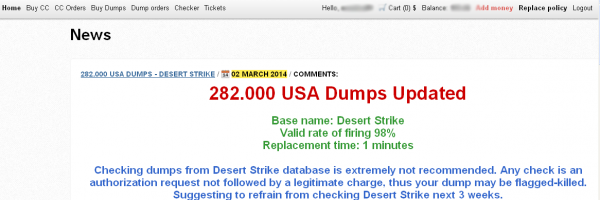
Last week’s story about steeply falling prices on credit and debit card data stolen from Target mentioned several reasons why many banks may not have already reissued all of their cards impacted by the breach. But it left out one other key reason: A huge backlog of orders at companies that manufacture credit and debit cards on behalf of financial institutions.
 Turns out, while the crooks responsible for monetizing the Target breach seem to have had little trouble counterfeiting stolen cards, the process by which banks obtain legitimate replacement cards for their customers is not always quite so speedy.
Turns out, while the crooks responsible for monetizing the Target breach seem to have had little trouble counterfeiting stolen cards, the process by which banks obtain legitimate replacement cards for their customers is not always quite so speedy.
I recently spoke with a gentleman who heads up security at a small federal credit union, and this individual said his institution ended up printing their own cards in-house after being told by their financial services provider that their order for some 2,000 new customer cards compromised in the Target breach would have to get behind a backlog of more than 2 million existing orders from other banks.
The credit union in question issues Visa-branded cards to its customers, but the actual physical cards are produced by Fiserv, a Brookfield, Wisc. financial services firm that also handles the online banking portals for a huge number of small to mid-sized financial institutions nationwide. In addition to servicing this credit union, Fiserv also prints cards for some of the biggest banks in the world, including Bank of America and Chase.
Shortly after the holidays, the credit union began alerting affected customers, notifying them that the institution would soon be reissuing cards. But when it actually went to place the order for the new cards, the institution was told it would have to get in line.
“They informed us that there was a backlog of 2 million cards, and said basically, ‘We’ll get to you when we get to you’,” the credit union source told KrebsOnSecurity.
Murray Walton, chief risk officer at Fiserv, acknowledged that the company has experienced extraordinarily high demand for new cards in the wake of the Target breach, but that Fiserv is quickly whittling down its existing backlog of orders.
“A large breach injects additional demand into a system that is already operating at near-peak capacity at year-end,” Walton said. “As a result, producers face the challenge of juggling existing contractual commitments with this incremental demand, and turn to mandatory overtime and staff augmentation to get the most out of their equipment and infrastructure. We believe we are managing this situation as well as possible, and are beginning to see our cycle times (order to delivery) diminish compared to a few weeks ago. Meanwhile, we note that fraud prevention is a multi-faceted challenge, and card reissue is only one arrow in the quiver. Alert consumers and behind-the-scenes fraud management programs are also essential.”
Faced with mounting customer service requests from account holders who’d been told to expect new cards, the credit union decided to take matters into its own hands.
“We have the capability to print out the cards ourselves at a local branch, so some of our software developers wrote some scripts to export the customer data and we had two people who ended up burning the midnight oil for several days making these cards by hand.”
 At issue is the “pingback” function, a feature built into WordPress and plenty of other CMS tools that is designed to notify (or ping) a site that you linked to their content. Unfortunately, like most things useful on the Web, the parasites and lowlifes of the world are turning pingbacks into a feature to be disabled, lest it be used to attack others.
At issue is the “pingback” function, a feature built into WordPress and plenty of other CMS tools that is designed to notify (or ping) a site that you linked to their content. Unfortunately, like most things useful on the Web, the parasites and lowlifes of the world are turning pingbacks into a feature to be disabled, lest it be used to attack others.