The past month has seen one blockbuster revelation after another about how our mobile phone and broadband providers have been leaking highly sensitive customer information, including real-time location data and customer account details. In the wake of these consumer privacy debacles, many are left wondering who’s responsible for policing these industries? How exactly did we get to this point? What prospects are there for changes to address this national privacy crisis at the legislative and regulatory levels? These are some of the questions we’ll explore in this article.

In 2015, the Federal Communications Commission under the Obama Administration reclassified broadband Internet companies as telecommunications providers, which gave the agency authority to regulate broadband providers the same way as telephone companies.
The FCC also came up with so-called “net neutrality” rules designed to prohibit Internet providers from blocking or slowing down traffic, or from offering “fast lane” access to companies willing to pay extra for certain content or for higher quality service.
In mid-2016, the FCC adopted new privacy rules for all Internet providers that would have required providers to seek opt-in permission from customers before collecting, storing, sharing and selling anything that might be considered sensitive — including Web browsing, application usage and location information, as well as financial and health data.
But the Obama administration’s new FCC privacy rules didn’t become final until December 2016, a month after then President-elect Trump was welcomed into office by a Republican controlled House and Senate.
Congress still had 90 legislative days (when lawmakers are physically in session) to pass a resolution killing the privacy regulations, and on March 23, 2017 the Senate voted 50-48 to repeal them. Approval of the repeal in the House passed quickly thereafter, and President Trump officially signed it on April 3, 2017.
In an op-ed published in The Washington Post, Ajit Pai — a former Verizon lawyer and President Trump’s pick to lead the FCC — said “despite hyperventilating headlines, Internet service providers have never planned to sell your individual browsing history to third parties.”

