With many people being laid off or working from home thanks to the Coronavirus pandemic, cybercrooks are almost certain to have more than their usual share of recruitable “money mules” — people who get roped into money laundering schemes under the pretense of a work-at-home job offer. Here’s the story of one upstart mule factory that spoofs a major nonprofit and tells new employees they’ll be collecting and transmitting donations for an international “Coronavirus Relief Fund.”
On the surface, the Web site for the Vasty Health Care Foundation certainly looks legitimate. It includes various sections on funding relief efforts around the globe, explaining that it “connects nonprofits, donors, and companies in nearly every country around the world.” The site says it’s a nonprofit with offices based in Nebraska and Quebec, Canada.
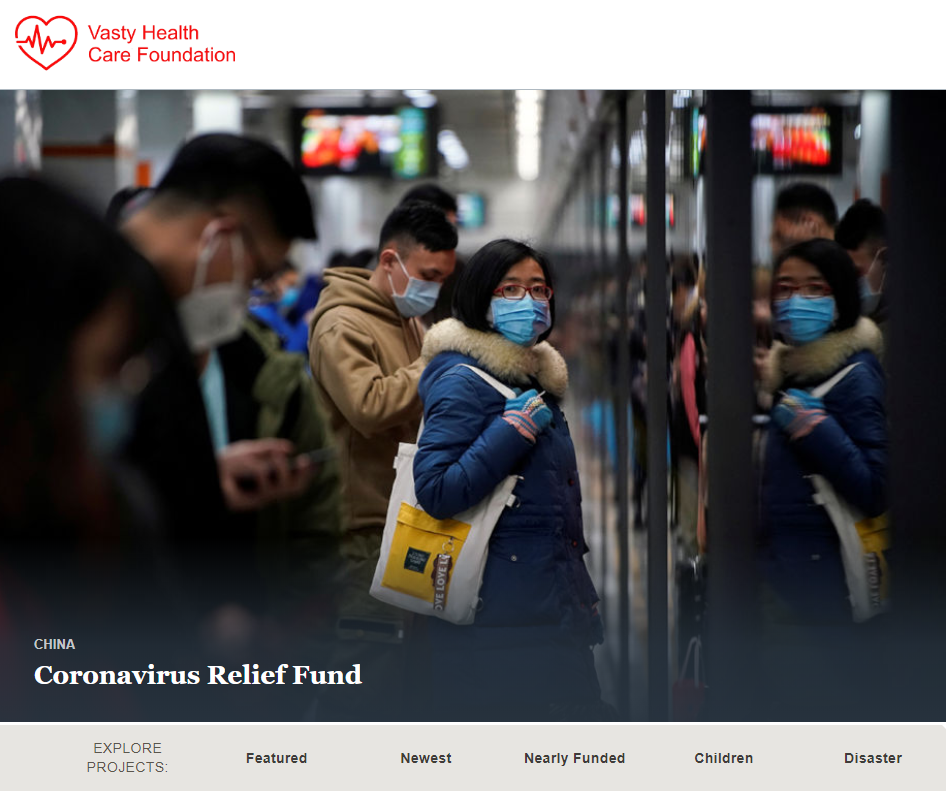
Vasty is a phony charity that pretends to raise money for Coronavirus victims but instead hires people to help launder stolen funds. This and the rest of the content at Vasty’s site was lifted from GlobalGiving, a legitimate charity that is helping people affected by the pandemic.
The “Vasty Health Care Foundation” is one of several fraudulent Web sites that recruit money mules in the name of helping Coronavirus victims. The content on Vasty’s site was lifted almost entirely from globalgiving.org, a legitimate charity that actually is trying to help people affected by the pandemic.
“We have been contacted by job seekers asking if we are related to some of these job opportunities they’ve been finding on Indeed.com and Monster.com,” said Kevin Conroy, chief product officer at GlobalGiving. “And we always tell them no that’s not from us, and not to cash any checks someone may be giving them in relation to those offers.”
The Vasty domain — vastyhealthcarefoundation[.]com — was registered just weeks ago, although the site claims its organization has been around for years.
The crooks behind this scheme also seem to have submitted the Vasty name in custom links at vetting sites like The Better Business Bureau and Guidestar that ultimately take one to a summary of data on GlobalGiving. No doubt this is part of an effort to lend legitimacy to the Vasty name (hovering over the links above reveals the trickery).
What proof is there that Vasty isn’t a legitimate charity? None of the dozens of Canadian mules contacted by this author responded to requests for comment. But KrebsOnSecurity received copious amounts of information about this scam from Milwaukee, Wisc. based Hold Security, which managed to intercept key file exchanges between threat actors through public file sharing services.
Among those files were a set of form letters and boilerplate email messages that describe the ideal candidate for the job at Vasty and welcome new recruits to the Vasty payroll. Here’s a look at part of the job description, which includes (not pictured) a description of the healthcare plans and other benefits allegedly offered to Vasty employees.

After congratulating applicants (everyone who applies is “hired”) on their new positions, Vasty asks the recruits to do some busy work. In this case, new hires are sent to local pharmacies on some bogus errand, such as to inspect the pricing of face masks and hand sanitizer products for price-gouging.
“Now we have the first task for you. You will have to perform a trip within your city. So that we can compensate for transportation costs along with your hourly rate, I ask you to keep receipts confirming your expenses.
LOCATION: Sam’s Geneva Street Pharmacy
ADDRESS: 284 Geneva St, St. Catharines, ON L2N 2E8
I ask you to go to the pharmacy at the specified address. We are increasingly receiving reports of private sellers violating the pricing policy for products such as: aspirin, face masks are loose surgical masks with elastic loops that go around the ears, hand sanitizers.”
New recruits are then asked to assemble and submit a written report of their observations at the store in question.
These types of menial, meaningless tasks are a typical tactic of money mule recruitment schemes and they serve two main purposes: They separate out slackers from people who really need and want a job, and they help the employee feel like he’s doing something useful and legitimate (aside from just moving money around, which if brought up too soon might make him question whether the job is legit). Continue reading





 , this patch batch addresses at least 115 security flaws. Twenty-six of those earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, meaning malware or miscreants could exploit them to gain complete, remote control over vulnerable computers without any help from users.
, this patch batch addresses at least 115 security flaws. Twenty-six of those earned Microsoft’s most-dire “critical” rating, meaning malware or miscreants could exploit them to gain complete, remote control over vulnerable computers without any help from users.