Coinbase and Overstock.com just fixed a serious glitch that allowed Overstock customers to buy any item at a tiny fraction of the listed price. Potentially more punishing, the flaw let anyone paying with bitcoin reap many times the authorized bitcoin refund amount on any canceled Overstock orders.
In January 2014, Overstock.com partnered with Coinbase to let customers pay for merchandise using bitcoin, making it among the first of the largest e-commerce vendors to accept the virtual currency.
On December 19, 2017, as the price of bitcoin soared to more than $17,000 per coin, Coinbase added support for Bitcoin Cash — an offshoot (or “fork”) from bitcoin designed to address the cryptocurrency’s scalability challenges.
As a result of the change, Coinbase customers with balances of bitcoin at the time of the fork were given an equal amount of bitcoin cash stored by Coinbase. However, there is a significant price difference between the two currencies: A single bitcoin is worth almost $15,000 right now, whereas a unit of bitcoin cash is valued at around $2,400.
On Friday, Jan. 5, KrebsOnSecurity was contacted by JB Snyder, owner of North Carolina-based Bancsec, a company that gets paid to break into banks and test their security. An early adopter of bitcoin, Snyder said he was using some of his virtual currency to purchase an item at Overstock when he noticed something alarming.
During the checkout process for those paying by bitcoin, Overstock.com provides the customer a bitcoin wallet address that can be used to pay the invoice and complete the transaction. But Snyder discovered that Overstock’s site just as happily accepted bitcoin cash as payment, even though bitcoin cash is currently worth only about 15 percent of the value of bitcoin.
To confirm and replicate Snyder’s experience firsthand, KrebsOnSecurity purchased a set of three outdoor solar lamps from Overstock for a grand total of $78.27.

The solar lights I purchased from Overstock.com to test Snyder’s finding. They cost $78.27 in bitcoin, but because I was able to pay for them in bitcoin cash I only paid $12.02.
After indicating I wished to pay for the lamps in bitcoin, the site produced a payment invoice instructing me to send exactly 0.00475574 bitcoins to a specific address.
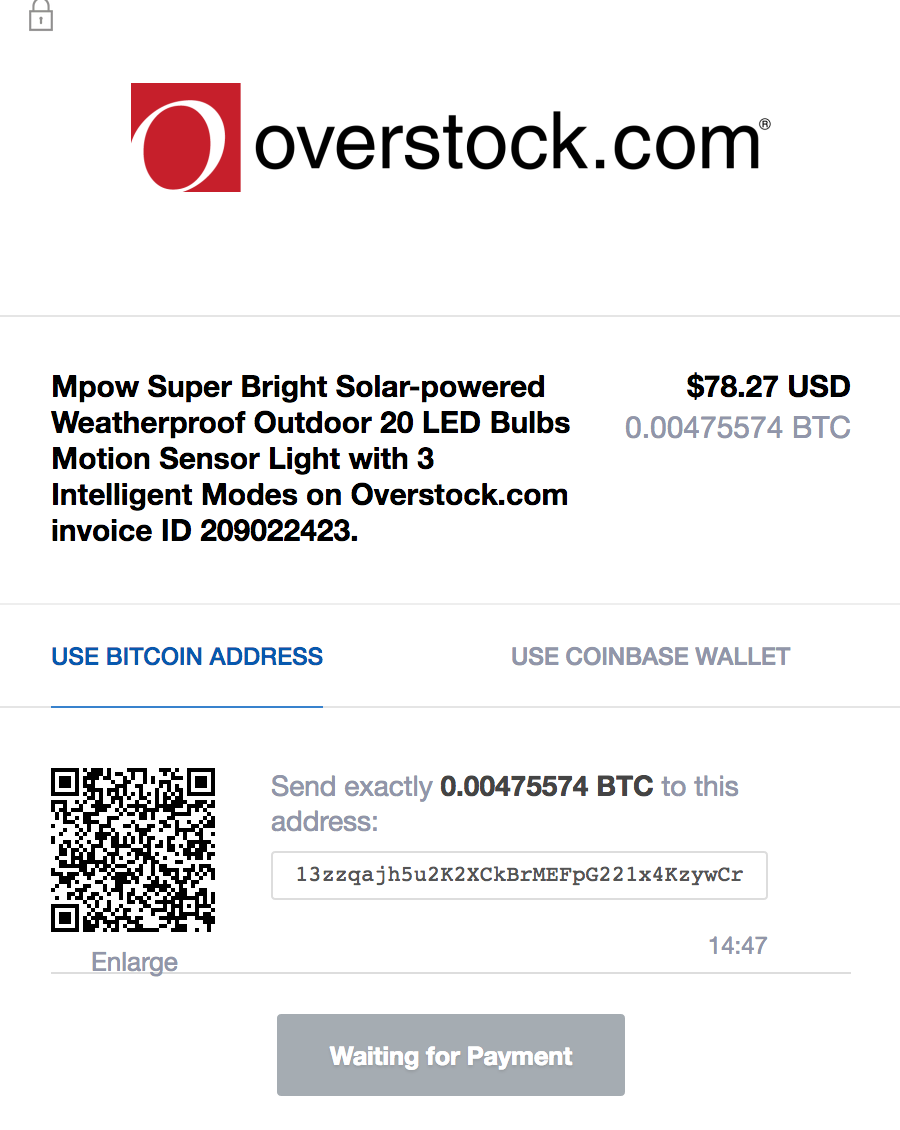
The payment invoice I received from Overstock.com.
Logging into Coinbase, I took the bitcoin address and pasted that into the “pay to:” field, and then told Coinbase to send 0.00475574 in bitcoin cash instead of bitcoin. The site responded that the payment was complete. Within a few seconds I received an email from Overstock congratulating me on my purchase and stating that the items would be shipped shortly.
I had just made a $78 purchase by sending approximately USD $12 worth of bitcoin cash. Crypto-currency alchemy at last!
But that wasn’t the worst part. I didn’t really want the solar lights, but also I had no interest in ripping off Overstock. So I cancelled the order. To my surprise, the system refunded my purchase in bitcoin, not bitcoin cash!

Consider the implications here: A dishonest customer could have used this bug to make ridiculous sums of bitcoin in a very short period of time. Let’s say I purchased one of the more expensive items for sale on Overstock, such as this $100,000, 3-carat platinum diamond ring. I then pay for it in Bitcoin cash, using an amount equivalent to approximately 1 bitcoin ($~15,000).
Then I simply cancel my order, and Overstock/Coinbase sends me almost $100,000 in bitcoin, netting me a tidy $85,000 profit. Rinse, wash, repeat. Continue reading





 This past year KrebsOnSecurity published nearly 160 stories, generating more than 11,000 reader comments. The pace of publications here slowed down in 2017, but then again I have been trying to focus on quality over quantity, and many of these stories took weeks or months to report and write.
This past year KrebsOnSecurity published nearly 160 stories, generating more than 11,000 reader comments. The pace of publications here slowed down in 2017, but then again I have been trying to focus on quality over quantity, and many of these stories took weeks or months to report and write.