Early in the afternoon on Friday, May, 3, I asked a friend to relay a message to his security contact at CCH, the cloud-based tax division of the global information services firm Wolters Kluwer in the Netherlands. The message was that the same file directories containing new versions of CCH’s software were open and writable by any anonymous user, and that there were suspicious files in those directories indicating some user(s) abused that access.
Shortly after that report, the CCH file directory for tax software downloads was taken offline. As of this publication, several readers have reported outages affecting multiple CCH Web sites. These same readers reported being unable to access their clients’ tax data in CCH’s cloud because of the ongoing outages. A Reddit thread is full of theories.
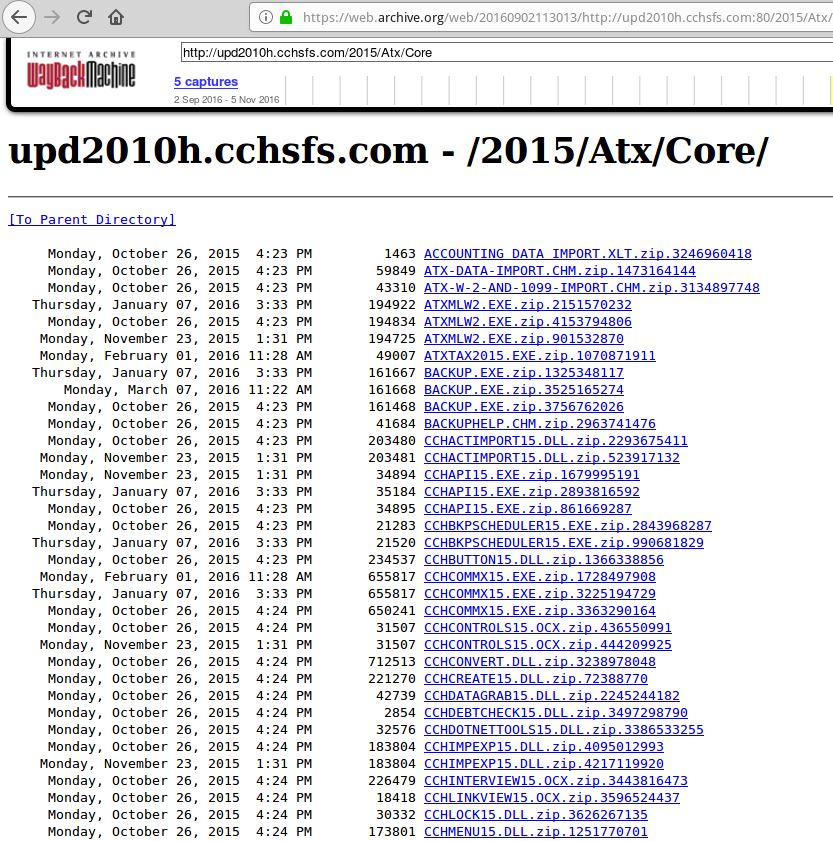
One of the many open and writable directories on CCH’s site before my report on Friday.
I do not have any information on whether my report about the world-writable file server had anything to do with the outages going on now at CCH. Nor did I see any evidence that any client data was exposed on the site.
What I did see in those CCH directories were a few odd PHP and text files, including one that seemed to be promoting two different and unrelated Russian language discussion forums.
I sent Wolters Kluwer an email asking how long the file server had been so promiscuous (allowing anyone to upload files to the server), and what the company was doing to validate the integrity of the software made available for download by CCH tax customers.
Marisa Westcott, vice president of marketing and communications at Wolters Kluwer, told KrebsOnSecurity on Friday that she would “check with the team to see if we can get some answers to your questions.”
But subsequent emails and phone calls have gone unreturned. Calls to the company’s main support number (800-739-9998) generate the voice message, “We are currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try your call again later.”
On Tuesday morning, Wolters Kluwer released an update on the extensive outage via Twitter, saying:
“Since yesterday, May 6, we are experiencing network and service interruptions affecting certain Wolters Kluwer platforms and applications. Out of an abundance of caution, we proactively took offline a number of other applications and we immediately began our investigation and remediation efforts. The secure use of our products and services is our top priority. we have ben able to restore network and services for a number – but not all — of our systems.”
