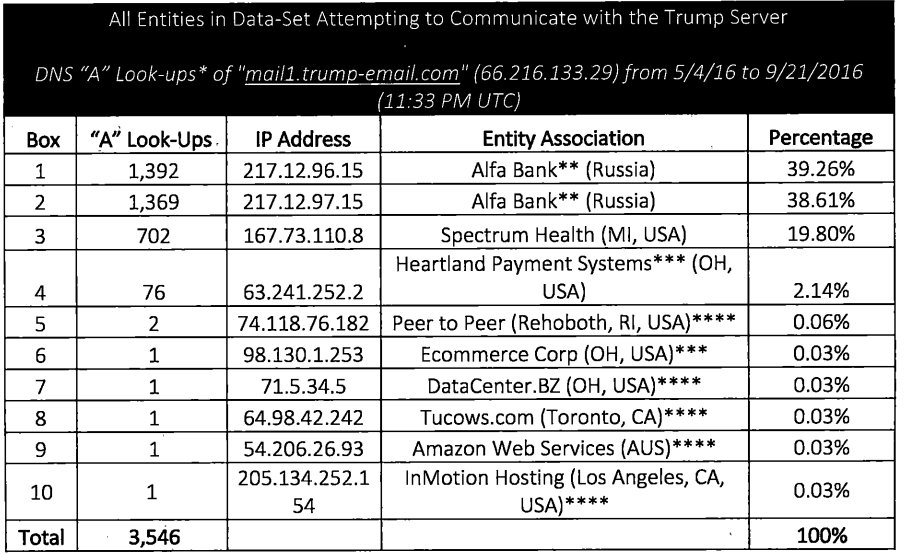
A recent phishing campaign targeting Coinbase users shows thieves are getting smarter about phishing one-time passwords (OTPs) needed to complete the login process. It also shows that phishers are attempting to sign up for new Coinbase accounts by the millions as part of an effort to identify email addresses that are already associated with active accounts.
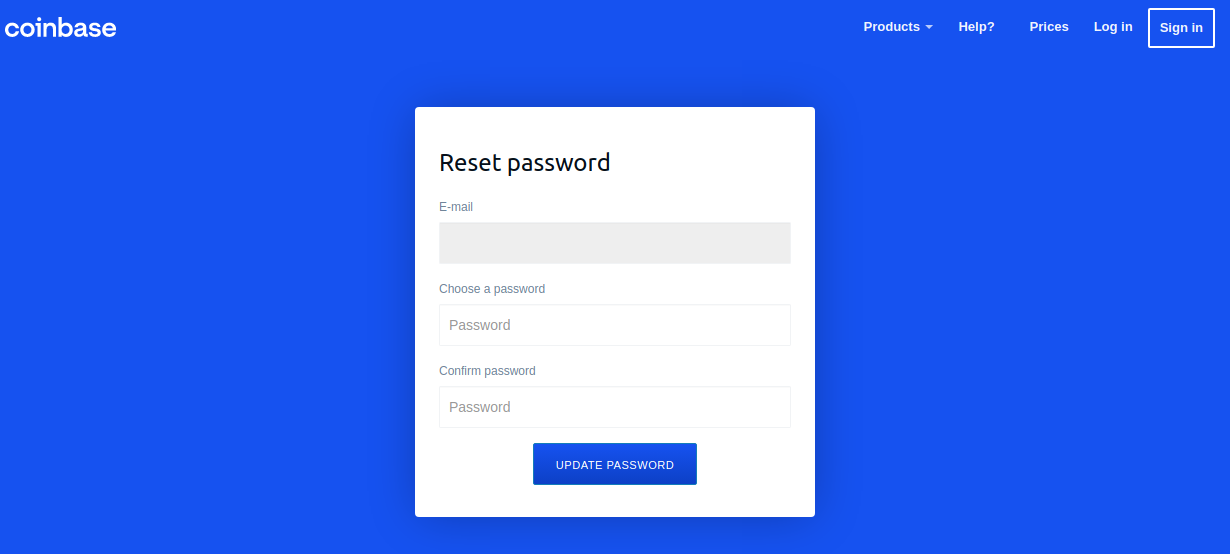
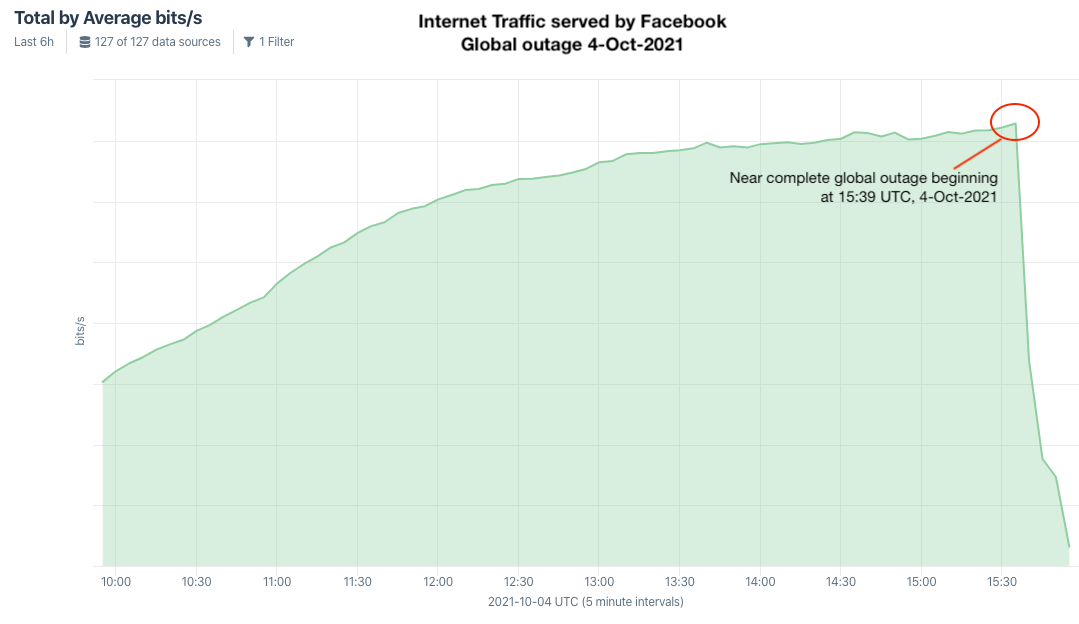
A Google-translated version of the now-defunct Coinbase phishing site, coinbase.com.password-reset[.]com
