An exhaustive inquiry published today by a consortium of investigative journalists says a three-part series KrebsOnSecurity published in 2015 on a Romanian ATM skimming gang operating in Mexico’s top tourist destinations disrupted their highly profitable business, which raked in an estimated $1.2 billion and enjoyed the protection of top Mexican authorities.
The multimedia investigation by the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) and several international journalism partners detailed the activities of the so-called Riviera Maya crime gang, allegedly a mafia-like group of Romanians who until very recently ran their own ATM company in Mexico called “Intacash” and installed sophisticated electronic card skimming devices inside at least 100 cash machines throughout Mexico.
According to the OCCRP, Riviera Maya’s skimming devices allowed thieves to clone the cards, which were used to withdraw funds from ATMs in other countries — often halfway around the world in places like India, Indonesia, and Taiwan.
Investigators say each skimmer captured on average 1,000 cards per month, siphoning about $200 from individual victim accounts. This allowed the crime gang to steal approximately $20 million monthly.
“The gang had little tricks,” OCCRP reporters recounted in their video documentary (above). “They would use the cards in different cities all over the globe and wait three months so banks would struggle to trace where the card had originally been cloned.”
In September 2015, I traveled to Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula to find and document almost two dozen ATMs in the region that were compromised with Bluetooth-based skimming devices. Unlike most skimmers — which can be detected by looking for out-of-place components attached to the exterior of a compromised cash machine — these skimmers were hooked to the internal electronics of ATMs operated by Intacash’s competitors by authorized personnel who’d reportedly been bribed or coerced by the gang.
But because the skimmers were Bluetooth-based, allowing thieves periodically to collect stolen data just by strolling up to a compromised machine with a mobile device, I was able to detect which ATMs had been hacked using nothing more than a cheap smart phone.
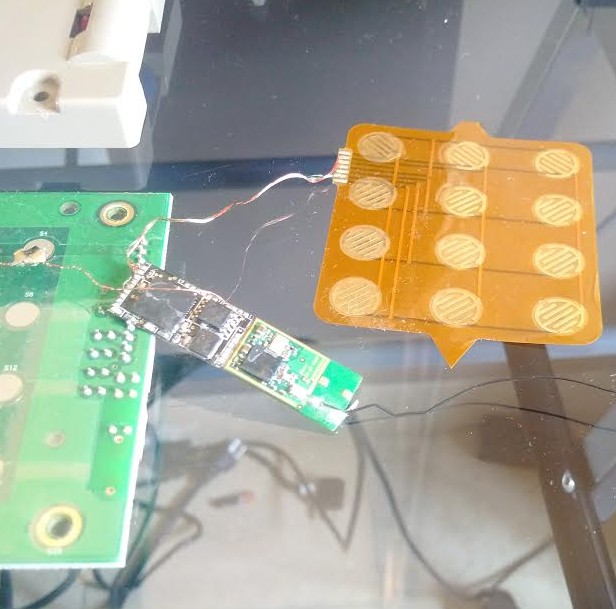
One of the Bluetooth-enabled PIN pads pulled from a compromised ATM in Mexico. The two components on the left are legitimate parts of the machine. The fake PIN pad made to be slipped under the legit PIN pad on the machine, is the orange bit, top right. The Bluetooth and data storage chips are in the middle.
Several days of wandering around Mexico’s top tourist areas uncovered these sophisticated skimmers inside ATMs in Cancun, Cozumel, Playa del Carmen and Tulum, including a compromised ATM in the lobby of my hotel in Cancun. OCCRP investigators said the gang also had installed the same skimmers in ATMs at tourist hotspots on the western coast of Mexico, in Puerto Vallarta, Sayulita and Tijuana.
Part III of my 2015 investigation concluded that Intacash was likely behind the scheme. An ATM industry source told KrebsOnSecurity at the time that his technicians had been approached by ATM installers affiliated with Intacash, offering those technicians many times their monthly salaries if they would provide periodic access to the machines they maintained.
The alleged leader of the Riviera Maya organization and principal owner of Intacash, 43-year-old Florian “The Shark” Tudor, is a Romanian with permanent residence in Mexico. Tudor claims he’s an innocent, legitimate businessman who’s been harassed and robbed by Mexican authorities.
Last year, police in Mexico arrested Tudor for illegal weapons possession, and raided his various properties there in connection with an investigation into the 2018 murder of his former bodyguard, Constantin Sorinel Marcu.
According to prosecution documents, Marcu and The Shark spotted my reporting shortly after it was published in 2015, and discussed what to do next on a messaging app:
The Shark: Krebsonsecurity.com See this. See the video and everything. There are two episodes. They made a telenovela.
Marcu: I see. It’s bad.
The Shark: They destroyed us. That’s it. Fuck his mother. Close everything.
The intercepted communications indicate The Shark also wanted revenge on whoever was responsible for leaking information about their operations.
The Shark: Tell them that I am going to kill them.
Marcu: Okay, I can kill them. Any time, any hour.
The Shark: They are checking all the machines. Even at banks. They found over 20.
Marcu: Whaaaat?!? They found? Already??











 May marks the third month in a row that Microsoft has pushed out fixes for more than 110 security flaws in its operating system and related software. At least 16 of the bugs are labeled “Critical,” meaning ne’er-do-wells can exploit them to install malware or seize remote control over vulnerable systems with little or no help from users.
May marks the third month in a row that Microsoft has pushed out fixes for more than 110 security flaws in its operating system and related software. At least 16 of the bugs are labeled “Critical,” meaning ne’er-do-wells can exploit them to install malware or seize remote control over vulnerable systems with little or no help from users.