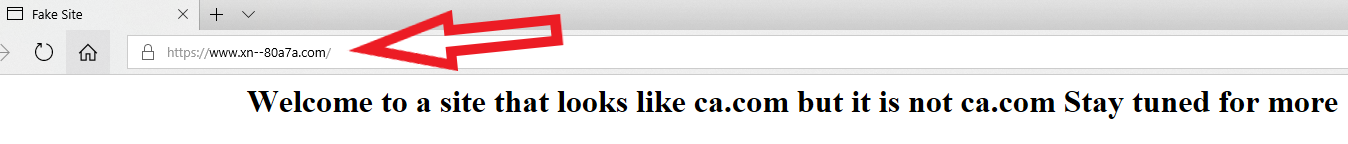
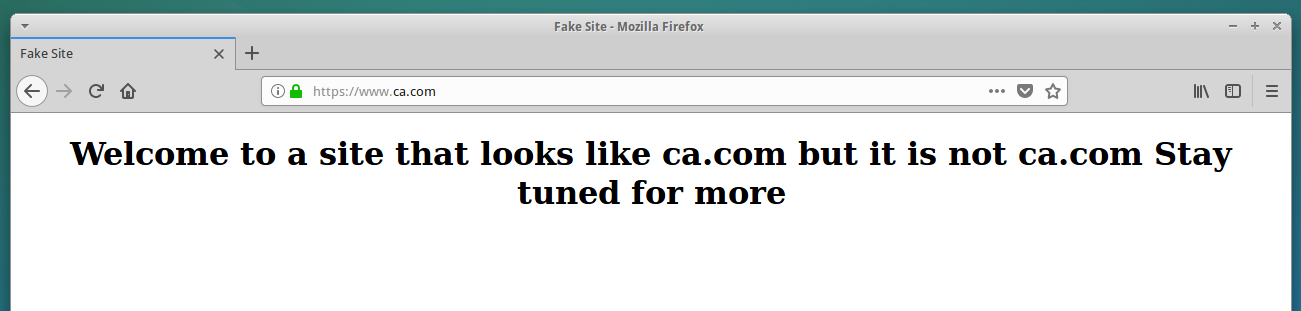
A 15-year-old security researcher has discovered a serious flaw in cryptocurrency hardware wallets made by Ledger, a French company whose popular products are designed to physically safeguard public and private keys used to receive or spend the user’s cryptocurrencies.

Ledger’s Nano-S cryptocurrency hardware wallet. Source: Amazon.
Hardware wallets like those sold by Ledger are designed to protect the user’s private keys from malicious software that might try to harvest those credentials from the user’s computer. The devices enable transactions via a connection to a USB port on the user’s computer, but they don’t reveal the private key to the PC.
Yet Saleem Rashid, a 15-year-old security researcher from the United Kingdom, discovered a way to acquire the private keys from Ledger devices. Rashid’s method requires an attacker to have physical access to the device, and normally such hacks would be unremarkable because they fall under the #1 rule of security — namely, if an attacker has physical access to your device, then it is not your device anymore.
The trouble is that consumer demand for Ledger’s products has frequently outpaced the company’s ability to produce them (it has sold over a million of its most popular Nano S models to date). This has prompted the company’s chief technology officer to state publicly that Ledger’s built-in security model is so robust that it is safe to purchase their products from a wide range of third-party sellers, including Amazon and eBay.

Ledger’s message to users regarding the lack of anti-tampering mechanisms on its cryptocurrency hardware wallets.
But Rashid discovered that a reseller of Ledger’s products could update the devices with malicious code that would lie in wait for a potential buyer to use it, and then siphon the private key and drain the user’s cryptocurrency account(s) when the user goes to use it.
The crux of the problem is that Ledger’s devices contain a secure processor chip and a non-secure microcontroller chip. The latter is used for a variety of non-security related purposes, from handling the USB connections to displaying text on the Ledger’s digital display, but the two chips still pass information between each other. Rashid found that an attacker could compromise the insecure processor (the microcontroller) on Ledger devices to run malicious code without being detected.
Ledger’s products do contain a mechanism for checking to ensure the code powering the devices has not been modified, but Rashid’s proof-of-concept code — being released today in tandem with an announcement from Ledger about a new firmware update designed to fix the bug — allows an attacker to force the device to sidestep those security checks.
“You’re essentially trusting a non-secure chip not to change what’s displayed on the screen or change what the buttons are saying,” Rashid said in an interview with KrebsOnSecurity. “You can install whatever you want on that non-secure chip, because the code running on there can lie to you.”
Kenneth White, director of the Open Crypto Audit Project, had an opportunity to review Rashid’s findings prior to their publication today. White said he was impressed with the elegance of the proof-of-concept attack code, which Rashid sent to Ledger approximately four months ago. A copy of Rashid’s research paper on the vulnerability is available here (PDF). A video of Rashid demonstrating his attack is below.
White said Rashid’s code subverts the security of the Ledger’s process for generating a backup code for a user’s private key, which relies on a random number generator that can be made to produce non-random results.
“In this case [the attacker] can set it to whatever he wants,” White said. “The victim generates keys and backup codes, but in fact those codes have been predicted by the attacker in advance because he controls the Ledger’s random number generator.”
Rashid said Ledger initially dismissed his findings as implausible. But in a blog post published today, Ledger says it has since fixed the flaw Rashid found — as well as others discovered and reported by different security researchers — in a firmware update that brings Ledger Nano S devices from firmware version 1.3.1 to version 1.4.1 (the company actually released the firmware update on March 6, potentially giving attackers time to reverse engineer Rashid’s method).
The company is still working on an update for its pricier Ledger Blue devices, which company chief security officer Charles Guillemet said should be ready soon. Guillemet said Nano-S devices should alert users that a firmware update is available when the customer first plugs the device into a computer.
“The vulnerability he found was based on the fact that the secure element tries to authenticate the microcontroller, and that authentication is not strong enough,” Guillemet told KrebsOnSecurity. “This update does authentication more tightly so that it’s not possible to fool the user.” Continue reading






 The Microsoft updates affect all supported Windows operating systems, as well as all supported versions of Internet Explorer/Edge, Office, Sharepoint and Exchange Server.
The Microsoft updates affect all supported Windows operating systems, as well as all supported versions of Internet Explorer/Edge, Office, Sharepoint and Exchange Server.