With the eyes of the world trained on Brazil for the 2014 FIFA World Cup, it seems a fitting time to spotlight a growing form of computer fraud that’s giving Brazilian banks and consumers a run for their money. Today’s post looks at new research into a mostly small-time cybercrime practice that in the aggregate appears to have netted thieves the equivalent of billions of dollars over the past two years.
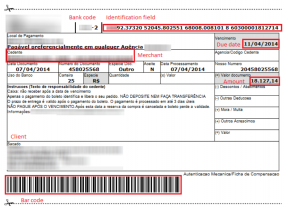
At issue is the “boleto” (officially “Boleto Bancario”), a popular payment method in Brazil that is used by consumers and for most business-to-business payments. Brazilians can use boletos to complete online purchases via their bank’s Web site, but unlike credit card payments — which can be disputed and reversed — payments made via boletos are not subject to chargebacks and can only be reverted by bank transfer.
Brazil has an extremely active and talented cybercrime underground, and increasingly Brazilian organized crime gangs are setting their sights on boleto users who bank online. This is typically done through malware that lies in wait until the user of the hacked PC visits their bank’s site and fills out the account information for the recipient of a boleto transaction. In this scenario, the unwitting victim submits the transfer for payment and the malware modifies the request by substituting a recipient account that the attackers control.
Many of the hijacked boleto transactions are low-dollar amounts, but in the aggregate these purloined payments can generate an impressive income stream for even a small malware gang. On Tuesday, for example, a source forwarded me a link to a Web-based control panel for a boleto-thieving botnet (see screenshot below); in this operation, we can see that the thieves had hijacked some 383 boleto transactions between February 2014 and the end of June, but had stolen the equivalent of nearly USD $250,000 during that time.
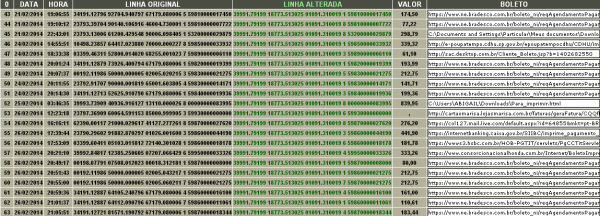
The records kept by a boleto-stealing botnet. Next to the date and time is the account of the intended recipient of the transfer; the “linha alterada” column shows the accounts used by the thieves to accept diverted payments. “Valor” refers to the amount, expressed in Brazilian Real.
But a recent discovery by researchers at RSA, the security division of EMC, exposes far more lucrative and ambitious boleto banditry. RSA says the fraud ring it is tracking — known as the “Bolware” operation — affects more than 30 different banks in Brazil, and may be responsible for up to $3.75 billion USD in losses. RSA arrived at this estimate based on the discovery of a similar botnet control panel that tracked nearly a half-million fraudulent transactions. Continue reading