The recent hacker break-in at Sony Pictures Entertainment appears to have involved the theft of far more than unreleased motion pictures: According to multiple sources, the intruders also stole more than 25 gigabytes of sensitive data on tens of thousands of Sony employees, including Social Security numbers, medical and salary information. What’s more, it’s beginning to look like the attackers may have destroyed data on an unknown number of internal Sony systems.
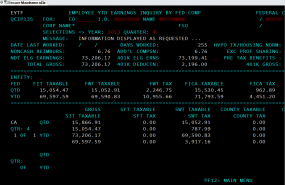
Screen shot from an internal audit report allegedly stolen from Sony and circulating on file-trading networks.
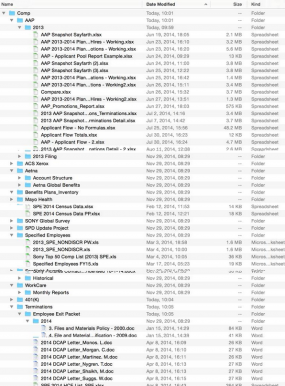
Several files being traded on torrent networks seen by this author include a global Sony employee list, a Microsoft Excel file that includes the name, location, employee ID, network username, base salary and date of birth for more than 6,800 individuals.
Sony officials could not be immediately reached for comment; a press hotline for the company rang for several minutes without answer, and email requests to the company went unanswered. But a comprehensive search on LinkedIn for dozens of the names in the list indicate virtually all correspond to current or former Sony employees.
Another file being traded online appears to be a status report from April 2014 listing the names, dates of birth, SSNs and health savings account data on more than 700 Sony employees. Yet another apparently purloined file’s name suggests it was the product of an internal audit from accounting firm Pricewaterhouse Coopers, and includes screen shots of dozens of employee federal tax records and other compensation data.
The latest revelations come more than a week after a cyberattack on Sony Pictures Entertainment brought down the company’s corporate email systems. A Sony spokesperson told Reuters that the company has since “restored a number of important services” and was “working closely with law enforcement officials to investigate the matter.”
Some of the files apparently taken from Sony that are now being traded on file-sharing networks.
Several media outlets reported at the time that Sony employees had been warned not to connect to the company’s corporate network or to check email, and noted that Sony’s IT departments had instructed employees to turn off their computers as well as disable Wi-Fi on all mobile devices.” Other reports cited unnamed investigators pointing to North Korean hackers as the source of the attack, although those reports could not be independently confirmed.
Such extreme precautions would make sense if the company’s network was faced with a cyber threat designed to methodically destroy files on corporate computers. Indeed, the FBI this week released a restricted “Flash Alert” warning of just such a threat, about an unnamed attack group that has been using malware designed to wipe computer hard drives — and the underlying “master boot record” (MBR) on the affected systems — of all data.
KrebsOnSecurity obtained a copy of the alert, which includes several file names and hashes (long strings of letters and numbers that uniquely identify files) corresponding to the file-wiping malware. The FBI does not specify where the malware was found or against whom it might have been used, noting only that “the FBI has high confidence that these indicators are being used by CNE [computer network exploitation] operators for further network exploitation.” The report also says the language pack referenced by the malicious files is Korean.
Continue reading →





![The card fraud shop "goodshop[dot]bz" is selling thousands of cards in its "Happy Winter Update."](https://krebsonsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/goodshophappywinter-600x356.png)