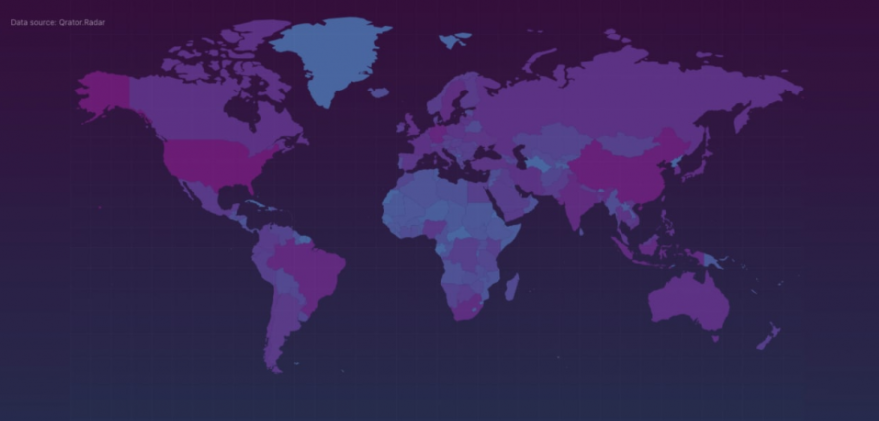
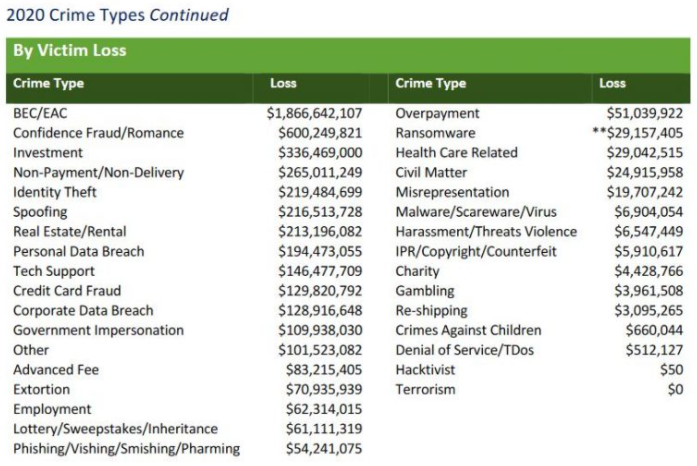
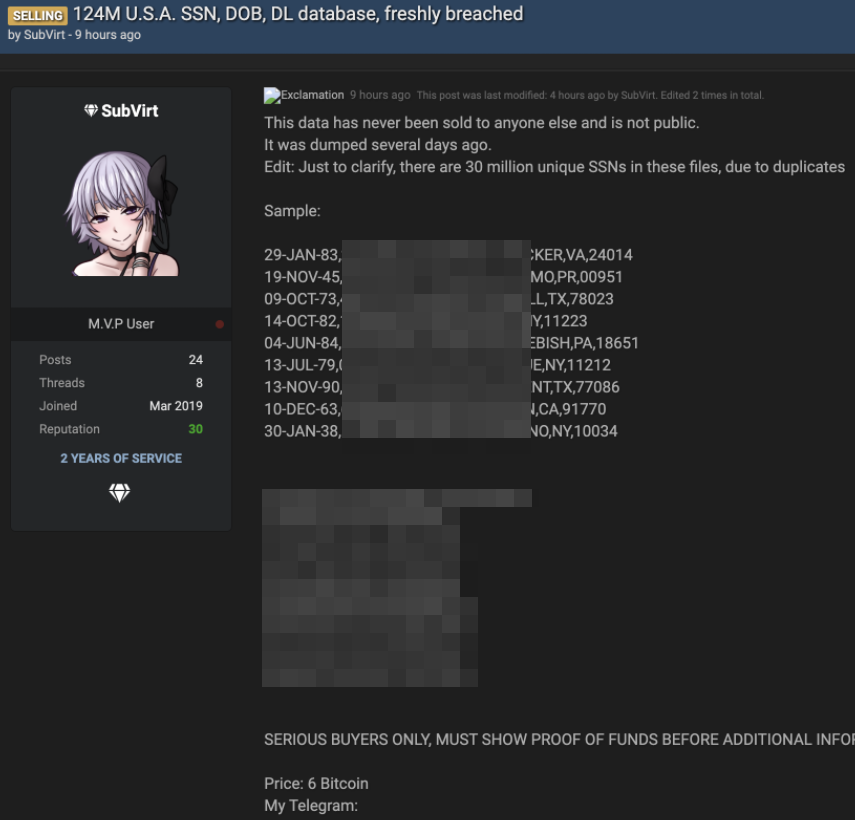
In May 2015, KrebsOnSecurity briefly profiled “The Manipulaters,” the name chosen by a prolific cybercrime group based in Pakistan that was very publicly selling spam tools and a range of services for crafting, hosting and deploying malicious email. Six years later, a review of the social media postings from this group shows they are prospering, while rather poorly hiding their activities behind a software development firm in Lahore that has secretly enabled an entire generation of spammers and scammers.
