The latest Jan. 6 committee hearing on Tuesday examined the role of conspiracy theory communities like 8kun[.]top and TheDonald[.]win in helping to organize and galvanize supporters who responded to former President Trump’s invitation to “be wild” in Washington, D.C. on that chaotic day. At the same time the committee was hearing video testimony from 8kun founder Jim Watkins, 8kun and a slew of similar websites were suddenly yanked offline. Watkins suggested the outage was somehow related to the work of the committee, but the truth is KrebsOnSecurity was responsible and the timing was pure coincidence.

In a follow-up video address to his followers, Watkins said the outage happened shortly after the Jan. 6 committee aired his brief video testimony.
“Then everything that I have anything to do with seemed to crash, so that there was no way for me to go out and talk to anybody,” Watkins said. “The whole network seemed to go offline at the same time, and that affected a lot of people.”
8kun and many other sites that continue to push the false narrative that the 2020 election was stolen from the 45th president have long been connected to the Internet via VanwaTech, a hosting firm based in Vancouver, Wash. In late October 2020, a phone call to VanwaTech’s sole provider of connectivity to the Internet resulted in a similar outage for 8kun.
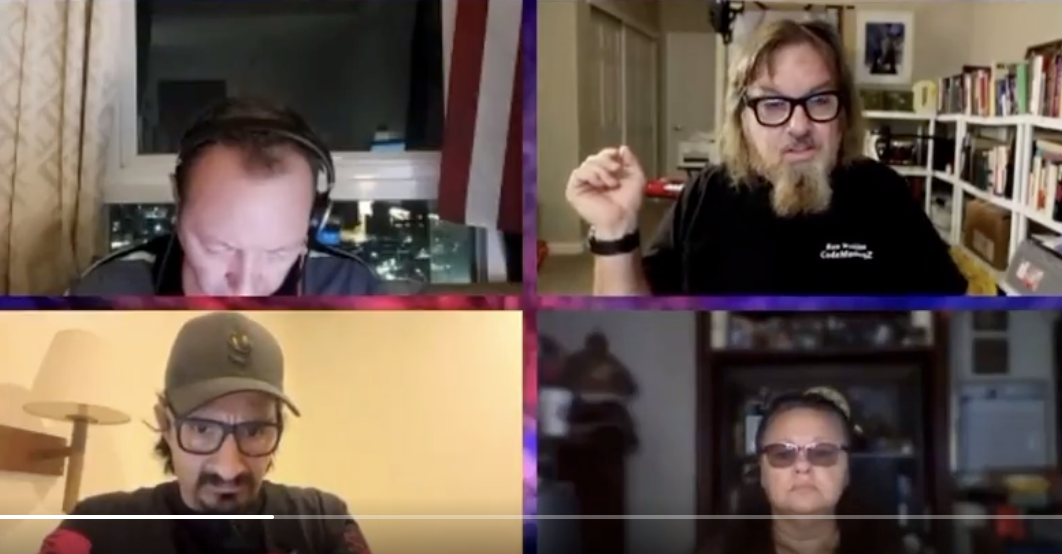
Jim Waktins (top right), in a video address to his followers on Tuesday after 8kun was taken offline.
Following that 2020 outage, 8kun and a large number of QAnon conspiracy sites found refuge in a Russian hosting provider. But when the anonymous “Q” leader of QAnon suddenly began posting on 8kun again earlier this month, KrebsOnSecurity received a tip that 8kun was once again connected to the larger Internet via a single upstream provider based in the United States.
On Sunday, July 10, KrebsOnSecurity contacted Psychz Networks, a hosting provider in Los Angeles, to see if they were aware that they were the sole Internet lifeline for 8kun et. al. Psychz confirmed that in response to a report from KrebsOnSecurity, VanwaTech was removed from its network around the time of the Jan. 6 hearing on Tuesday.
8kun and its archipelago of conspiracy theory communities have once again drifted back into the arms of a Russian hosting provider (AS207651), which is connected to the larger Internet via two providers. Those include AS31500 — which appears to be owned by Russians but is making a fair pretense at being located in the Caribbean; and AS28917, in Vilnius, Lithuania.
8kun’s newfound Russian connections will likely hold, but Lithuania may be a different story. Late last month, pro-Russian hackers claimed responsibility for an extensive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack against Lithuanian state and private websites, which reportedly was in response to Vilnius’s decision to cease the transit of some goods under European Union sanctions to Russia’s Kaliningrad exclave.
Many have speculated that Jim Watkins and/or his son Ron are in fact “Q,” the anonymous persona behind the QAnon conspiracy theory, which held that Former President Trump was secretly working to save the world from a satanic cult of pedophiles and cannibals.
8chan/8kun has been linked to white supremacism, neo-Nazism, antisemitism, multiple mass shootings, and is known for hosting child pornography. After three mass shootings in 2019 revealed the perpetrators had spread their manifestos on 8chan and even streamed their killings live there, 8chan was ostracized by one Internet provider after another.
In 2019, the FBI identified QAnon as a potential domestic terror threat, noting that some of its followers have been linked to violent incidents motivated by fringe beliefs.
The Jan. 6 hearing referenced in this story is available via CSPAN.