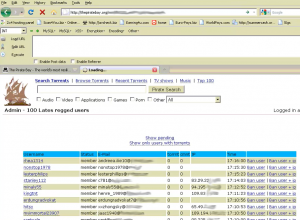
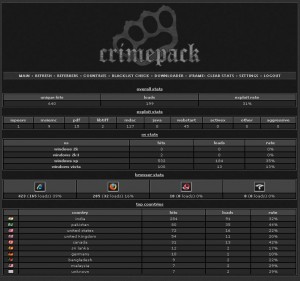
Security weaknesses in the hugely popular file-sharing Web site thepiratebay.org have exposed the user names, e-mail and Internet addresses of more than 4 million Pirate Bay users, according to information obtained by KrebsOnSecurity.com.
An Argentinian hacker named Ch Russo said he and two of his associates discovered multiple SQL injection vulnerabilities that let them into the user database for the site. Armed with this access, the hackers had the ability to create, delete, modify or view all user information, including the number and name of file trackers or torrents uploaded by users.
Russo maintains that at no time did he or his associates alter or delete information in The Pirate Bay database. But he acknowledges that they did briefly consider how much this access and information would be worth to anti-piracy companies employed by entertainment industry lobbying groups like the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) and the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA), each of which has assiduously sought to sink The Pirate Bay on grounds that the network facilitates copyright infringement.
That effort has largely failed, but both industries have been busy suing individual music and movie downloaders for alleged copyright violations, often obtaining substantial monetary damages when defendants settled the charges out of court. In almost every case, the entertainment industry learned the identities of file-sharing users by subpoenaing subscriber information from Internet service providers based on the user’s Internet address.
“Probably these groups would be very interested in this information, but we are not [trying] to sell it,” Russo told KrebsOnSecurity.com in a phone interview. “Instead we wanted to tell people that their information may not be so well protected.”