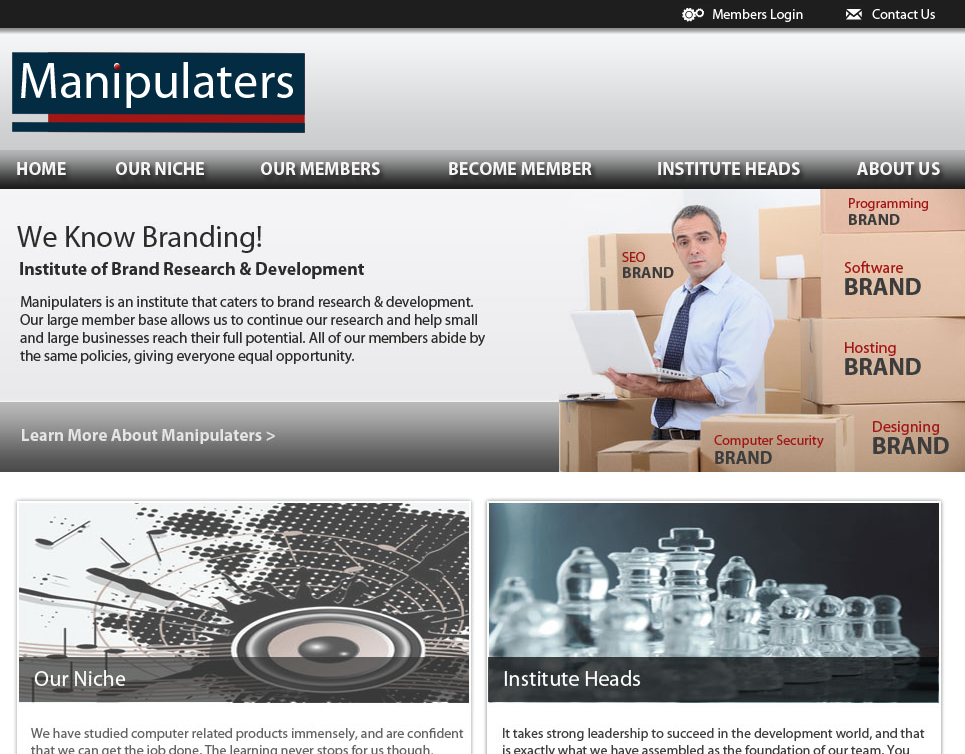
The Web site in 2015 for the “Manipulaters Team,” a group of Pakistani hackers behind the dark web identity “Saim Raza,” who sells spam and malware tools and services.
The Manipulaters’ core brand in the underground is a shared cybercriminal identity named “Saim Raza,” who for the past decade across dozens of cybercrime sites and forums has peddled a popular spamming and phishing service variously called “Fudtools,” “Fudpage,” “Fudsender,” etc.
The common acronym in nearly all of Saim Raza’s domains over the years — “FUD” — stands for “Fully Un-Detectable,” and it refers to cybercrime resources that will evade detection by security tools like antivirus software or anti-spam appliances.