FCC Commissioner Ajit Pai.
“That’s simply not how online advertising works,” Pai wrote. “And doing so would violate ISPs’ privacy promises. Second, Congress’s decision last week didn’t remove existing privacy protections; it simply cleared the way for us to work together to reinstate a rational and effective system for protecting consumer privacy.”
Sen. Bill Nelson (D-Fla.) came to a different conclusion, predicting that the repeal of the FCC privacy rules would allow broadband providers to collect and sell a “gold mine of data” about customers.
“Your mobile broadband provider knows how you move about your day through information about your geolocation and internet activity through your mobile device,” Nelson said. The Senate resolution “will take consumers out of this driver’s seat and place the collection and use of their information behind a veil of secrecy.”
Meanwhile, pressure was building on the now Republican-controlled FCC to repeal the previous administration’s net neutrality rules. The major ISPs and mobile providers claimed the new regulations put them at a disadvantage relative to competitors that were not regulated by the FCC, such as Amazon, Apple, Facebook and Google.
On Dec. 14, 2017, FCC Chairman Pai joined two other Republic FCC commissioners in a 3-2 vote to dismantle the net neutrality regulations.
As The New York Times observed after the net neutrality repeal, “the commission’s chairman, Ajit Pai, vigorously defended the repeal before the vote. He said the rollback of the rules would eventually benefit consumers because broadband providers like AT&T and Comcast could offer them a wider variety of service options.”
“We are helping consumers and promoting competition,” Mr. Pai said. “Broadband providers will have more incentive to build networks, especially to underserved areas.”
MORE OR LESS CHOICE?
Some might argue we’ve seen reduced competition and more industry consolidation since the FCC repealed the rules. Major broadband and mobile provider AT&T and cable/entertainment giant Time Warner are now fighting the Justice Department in a bid to merge. Two of the four-largest mobile telecom and broadband providers — T-Mobile and Sprint — have announced plans for a $26 billion merger.
The FCC privacy rules from 2016 that were overturned by Congress sought to give consumers more choice about how their data was to be used, stored and shared. But consumers now have less “choice” than ever about how their mobile provider shares their data and with whom. Worse, the mobile and broadband providers themselves are failing to secure their own customers’ data.
This month, it emerged that the major mobile providers have been giving commercial third-parties the ability to instantly look up the precise location of any mobile subscriber in real time. KrebsOnSecurity broke the news that one of these third parties — LocationSmart — leaked this ability for years to anyone via a buggy component on its Web site.
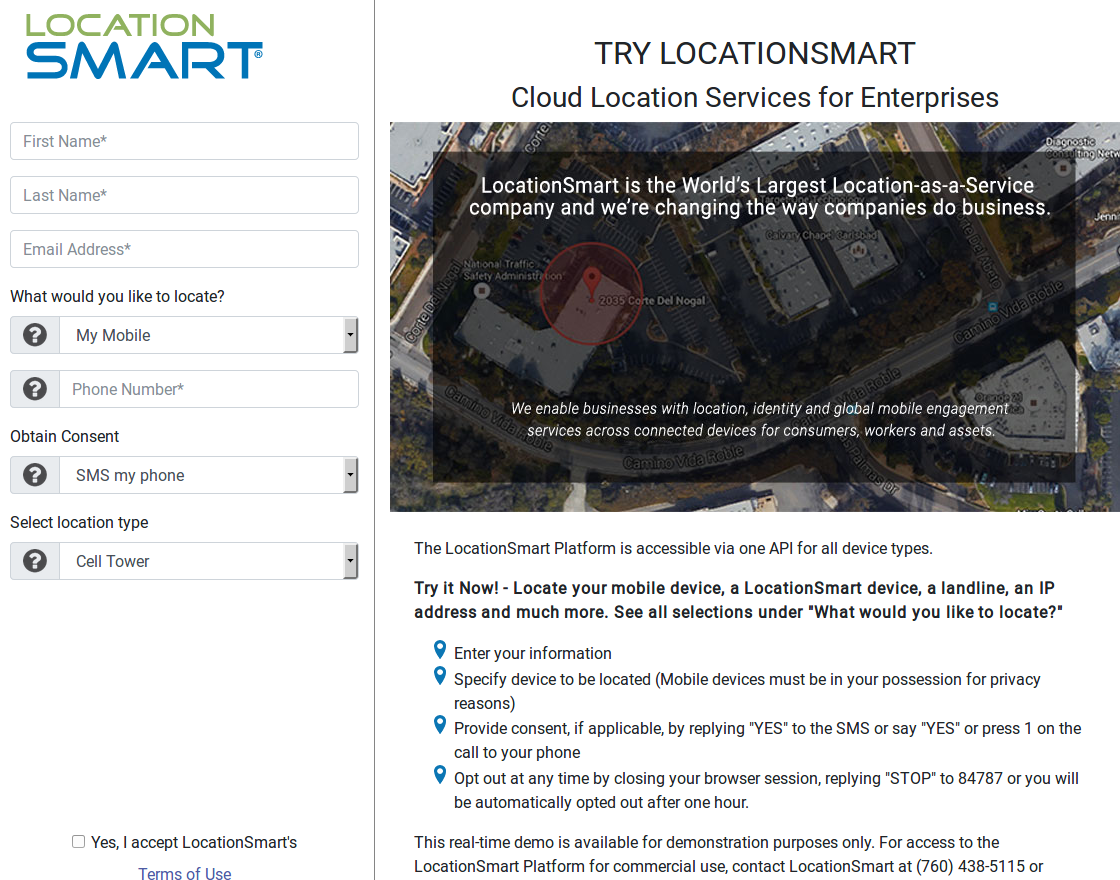
LocationSmart’s demo page featured a buggy component which allowed anyone to look up anyone else’s mobile device location, in real time, and without consent.
We also learned that another California company — Securus Technologies — was selling real-time location lookups to a number of state and local law enforcement agencies, and that accounts for dozens of those law enforcement officers were obtained by hackers. Securus, it turned out, was ultimately getting its data from LocationSmart.
This week, researchers discovered that a bug in T-Mobile’s Web site let anyone access the personal account details of any customer with just their cell phone number, including full name, address, account number and some cases tax ID numbers.
Not to be outdone, Comcast was revealed to have exposed sensitive information on customers through a buggy component of its Web site that could be tricked into displaying the home address where the company’s wireless router is located, as well as the router’s Wi-Fi name and password.
It’s not clear how FCC Chairman Pai intends to “reinstate a rational and effective system for protecting consumer privacy,” as he pledged after voting last year to overturn the 2015 privacy rules. The FCC reportedly has taken at least tentative steps to open an inquiry into the LocationSmart debacle, although Sen. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) has called on Chairman Pai to recuse himself on the inquiry because Pai once represented Securus as an attorney. (Wyden also had some choice words for the wireless companies).
The major wireless carriers all say they do not share customer location data without customer consent or in response to a court order or subpoena. Consent. All of these carriers pointed me to their privacy policies. It could be the carriers believe these policies clearly explain that simply by using their wireless device customers have opted-in to having their real-time location data sold or given to third-party companies.
Michelle De Mooy, director of the privacy and data project at the Center for Democracy & Technology (CDT), said if the mobile giants are burying that disclosure in privacy policy legalese, that’s just not good enough.
“Even if they say, ‘Our privacy policy says we can do this,’ it violates peoples’ reasonable expectations of when and why their location data is being collected and how that’s going to be used. It’s not okay to simply point to your privacy policies and expect that to be enough.”
Continue reading →






 Most of the critical fixes are in Microsoft browsers or browser components. One of the flaws,
Most of the critical fixes are in Microsoft browsers or browser components. One of the flaws, 
 In
In