Coinbase is the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency exchange, with roughly 68 million users from over 100 countries. The now-defunct phishing domain at issue — coinbase.com.password-reset[.]com — was targeting Italian Coinbase users (the site’s default language was Italian). And it was fairly successful, according to Alex Holden, founder of Milwaukee-based cybersecurity firm Hold Security.
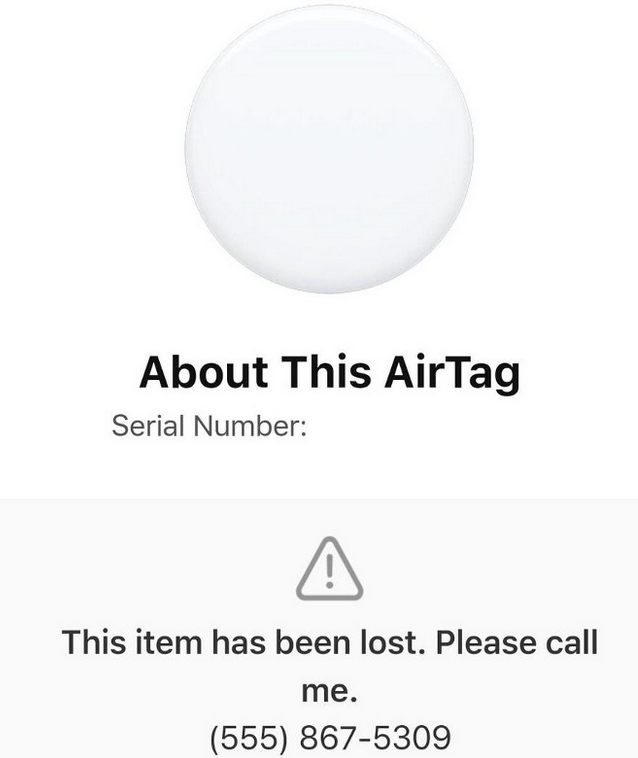
Holden’s team managed to peer inside some poorly hidden file directories associated with that phishing site, including its administration page. That panel, pictured in the redacted screenshot below, indicated the phishing attacks netted at least 870 sets of credentials before the site was taken offline.