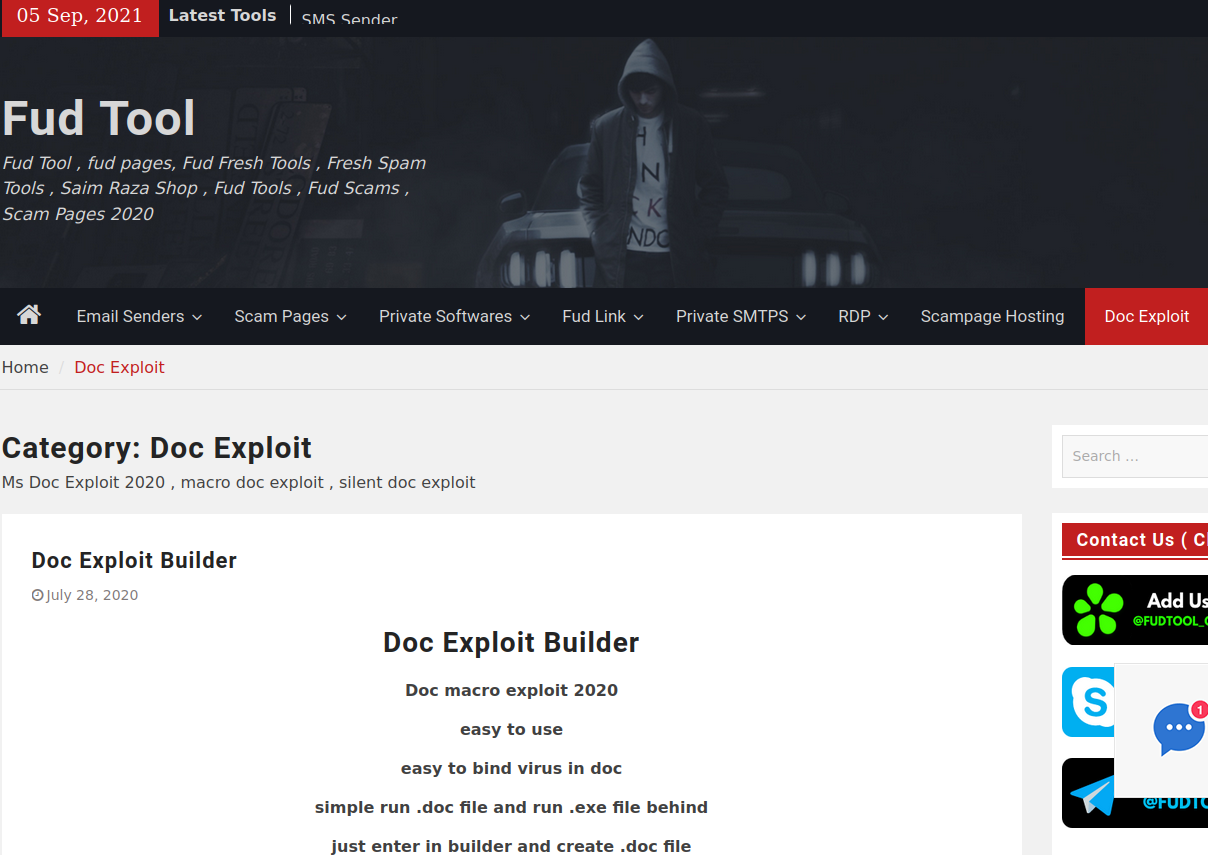
One of several current Fudtools sites run by The Manipulaters.
The current website for Saim Raza’s Fud Tools (above) offers phishing templates or “scam pages” for a variety of popular online sites like Office365 and Dropbox. They also sell “Doc Exploit” products that bundle malicious software with innocuous Microsoft Office documents; “scampage hosting” for phishing sites; a variety of spam blasting tools like HeartSender; and software designed to help spammers route their malicious email through compromised sites, accounts and services in the cloud.
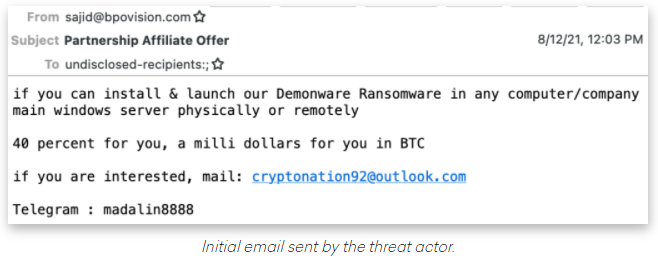
For years leading up to 2015, “admin@manipulaters.com” was the name on the registration records for thousands of scam domains that spoofed some of the world’s top banks and brand names, but particularly Apple and Microsoft. When confronted about this, The Manipulaters founder Madih-ullah Riaz replied, “We do not deliberately host or allow any phishing or any other abusive website. Regarding phishing, whenever we receive complaint, we remove the services immediately. Also we are running business since 2006.”

