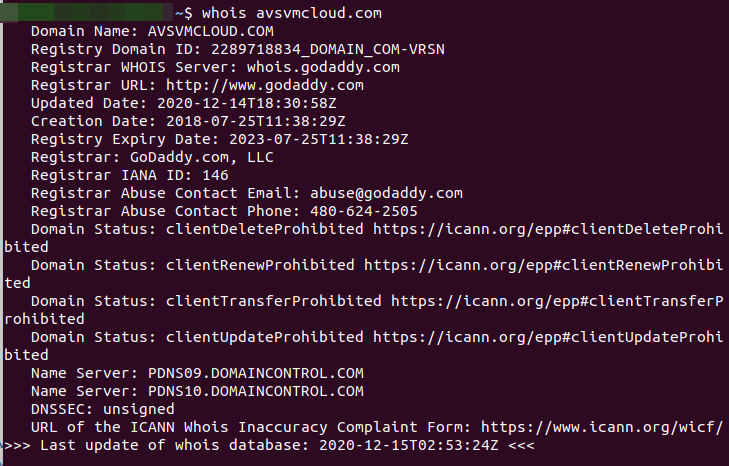
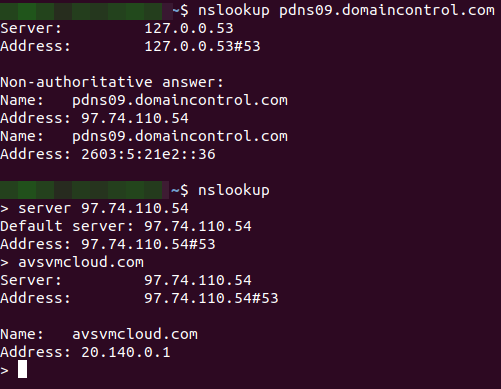
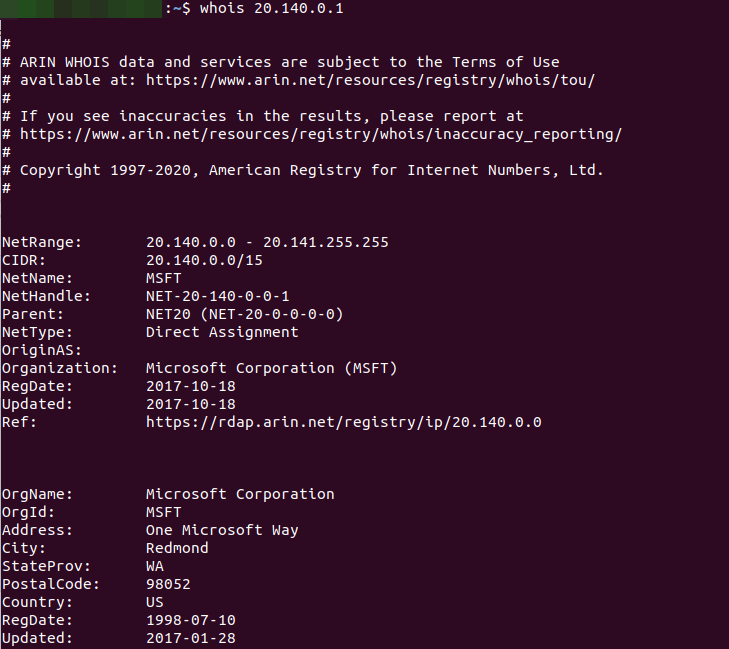
U.S. government cybersecurity agencies warned this week that the attackers behind the widespread hacking spree stemming from the compromise at network software firm SolarWinds used weaknesses in other, non-SolarWinds products to attack high-value targets. According to sources, among those was a flaw in software virtualization platform VMware, which the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) warned on Dec. 7 was being used by Russian hackers to impersonate authorized users on victim networks.
On Dec. 7, 2020, the NSA said “Russian state-sponsored malicious cyber actors are exploiting a vulnerability in VMware Access and VMware Identity Manager products, allowing the actors access to protected data and abusing federated authentication.”