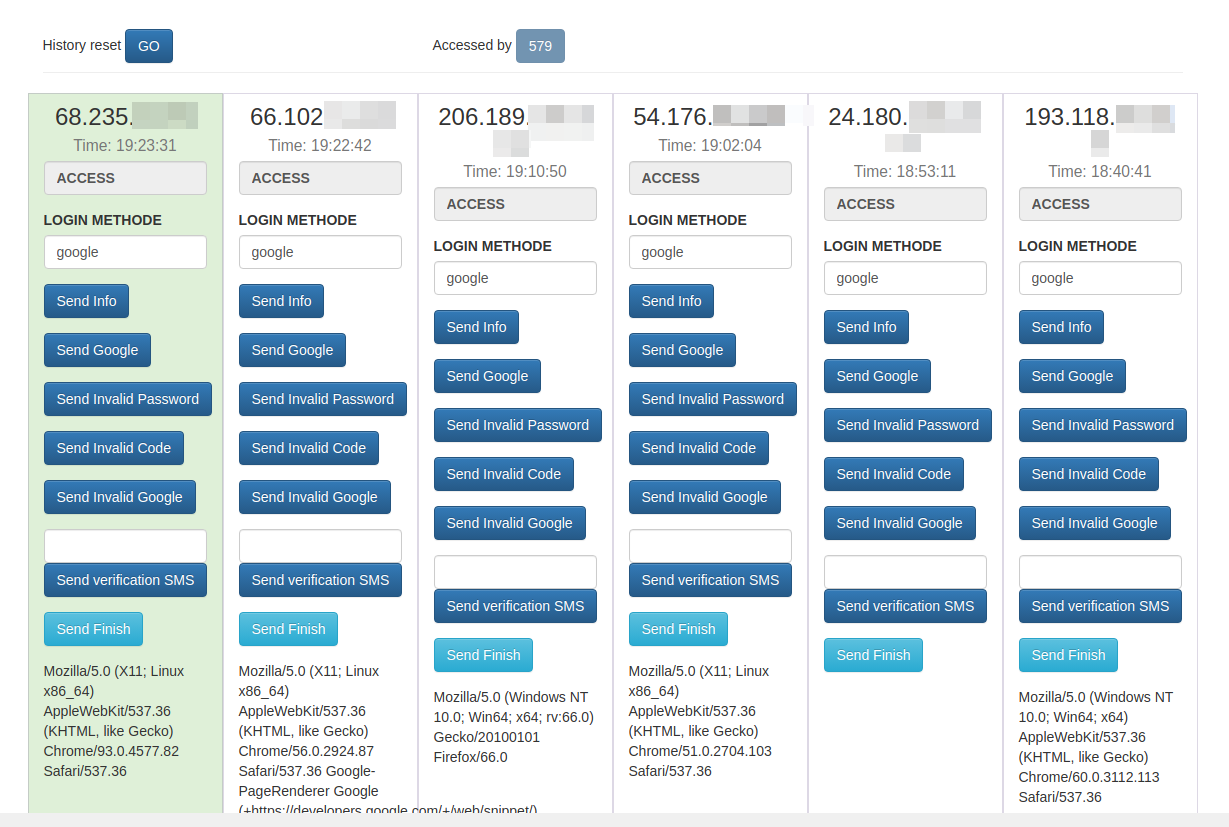
The Coinbase phishing panel.
