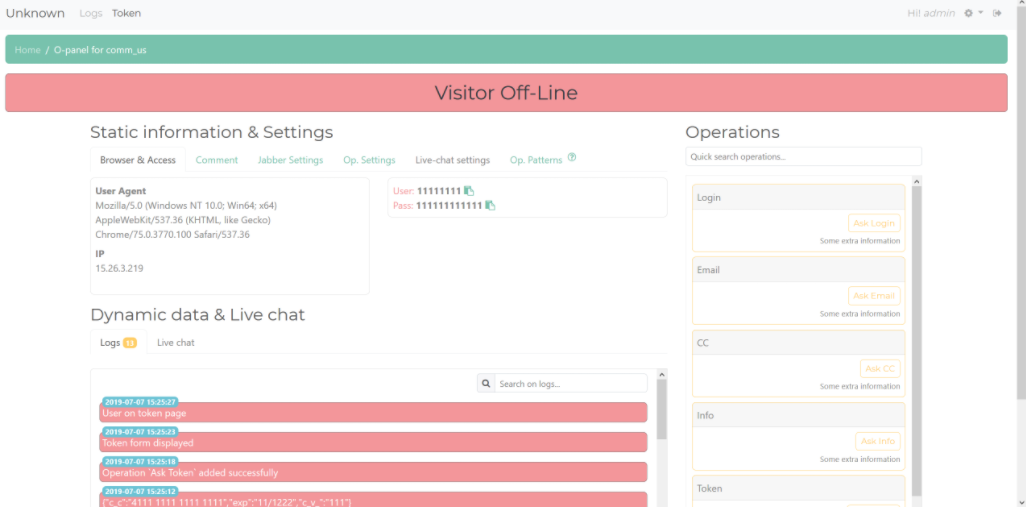
These prisoners tried to apply for jobless benefits. Personal information from the inmate IDs has been redacted. Image: ID.me
A new report (PDF) from the Labor Department’s Office of Inspector General (OIG) found that from March through October of 2020, some $3.5 billion in fraudulent jobless benefits — nearly two-thirds of the phony claims it reviewed — was paid out to individuals with Social Security numbers filed in multiple states. Almost $100 million went to more than 13,000 ineligible people who are currently in prison.
The OIG acknowledges that the total losses from all states is likely to be tens of billions of dollars. Indeed, just one state — California — disclosed last month that hackers, identity thieves and overseas criminal rings stole more than $11 billion in jobless benefits from the state last year. That’s roughly 10 percent of all claims.
Bloomberg Law reports that in response to a flood of jobless claims that exploit the lack of information sharing among states, the Labor Dept. urged the states to use a federally funded hub designed to share applicant data and detect fraudulent claims filed in more than one state. But as the OIG report notes, participation in the hub is voluntary, and so far only 32 of 54 state or territory workforce agencies in the U.S. are using it.
Much of this fraud exploits weak authentication methods used by states that have long sought to verify applicants using static, widely available information such as Social Security numbers and birthdays. Many states also lacked the ability to tell when multiple payments were going to the same bank accounts.
To make matters worse, as the Coronavirus pandemic took hold a number of states dramatically pared back the amount of information required to successfully request a jobless benefits claim.
77,000 NEW (AB)USERS EACH DAY
In response, 15 states have now allied with McLean, Va.-based ID.me to shore up their authentication efforts, with six more states under contract to use the service in the coming months. That’s a minor coup for a company launched in 2010 with the goal of helping e-commerce sites validate the identities of customers for the purposes of granting discounts for veterans, teachers, students, nurses and first responders.
ID.me says it now has more than 36 million people signed up for accounts, with roughly 77,000 new users signing up each day. Naturally, a big part of that growth has come from unemployed people seeking jobless benefits.
To screen out fraudsters, ID.me requires applicants to supply a great deal more information than previously requested by the states, such as images of their driver’s license or other government-issued ID, copies of utility or insurance bills, and details about their mobile phone service.
When an applicant doesn’t have one or more of the above — or if something about their application triggers potential fraud flags — ID.me may require a recorded, live video chat with the person applying for benefits.
This has led to some fairly amusing attempts to circumvent their verification processes, said ID.me founder and CEO Blake Hall. For example, it’s not uncommon for applicants appearing in the company’s video chat to don disguises. The Halloween mask worn by the applicant pictured below is just one example.

Image: ID.me
Hall said the company’s service is blocking a significant amount of “first party” fraud — someone using their own identity to file in multiple states where they aren’t eligible — as well as “third-party” fraud, where people are tricked into giving away identity data that thieves then use to apply for benefits.
“There’s literally every form of attack, from nation states and organized crime to prisoners,” Hall said. “It’s like the D-Day of fraud, this is Omaha Beach we’re on right now. The amount of fraud we are fighting is truly staggering.”
According to ID.me, a major driver of phony jobless claims comes from social engineering, where people have given away personal data in response to romance or sweepstakes scams, or after applying for what they thought was a legitimate work-from-home job.
“A lot of this is targeting the elderly,” Hall said. “We’ve seen [videos] of people in nursing homes, where folks off camera are speaking for them and holding up documents.”
“We had one video where the person applying said, ‘I’m here for the prize money,'” Hall continued. “Another elderly victim started weeping when they realized they weren’t getting a job and were the victim of a job scam. In general though, the job scam stuff hits younger people harder and the romance and prize money stuff hits elderly people harder.”
Many other phony claims are filed by people who’ve been approached by fraudsters promising them a cut of any unemployment claims granted in their names.
“That person is told to just claim that they had their identity stolen when and if law enforcement ever shows up,” Hall said.
Continue reading →