Later this month, all of the three major consumer credit bureaus will be required to offer free credit freezes to all Americans and their dependents. Maybe you’ve been holding off freezing your credit file because your home state currently charges a fee for placing or thawing a credit freeze, or because you believe it’s just not worth the hassle. If that accurately describes your views on the matter, this post may well change your mind.

A credit freeze — also known as a “security freeze” — restricts access to your credit file, making it far more difficult for identity thieves to open new accounts in your name.
Currently, many states allow the big three bureaus — Equifax, Experian and TransUnion — to charge a fee for placing or lifting a security freeze. But thanks to a federal law enacted earlier this year, after Sept. 21, 2018 it will be free to freeze and unfreeze your credit file and those of your children or dependents throughout the United States.
KrebsOnSecurity has for many years urged readers to freeze their files with the big three bureaus, as well as with a distant fourth — Innovis — and the NCTUE, an Equifax-operated credit checking clearinghouse relied upon by most of the major mobile phone providers.
There are dozens of private companies that specialize in providing consumer credit reports and scores to specific industries, including real estate brokers, landlords, insurers, debt buyers, employers, banks, casinos and retail stores. A handy PDF produced earlier this year by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) lists all of the known entities that maintain, sell or share credit data on U.S. citizens.
The CFPB’s document includes links to Web sites for 46 different consumer credit reporting entities, along with information about your legal rights to obtain data in your reports and dispute suspected inaccuracies with the companies as needed. My guess is the vast majority of Americans have never heard of most of these companies.
Via numerous front-end Web sites, each of these mini credit bureaus serve thousands or tens of thousands of people who work in the above mentioned industries and who have the ability to pull credit and other personal data on Americans. In many cases, online access to look up data through these companies is secured by nothing more than a username and password that can be stolen or phished by cybercrooks and abused to pull privileged information on consumers.
In other cases, it’s trivial for anyone to sign up for these services. For example, how do companies that provide background screening and credit report data to landlords decide who can sign up as a landlord? Answer: Anyone can be a landlord (or pretend to be one).
SCORE ONE FOR FREEZES
The truly scary part? Access to some of these credit lookup services is supposed to be secured behind a login page, but often isn’t. Consider the service pictured below, which for $44 will let anyone look up the credit score of any American who hasn’t already frozen their credit files with the big three. Worse yet, you don’t even need to have accurate information on a target — such as their Social Security number or current address.
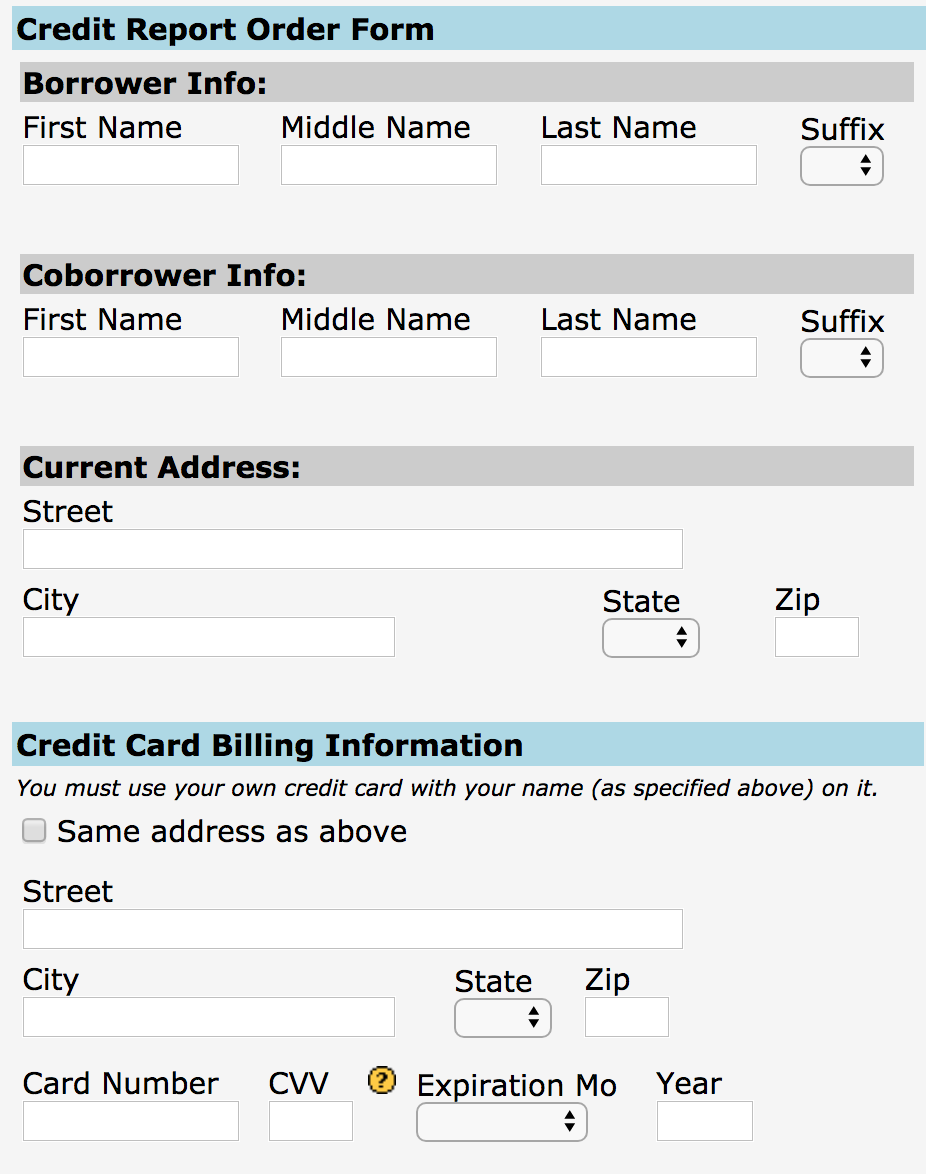
KrebsOnSecurity was made aware of this particular portal by Alex Holden, CEO of Milwaukee, Wisc.-based cybersecurity firm Hold Security LLC [full disclosure: This author is listed as an adviser to Hold Security, however this is and always has been a volunteer role for which I have not been compensated].