Holden said each time a new victim submitted credentials at the Coinbase phishing site, the administrative panel would make a loud “ding” — presumably to alert whoever was at the keyboard on the other end of this phishing scam that they had a live one on the hook.
In each case, the phishers manually would push a button that caused the phishing site to ask visitors for more information, such as the one-time password from their mobile app.
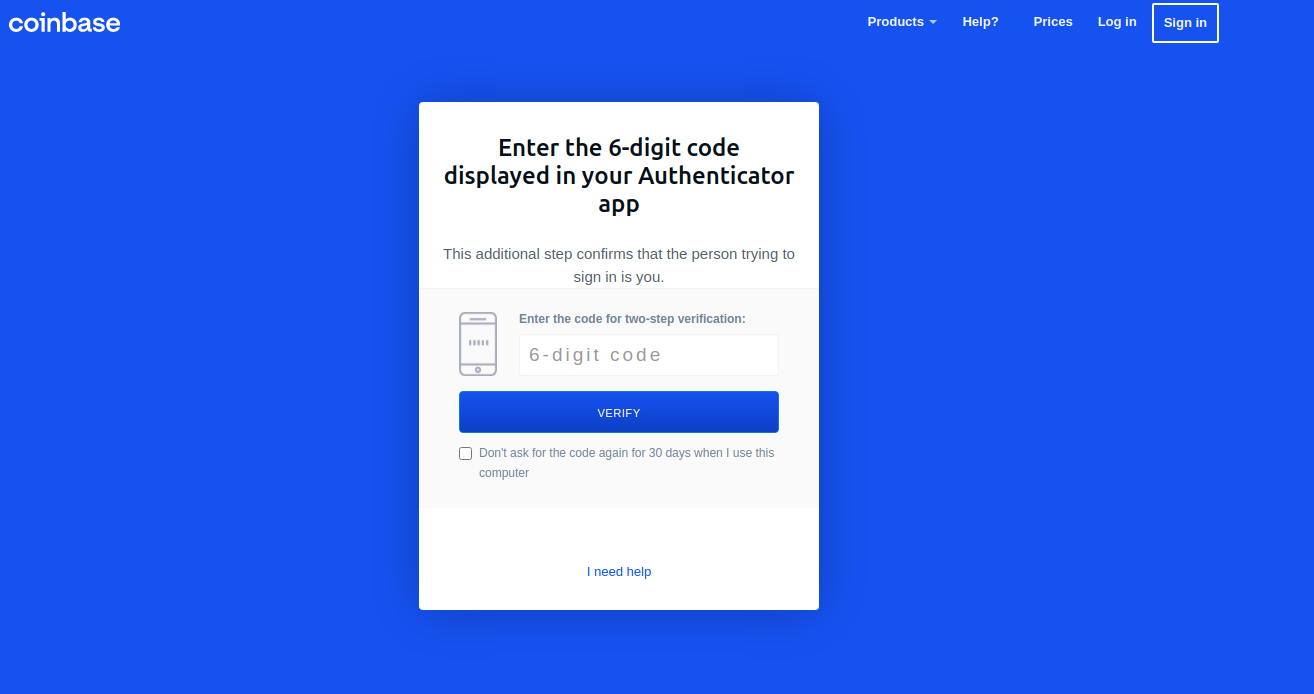
“These guys have real-time capabilities of soliciting any input from the victim they need to get into their Coinbase account,” Holden said.
Pressing the “Send Info” button prompted visitors to supply additional personal information, including their name, date of birth, and street address. Armed with the target’s mobile number, they could also click “Send verification SMS” with a text message prompting them to text back a one-time code.
