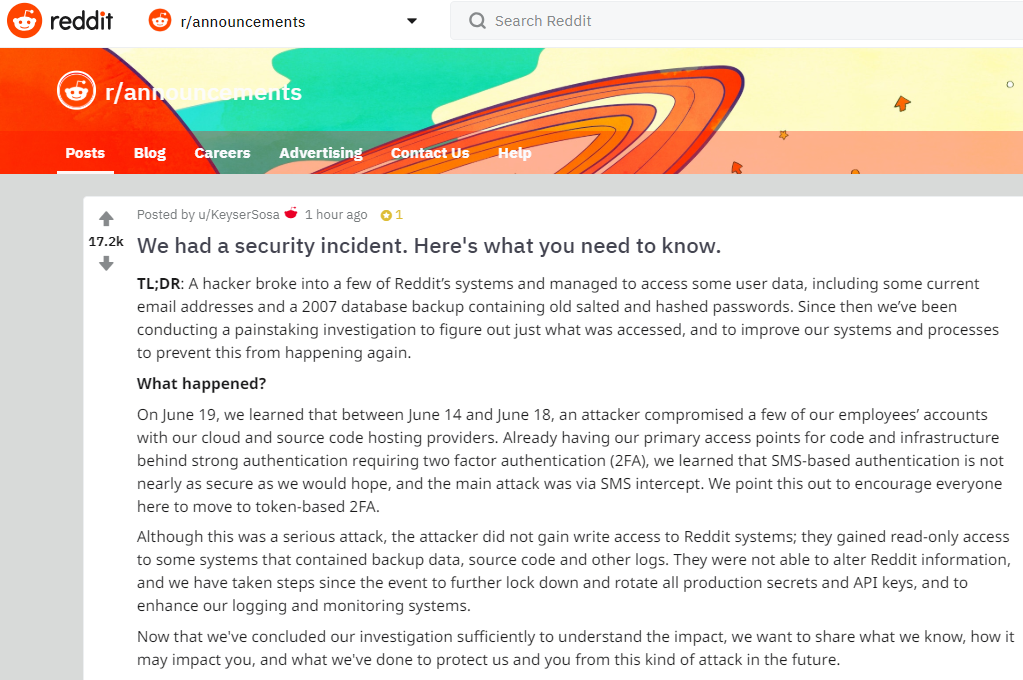
Police in Florida have arrested a 25-year-old man accused of being part of a multi-state cyber fraud ring that hijacked mobile phone numbers in online attacks that siphoned hundreds of thousands of dollars worth of bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies from victims.
On July 18, 2018, Pasco County authorities arrested Ricky Joseph Handschumacher, an employee of the city of Port Richey, Fla, charging him with grand theft and money laundering. Investigators allege Handschumacher was part of a group of at least nine individuals scattered across multiple states who for the past two years have drained bank accounts via an increasingly common scheme involving mobile phone “SIM swaps.”
A SIM card is the tiny, removable chip in a mobile device that allows it to connect to the provider’s network. Customers can legitimately request a SIM swap when their existing SIM card has been damaged, or when they are switching to a different phone that requires a SIM card of another size.
But SIM swaps are frequently abused by scam artists who trick mobile providers into tying a target’s service to a new SIM card and mobile phone that the attackers control. Unauthorized SIM swaps often are perpetrated by fraudsters who have already stolen or phished a target’s password, as many banks and online services rely on text messages to send users a one-time code that needs to be entered in addition to a password for online authentication.
In some cases, fraudulent SIM swaps succeed thanks to lax authentication procedures at mobile phone stores. In other instances, mobile store employees work directly with cyber criminals to help conduct unauthorized SIM swaps, as appears to be the case with the crime gang that allegedly included Handschumacher.
A WORRIED MOM
According to court documents, investigators first learned of the group’s activities in February 2018, when a Michigan woman called police after she overheard her son talking on the phone and pretending to be an AT&T employee. Officers responding to the report searched the residence and found multiple cell phones and SIM cards, as well as files on the kid’s computer that included “an extensive list of names and phone numbers of people from around the world.”
The following month, Michigan authorities found the same individual accessing personal consumer data via public Wi-Fi at a local library, and seized 45 SIM cards, a laptop and a Trezor wallet — a hardware device designed to store crytpocurrency account data. In April 2018, the mom again called the cops on her son — identified only as confidential source #1 (“CS1”) in the criminal complaint — saying he’d obtained yet another mobile phone.
Once again, law enforcement officers were invited to search the kid’s residence, and this time found two bags of SIM cards and numerous driver’s licenses and passports. Investigators said they used those phony documents to locate and contact several victims; two of the victims each reported losing approximately $150,000 in cryptocurrencies after their phones were cloned; the third told investigators her account was drained of $50,000.
CS1 later told investigators he routinely conducted the phone cloning and cashouts in conjunction with eight other individuals, including Handschumacher, who allegedly used the handle “coinmission” in the group’s daily chats via Discord and Telegram. Search warrants revealed that in mid-May 2018 the group worked in tandem to steal 57 bitcoins from one victim — then valued at almost $470,000 — and agreed to divide the spoils among members.
GRAND PLANS
Investigators soon obtained search warrants to monitor the group’s Discord server chat conversations, and observed Handschumacher allegedly bragging in these chats about using the proceeds of his alleged crimes to purchase land, a house, a vehicle and a “quad vehicle.” Interestingly, Handschumacher’s public Facebook page remains public, and is replete with pictures that he posted of recent new vehicle aquisitions, including a pickup truck and multiple all-terrain vehicles and jet skis.
The Pasco County Sheriff’s office says their surveillance of the Discord server revealed that the group routinely paid employees at cellular phone companies to assist in their attacks, and that they even discussed a plan to hack accounts belonging to the CEO of cryptocurrency exchange Gemini Trust Company. The complaint doesn’t mention the CEO by name, but the current CEO is bitcoin billionaire Tyler Winklevoss, who co-founded the exchange along with his twin brother Cameron.
“Handschumacher and another co-conspirator talk about compromising the CEO of Gemini and posted his name, date of birth, Skype username and email address into the conversation,” the complaint reads. “Handschumacher and the co-conspirators discuss compromising the CEO’s Skype account and T-Mobile account. The co-conspirator states he will call his ‘guy’ at T-Mobile to ask about the CEO’s account.” Continue reading



 TCM is a subsidiary of Washington, D.C.-based ICBA Bancard Inc., which helps community banks provide a credit card option to their customers using bank-branded cards.
TCM is a subsidiary of Washington, D.C.-based ICBA Bancard Inc., which helps community banks provide a credit card option to their customers using bank-branded cards.
 In such a scenario, the attacker might configure the link to lead to an “exploit kit,” crimeware designed to be stitched into hacked or malicious sites that exploits a variety of Web-browser vulnerabilities for the purposes of installing malware of the attacker’s choosing.
In such a scenario, the attacker might configure the link to lead to an “exploit kit,” crimeware designed to be stitched into hacked or malicious sites that exploits a variety of Web-browser vulnerabilities for the purposes of installing malware of the attacker’s choosing.