Holden’s wife Lisa is a mortgage broker, and as such she has access to a more full-featured version of the above-pictured consumer data lookup service (among others) for the purposes of helping clients determine a range of mortgage rates available. Mrs. Holden said the version of this service that she has access to will return accurate, current and complete credit file information on consumers even if one enters a made-up SSN and old address on an individual who hasn’t yet frozen their credit files with the big three.
“I’ve noticed in the past when I do a hard pull on someone’s credit report and the buyer gave me the wrong SSN or transposed some digits, not only will these services give me their credit report and full account history, it also tells you what their correct SSN is,” Mrs. Holden said.
With Mr. Holden’s permission, I gave the site pictured above an old street address for him plus a made-up SSN, and provided my credit card number to pay for the report. The document generated by that request said TransUnion and Experian were unable to look up his credit score with the information provided. However, Equifax not only provided his current credit score, it helpfully corrected the false data I entered for Holden, providing the last four digits of his real SSN and current address.
“We assume our credit report is keyed off of our SSN or something unique about ourselves,” Mrs. Holden said. “But it’s really keyed off your White Pages information, meaning anyone can get your credit report if they are in the know.”
I was pleased to find that I was unable to pull my own credit score through this exposed online service, although the site still charged me $44. The report produced simply said the consumer in question had requested that access to this information be restricted. But the real reason was simply that I’ve had my credit file frozen for years now.
Many media outlets are publishing stories this week about the one-year anniversary of the breach at Equifax that exposed the personal and financial data on more than 147 million people. But it’s important for everyone to remember that as bad as the Equifax breach was (and it was a total dumpster fire all around), most of the consumer data exposed in the breach has been for sale in the cybercrime underground for many years on a majority of Americans — including access to consumer credit reports. If anything, the Equifax breach may have simply helped ID thieves refresh some of those criminal data stores.
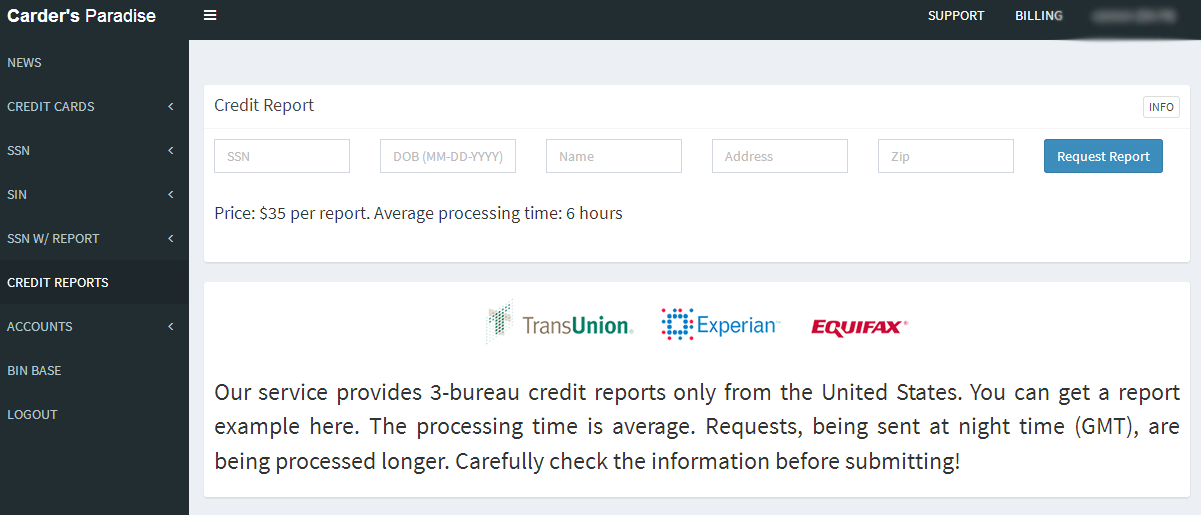
It costs $35 worth of bitcoin through this cybercrime service to pull someone’s credit file from the three major credit bureaus. There are many services just like this one, which almost certainly abuse hacked accounts from various industries that have “legitimate” access to consumer credit reports.
Continue reading →






 As per usual, the bulk of the fixes from Microsoft tackle security weaknesses in the company’s Web browsers, Internet Explorer and Edge. Patches also are available for Windows, Office, Sharepoint, and the .NET Framework, among other components.
As per usual, the bulk of the fixes from Microsoft tackle security weaknesses in the company’s Web browsers, Internet Explorer and Edge. Patches also are available for Windows, Office, Sharepoint, and the .NET Framework, among other components.