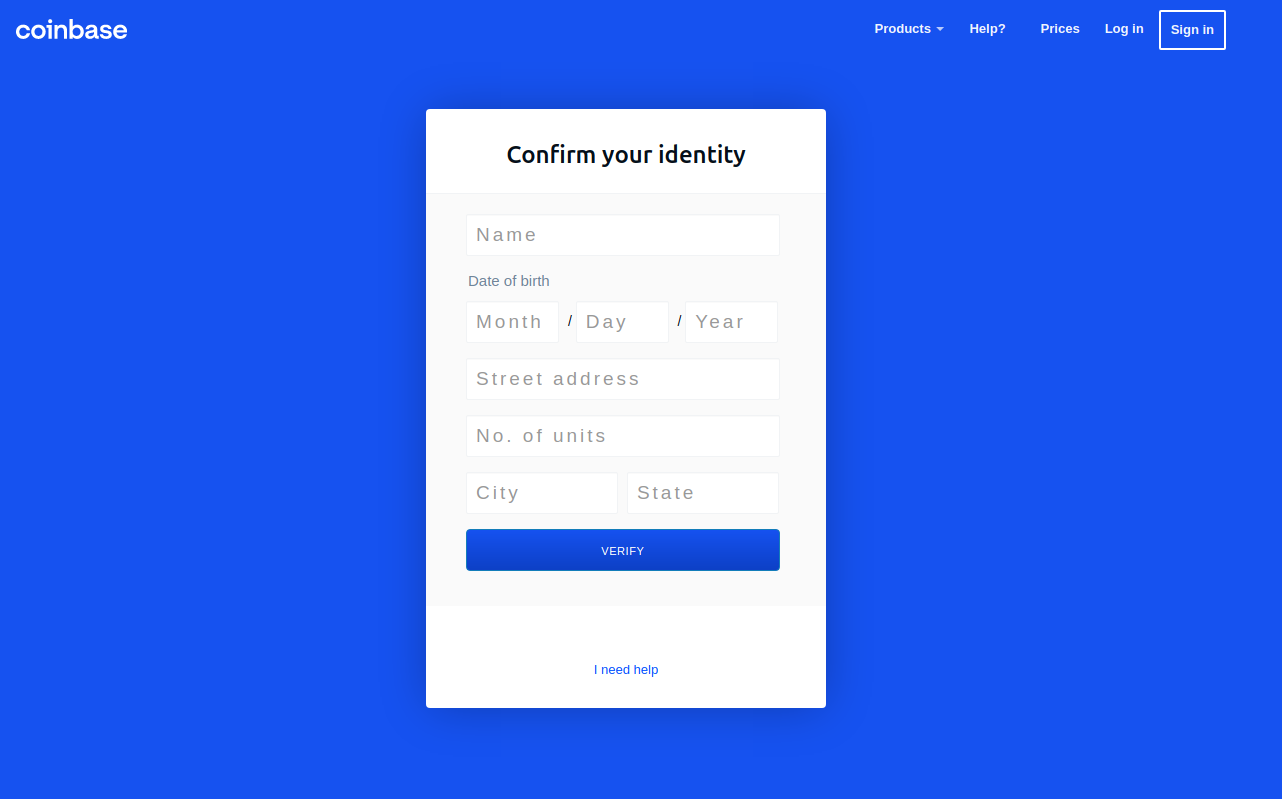
SIFTING COINBASE FOR ACTIVE USERS
Holden said the phishing group appears to have identified Italian Coinbase users by attempting to sign up new accounts under the email addresses of more than 2.5 million Italians. His team also managed to recover the username and password data that victims submitted to the site, and virtually all of the submitted email addresses ended in “.it”.
But the phishers in this case likely weren’t interested in registering any accounts. Rather, the bad guys understood that any attempts to sign up using an email address tied to an existing Coinbase account would fail. After doing that several million times, the phishers would then take the email addresses that failed new account signups and target them with Coinbase-themed phishing emails.
Holden’s data shows this phishing gang conducted hundreds of thousands of halfhearted account signup attempts daily. For example, on Oct. 10 the scammers checked more than 216,000 email addresses against Coinbase’s systems. The following day, they attempted to register 174,000 new Coinbase accounts. Continue reading