KrebsOnSecurity recently featured the story of a Brazilian man who was peppered with phishing attacks trying to steal his Apple iCloud username and password after his wife’s phone was stolen in a brazen daylight mugging. Today, we’ll take an insider’s look at an Apple iCloud phishing gang that appears to work quite closely with organized crime rings — within the United States and beyond — to remotely unlock and erase stolen Apple devices.
Victims of iPhone theft can use the Find My iPhone feature to remotely locate, lock or erase their iPhone — just by visiting Apple’s site and entering their iCloud username and password. Likewise, an iPhone thief can use those iCloud credentials to remotely unlock the victim’s stolen iPhone, wipe the device, and resell it. As a result, iPhone thieves often subcontract the theft of those credentials to third-party iCloud phishing services. This story is about one of those services.
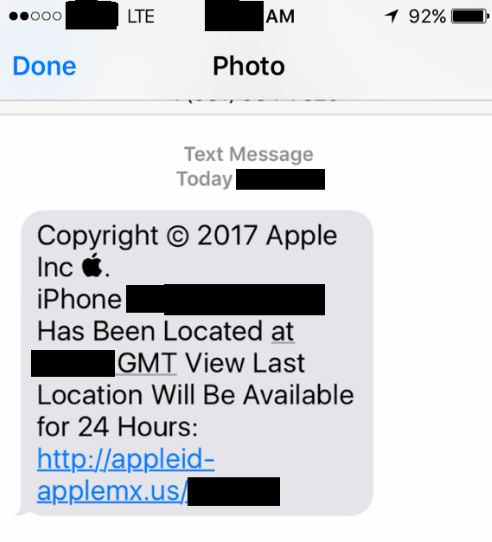
The iCloud account phishing text that John’s friend received months after losing a family iPhone.
Recently, I heard from a security professional whose close friend received a targeted attempt to phish his Apple iCloud credentials. The phishing attack came several months after the friend’s child lost his phone at a public park in Virginia. The phish arrived via text message and claimed to have been sent from Apple. It said the device tied to his son’s phone number had been found, and that its precise location could be seen for the next 24 hours by clicking a link embedded in the text message.
That security professional source — referred to as “John” for simplicity’s sake — declined to be named or credited in this story because some of the actions he took to gain the knowledge presented here may run afoul of U.S. computer fraud and abuse laws.
John said his friend clicked on the link in the text message he received about his son’s missing phone and was presented with a fake iCloud login page: appleid-applemx[dot]us. A lookup on that domain indicates it is hosted on a server in Russia that is or was shared by at least 140 other domains — mostly other apparent iCloud phishing sites — such as accounticloud[dot]site; apple-appleid[dot]store; apple-devicefound[dot]org; and so on (a full list of the domains at that server is available here).
While the phishing server may be hosted in Russia, its core users appear to be in a completely different part of the world. Examining the server more closely, John noticed that it was (mis)configured in a way that leaked data about various Internet addresses that were seen recently accessing the server, as well as the names of specific directories on the server that were being accessed.
After monitoring that logging information for some time, my source discovered there were five Internet addresses that communicated with the server multiple times a day, and that those address corresponded to devices located in Argentina, Colombia, Ecuador and Mexico.
He also found a file openly accessible on the Russian server which indicated that an application running on the server was constantly sending requests to imei24.com and imeidata.net — services that allow anyone to look up information about a mobile device by entering its unique International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number. These services return a variety of information, including the make and model of the phone, whether Find My iPhone is enabled for the device, and whether the device has been locked or reported stolen.
John said that as he was conducting additional reconnaissance of the Russian server, he tried to access “index.php” — which commonly takes one to a site’s home page — when his browser was redirected to “login.php” instead. The resulting page, pictured below, is a login page for an application called “iServer.” The login page displays a custom version of Apple’s trademarked logo as part of a pirate’s skull and crossbones motif, set against a background of bleeding orange flames.
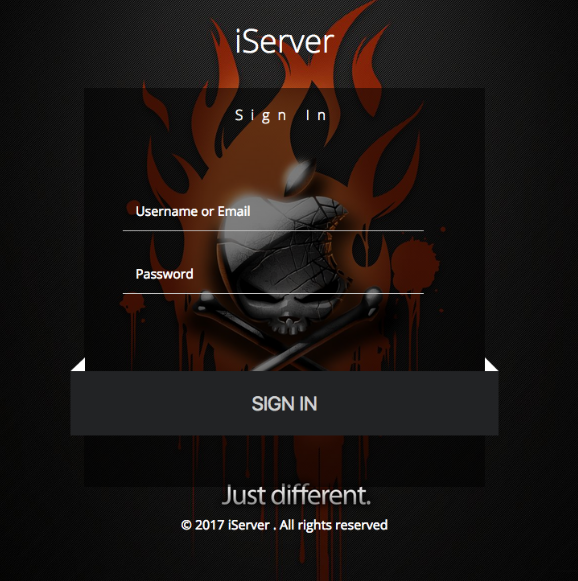
The login page for an Apple iCloud credential phishing operation apparently used to unlock and remotely wipe stolen iPhones.