The IT network of The Manipulaters, circa 2013. Image: Facebook
Two years later, KrebsOnSecurity received an email from Riaz asking to have his name and that of his business partner removed from the 2015 story, saying it had hurt his company’s ability to maintain stable hosting for their stable of domains.
“We run web hosting business and due to your post we got very serious problems especially no data center was accepting us,” Riaz wrote in a May 2017 email. “I can see you post on hard time criminals we are not criminals, at least it was not in our knowledge.”
Riaz said the problem was his company’s billing system erroneously used The Manipulators’ name and contact information instead of its clients in WHOIS registration records. That oversight, he said, caused many researchers to erroneously attribute to them activity that was coming from just a few bad customers.
“We work hard to earn money and it is my request, 2 years of my name in your wonderful article is enough punishment and we learned from our mistakes,” he concluded.
The Manipulaters have indeed learned a few new tricks, but keeping their underground operations air-gapped from their real-life identities is mercifully not one of them.
ZERO OPERATIONAL SECURITY
Phishing domain names registered to The Manipulaters included an address in Karachi, with the phone number 923218912562. That same phone number is shared in the WHOIS records for 4,000+ domains registered through domainprovider[.]work, a domain controlled by The Manipulaters that appears to be a reseller of another domain name provider.
One of Saim Raza’s many ads in the cybercrime underground for his Fudtools service promotes the domain fudpage[.]com, and the WHOIS records for that domain share the same Karachi phone number. Fudpage’s WHOIS records list the contact as “admin@apexgrand.com,” which is another email address used by The Manipulaters to register domains.
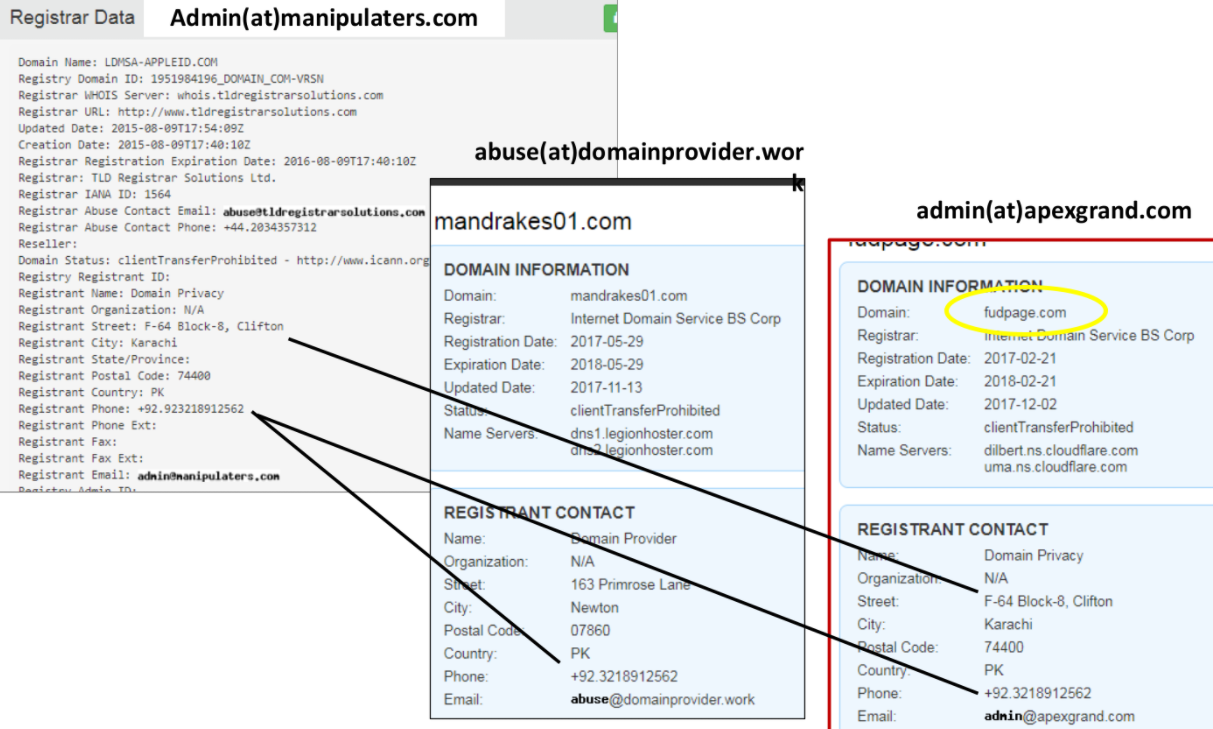
As I noted in 2015, The Manipulaters Team used domain name service (DNS) settings from another blatantly fraudulent service called ‘FreshSpamTools[.]eu,’ which was offered by a fellow Pakistani who also conveniently sold phishing toolkits targeting a number of big banks.