VMware released a software update to plug the security hole (CVE-2020-4006) on Dec. 3, and said it learned about the flaw from the NSA.
The NSA advisory (PDF) came less than 24 hours before cyber incident response firm FireEye said it discovered attackers had broken into its networks and stolen more than 300 proprietary software tools the company developed to help customers secure their networks.
On Dec. 13, FireEye disclosed that the incident was the result of the SolarWinds compromise, which involved malicious code being surreptitiously inserted into updates shipped by SolarWinds for users of its Orion network management software as far back as March 2020.
In its advisory on the VMware vulnerability, the NSA urged patching it “as soon as possible,” specifically encouraging the National Security System, Department of Defense, and defense contractors to make doing so a high priority.
The NSA said that in order to exploit this particular flaw, hackers would already need to have access to a vulnerable VMware device’s management interface — i.e., they would need to be on the target’s internal network (provided the vulnerable VMware interface was not accessible from the Internet). However, the SolarWinds compromise would have provided that internal access nicely.
In response to questions from KrebsOnSecurity, VMware said it has “received no notification or indication that the CVE 2020-4006 was used in conjunction with the SolarWinds supply chain compromise.”
VMware added that while some of its own networks used the vulnerable SolarWinds Orion software, an investigation has so far revealed no evidence of exploitation.
“While we have identified limited instances of the vulnerable SolarWinds Orion software in our environment, our own internal investigation has not revealed any indication of exploitation,” the company said in a statement. “This has also been confirmed by SolarWinds own investigations to date.”
On Dec. 17, DHS’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) released a sobering alert on the SolarWinds attack, noting that CISA had evidence of additional access vectors other than the SolarWinds Orion platform.
CISA’s advisory specifically noted that “one of the principal ways the adversary is accomplishing this objective is by compromising the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) signing certificate using their escalated Active Directory privileges. Once this is accomplished, the adversary creates unauthorized but valid tokens and presents them to services that trust SAML tokens from the environment. These tokens can then be used to access resources in hosted environments, such as email, for data exfiltration via authorized application programming interfaces (APIs).”
Indeed, the NSA’s Dec. 7 advisory said the hacking activity it saw involving the VMware vulnerability “led to the installation of a web shell and follow-on malicious activity where credentials in the form of SAML authentication assertions were generated and sent to Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), which in turn granted the actors access to protected data.”
Also on Dec. 17, the NSA released a far more detailed advisory explaining how it has seen the VMware vulnerability being used to forge SAML tokens, this time specifically referencing the SolarWinds compromise.
Asked about the potential connection, the NSA said only that “if malicious cyber actors gain initial access to networks through the SolarWinds compromise, the TTPs [tactics, techniques and procedures] noted in our December 17 advisory may be used to forge credentials and maintain persistent access.”
“Our guidance in this advisory helps detect and mitigate against this, no matter the initial access method,” the NSA said.
Continue reading →






 Like so many Q drops, Queequeg’s tattoos tell a mysterious tale, but we never quite learn what that full story is. Indeed, the artist who etched them into Queequeg’s body is long dead, and the cannibal himself can’t seem to explain what it all means.
Like so many Q drops, Queequeg’s tattoos tell a mysterious tale, but we never quite learn what that full story is. Indeed, the artist who etched them into Queequeg’s body is long dead, and the cannibal himself can’t seem to explain what it all means.
 With the ongoing disruption to life and livelihood wrought by the Covid-19 pandemic, 2020 has been a fairly horrid year by most accounts. And it’s perhaps fitting that this was also a leap year, piling on an extra day to a solar rotation that most of us probably can’t wait to see in the rearview mirror.
With the ongoing disruption to life and livelihood wrought by the Covid-19 pandemic, 2020 has been a fairly horrid year by most accounts. And it’s perhaps fitting that this was also a leap year, piling on an extra day to a solar rotation that most of us probably can’t wait to see in the rearview mirror.