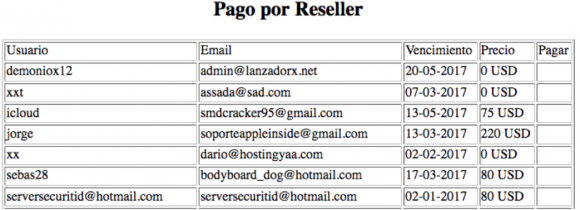
John told me that in addition to serving up that login page, the server also returned the HTML contents of the “index.php” he originally requested from the server. When he saved the contents of index.php to his computer and viewed it as a text file, he noticed it inexplicably included a list of some 137 user names, email addresses and expiration dates for various users who’d apparently paid a monthly fee to access the iCloud phishing service.
“These appear to be ‘resellers’ or people that have access to the crimeware server,” my source said of the user information listed in the server’s “index.php” file.
John told KrebsOnSecurity that with very little effort he was able to guess the password of at least two other users listed in that file. After John logged into the iCloud phishing service with those credentials, the service informed him that the account he was using was expired. John was then prompted to pay for at least one more month subscription access to the server to continue.
Playing along, John said he clicked the “OK” button indicating he wished to renew his subscription, and was taken to a shopping cart hosted on the domain hostingyaa[dot]com. That payment form in turn was accepting PayPal payments for an account tied to an entity called HostingYaa LLC; viewing the HTML source on that payment page revealed the PayPal account was tied to the email address “admin@hostingyaa[dot]com.”
According to the file coughed up by the Russian server, the first username in that user list — demoniox12 — is tied to an email address admin@lanzadorx.net and to a zero-dollar subscription to the phishing service. This strongly indicates the user in question is an administrator of this phishing service.
A review of Lanzadorx[dot]net indicates that it is a phishing-as-a-service offering that advertises the ability to launch targeted phishing attacks at a variety of free online services, including accounts at Apple, Hotmail, Gmail and Yahoo, among others.
A reverse WHOIS lookup ordered from Domaintools.com shows that the admin@lanzadorx.net email is linked to the registration data for exactly two domains — hostingyaa[dot]info and lanzadorx[dot]net [full disclosure: Domaintools is currently one of several advertisers on KrebsOnSecurity].
Hostingyaa[dot]info is registered to a Dario Dorrego, one of the other zero-dollar accounts included near the top of the list of users that are authorized to access the iCloud phishing service. The site says Dorrego’s account corresponds to the email address dario@hostingyaa[dot]com. That name Dario Dorrego also appears in the site registration records for 31 other Web site domains, all of which are listed here.
John said he was able to guess the passwords for at least six other accounts on the iCloud phishing service, including one particularly interesting user and possible reseller of the service who picked the username “Jonatan.” Below is a look at the home screen for Jonatan’s account on this iCloud phishing service. We can see the system indicates Jonatan was able to obtain at least 65 “hacked IDs” through this service, and that he pays USD $80 per month for access to it.
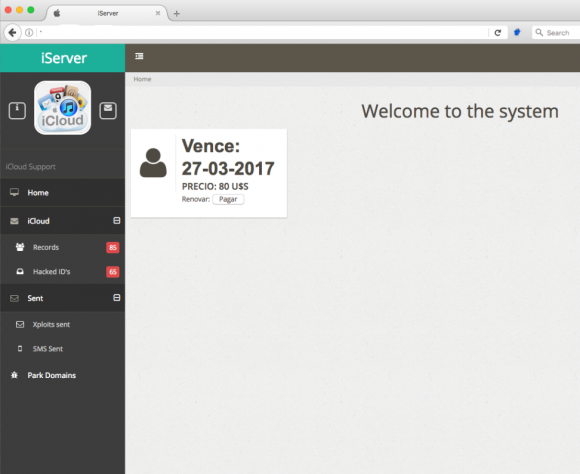
“Jonatan,” a user of this iCloud account credential phishing service. Note the left side panel indicates the number of records and hacked IDs recorded for Jonatan’s profile.
Continue reading →
 On Thursday, March 16, the CEO of Defense Point Security, LLC — a Virginia company that bills itself as “the choice provider of cyber security services to the federal government” — told all employees that their W-2 tax data was handed directly to fraudsters after someone inside the company got caught in a phisher’s net.
On Thursday, March 16, the CEO of Defense Point Security, LLC — a Virginia company that bills itself as “the choice provider of cyber security services to the federal government” — told all employees that their W-2 tax data was handed directly to fraudsters after someone inside the company got caught in a phisher’s net.





 Microsoft’s
Microsoft’s 



 On March 5, a security researcher named Bashis posted to
On March 5, a security researcher named Bashis posted to