Accounting Today reports today that a PR representative from Wolters Kluwer Tax & Accounting, which makes the CCH products, confirmed the outage was the result of a malware attack: Continue reading








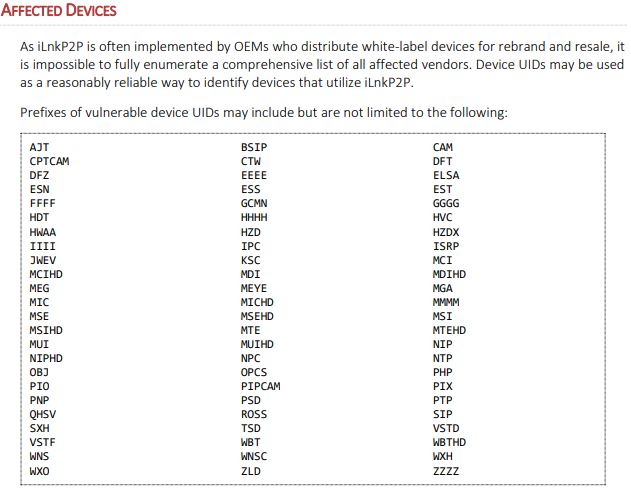
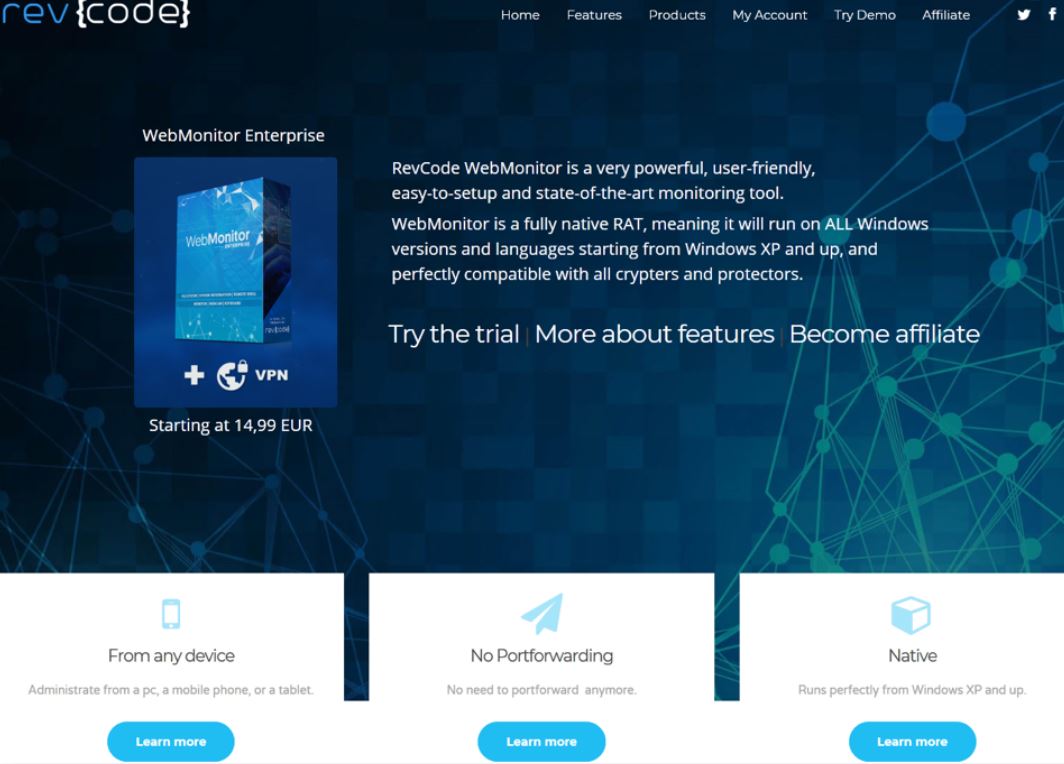
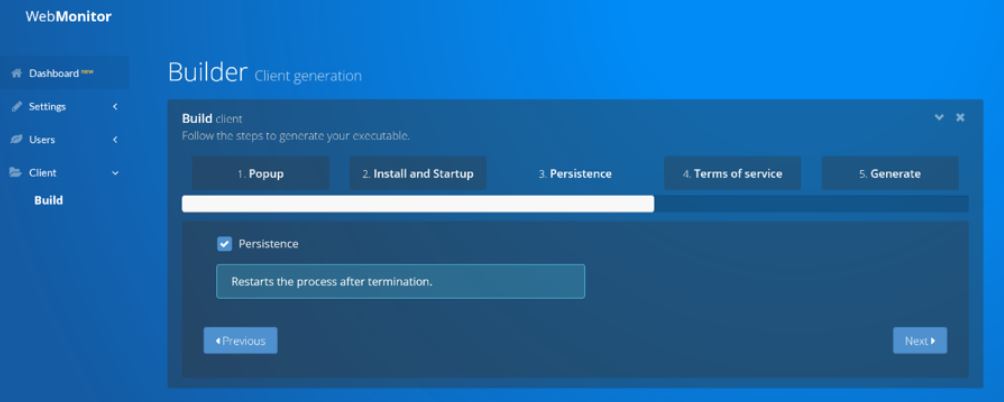


 And yet, here I am again writing the second story this week about a possibly serious security breach at an Indian company that provides IT support and outsourcing for a ridiculous number of major U.S. corporations (spoiler alert: the second half of this story actually contains quite a bit of news about the breach investigation).
And yet, here I am again writing the second story this week about a possibly serious security breach at an Indian company that provides IT support and outsourcing for a ridiculous number of major U.S. corporations (spoiler alert: the second half of this story actually contains quite a bit of news about the breach investigation).