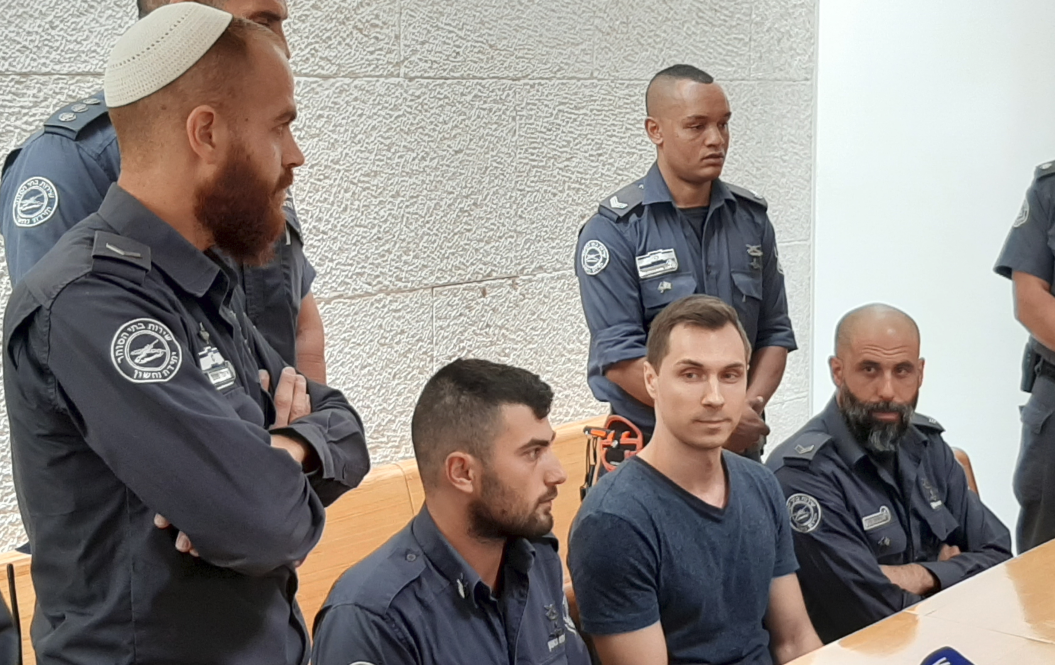
Aleksei Burkov, seated second from right, attends a hearing in Jerusalem in 2015. Image: Andrei Shirokov / Tass via Getty Images.
Aleksei Burkov, a cybercriminal who long operated two of Russia’s most exclusive underground hacking forums, was arrested in 2015 by Israeli authorities. The Russian government fought Burkov’s extradition to the U.S. for four years — even arresting and jailing an Israeli woman to force a prisoner swap. That effort failed: Burkov was sent to America, pleaded guilty, and was sentenced to nine years in prison. But a little more than a year later, he was quietly released and deported back to Russia. Now some Republican lawmakers are asking why a Russian hacker once described as “an asset of supreme importance” was allowed to shorten his stay.
A native of St. Petersburg, Russia, Burkov admitted to running CardPlanet, a site that sold more than 150,000 stolen credit card accounts, and to being a founder of DirectConnection — a closely guarded online community that attracted some of the world’s most-wanted Russian hackers.
But Burkov’s cybercriminal activities spanned far beyond mere credit card fraud. A 2019 deep dive into Burkov’s hacker alias “K0pa” revealed he also was co-administrator of the secretive Russian cybercrime forum “Mazafaka.” Like DirectConnection, Mazafaka’s member roster was a veritable “Who’s Who?” of the Russian hacker underground, and K0pa played a key role in vetting new members and settling disputes for both communities.
K0pa’s elevated status in the Russian cybercrime community made him one of the most connected malicious hackers ever apprehended by U.S. authorities. As I wrote at the time of Burkov’s extradition, the Kremlin was probably concerned that he simply knew too much about Russia’s propensity to outsource certain activities to its criminal hacker community.
“To my knowledge, no one has accused Burkov of being some kind of cybercrime fixer or virtual badguy Rolodex for the Russian government,” KrebsOnSecurity wrote in 2019. “On the other hand, from his onetime lofty perch atop some of the most exclusive Russian cybercrime forums, K0pa certainly would have fit that role nicely.”
Burkov was arrested in December 2015 on an international warrant while visiting Israel, and over the ensuing four years the Russian government aggressively sought to keep him from being extradited to the United States.
When Israeli authorities turned down requests to send him back to Russia — supposedly to face separate hacking charges there — the Russians imprisoned Israeli citizen Naama Issachar on trumped-up drug charges in a bid to trade prisoners. Nevertheless, Burkov was extradited to the United States in November 2019.
And if there were any doubts Issachar was jailed for use as a political pawn, Russian President Vladimir Putin erased those by pardoning her in January 2020, just hours after Burkov pleaded guilty in the United States.
In June 2020, Burkov was sentenced to nine years in prison. But a little more than a year later — Aug. 25, 2021 — Burkov was released and deported back to Russia. According to a letter (PDF) sent Monday by four Republican House lawmakers to White House National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan, U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) officials escorted Burkov onto a plane destined for Moscow shortly after his release. Continue reading