The WHOIS records for FreshSpamTools briefly list the email address bilal.waddaich@gmail.com, which corresponds to the email address for a Facebook account of a Bilal “Sunny” Ahmad Warraich (a.k.a. Bilal Waddaich).
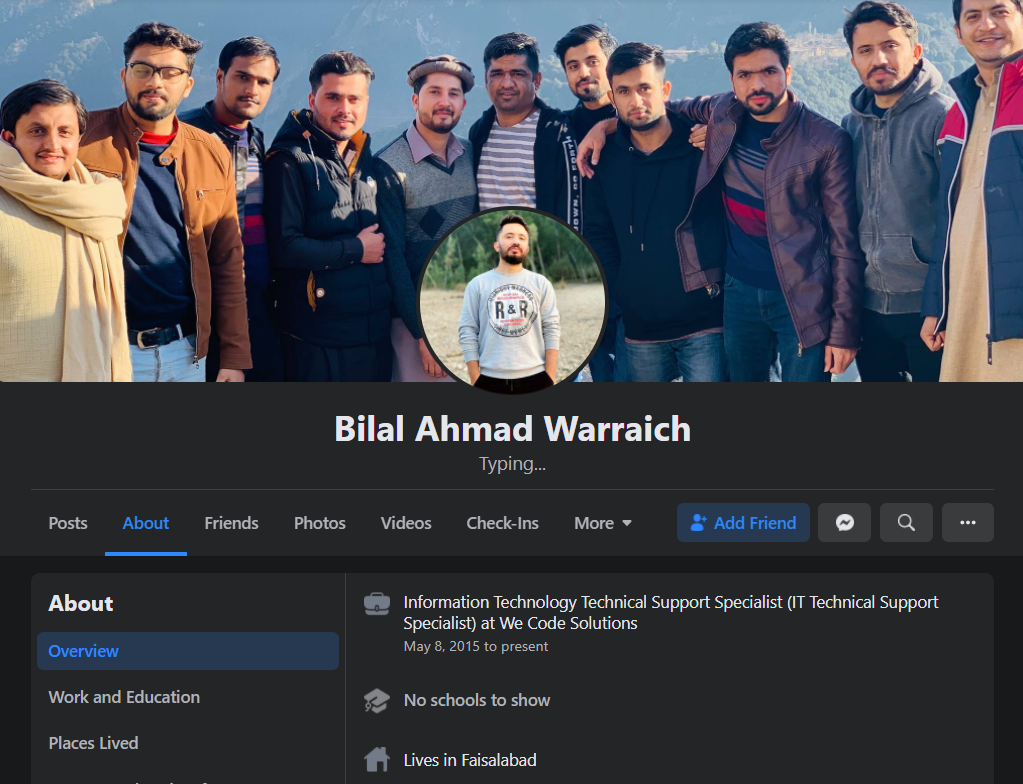
Bilal Waddaich’s current Facebook profile photo includes many current and former employees of We Code Solutions.
Warraich’s Facebook profile says he works as an IT support specialist at a software development company in Lahore called We Code Solutions.
The We Code Solutions website.
A review of the hosting records for the company’s website wecodesolutions[.]pk show that over the past three years it has shared a server with just a handful of other domains, including:
-saimraza[.]tools
-fud[.]tools
-heartsender[.]net
-fudspampage[.]com
-fudteam[.]com
-autoshopscript[.]com
-wecodebilling[.]com
-antibotspanel[.]com
-sellonline[.]tools
FUD CO
The profile image atop Warraich’s Facebook page is a group photo of current and former We Code Solutions employees. Helpfully, many of the faces in that photo have been tagged and associated with their respective Facebook profiles.
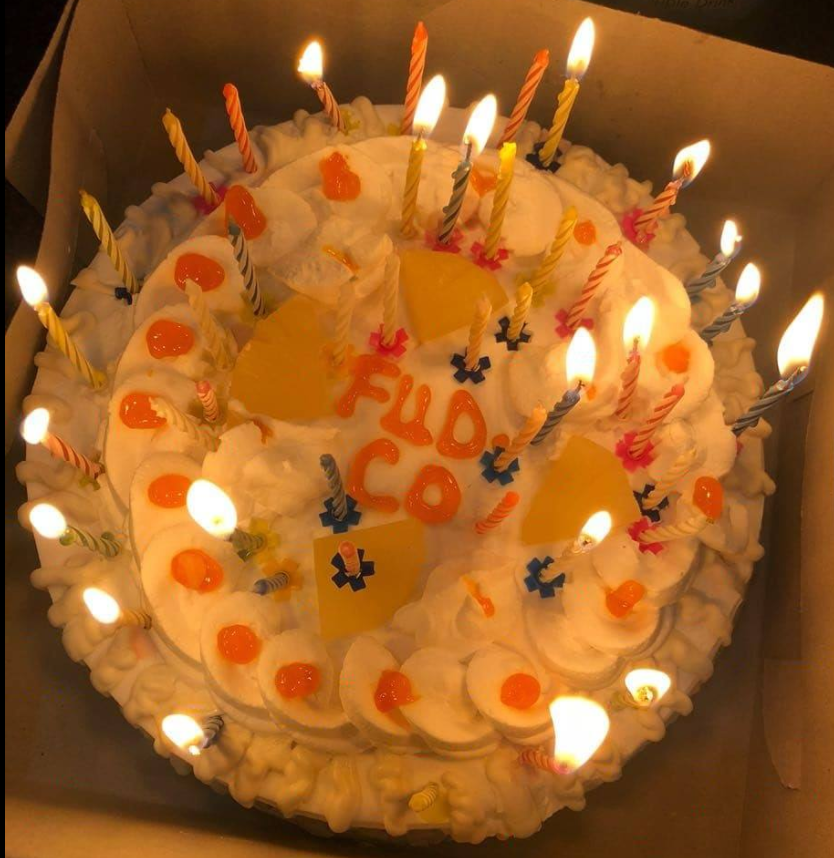
For example, the Facebook profile of Burhan Ul Haq, a.k.a. “Burhan Shaxx” says he works in human relations and IT support for We Code Solutions. Scanning through Ul Haq’s endless selfies on Facebook, it’s impossible to ignore a series of photos featuring various birthday cakes and the words “Fud Co” written in icing on top.
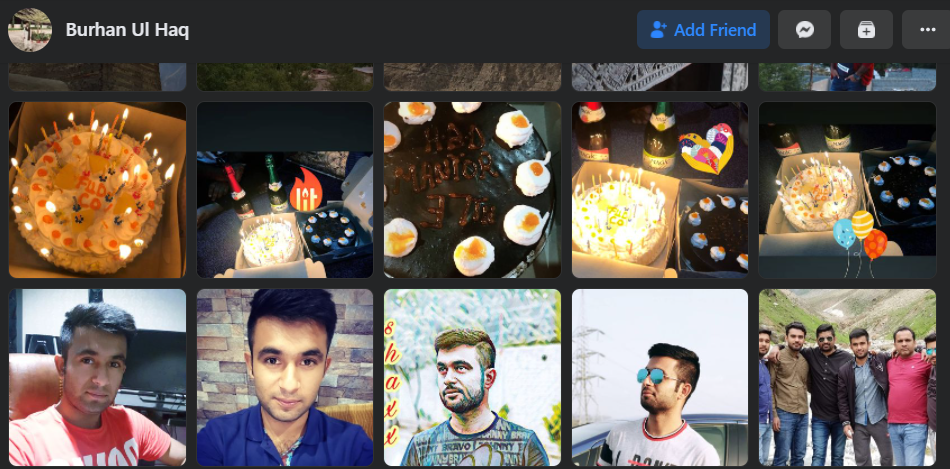
Burhan Ul Haq’s photos show many Fud Co-themed cakes the We Code Solutions employees enjoyed on the anniversary of the Manipulaters Team.
Yes, from a review of the Facebook postings of We Code Solutions employees, it appears that for at least the last five years this group has celebrated an anniversary every May with a Fud Co cake, non-alcoholic sparkling wine, and a Fud Co party or group dinner. Let’s take a closer look at that delicious cake:
 Continue reading →
Continue reading →